* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry B Date: ______ 6.2 Properties of Parallelograms
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Signed graph wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
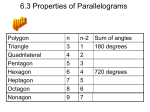
Geometry B Date: _____________ 6.2 Properties of Parallelograms Objective: Apply and use properties of parallelograms to solve problems Recall: Quadrilaterals are polygons with ___________ sides and ____________ angles. The sum of their interior angles is _____________ Some quadrilaterals have special properties and are given their own name. Parallelogram Definition: ________________________________________________________________ Properties: o Opposite sides are _____________________ and _____________________ o Opposite angles are __________________________ o Same-side (consecutive interior) angles are ____________________________ o Diagonals in a parallelogram _________________ one another. This means when diagonals cross, they _______________________________ Naming Parallelograms: _____________________ or _____________________ Ex. 1: Using Properties of Parallelograms In CDEF, DE = 74 mm, DG = 31 mm, and mFCD = 42°. a. Find CF b. Find mEFC c. Find DF Ex. 2: Using Properties of Parallelograms to Find Measures WXYZ is a parallelogram. a. Find YZ b. Find mZ Practice: EFGH is a parallelogram. a. Find JG. b. Find FH Ex. 3: Quadrilaterals in the Coordinate Plane Three vertices of JKLM are J(3, –8), K(–2, 2), and L(2, 6). Find the coordinates of vertex M. (Since JKLM is a parallelogram, both pairs of opposite sides must be parallel.) Step 1: Graph the given points. L ____ Step 2: Find the slope of KL by counting the units from K to L. K Step 3: Start at J and count the same number of units. Step 4: Count the slope to verify _____ _____ that LM || KJ J Practice: Three vertices of vertex R. PQRS are P(–3, –2), Q(–1, 4), and S(5, 0). Find the coordinates of Q S P HW: 6.2 Worksheet