* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide exam sample questions_PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
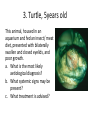
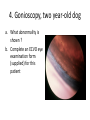
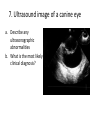
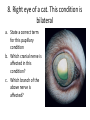
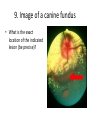
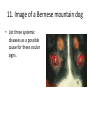
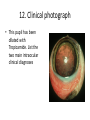
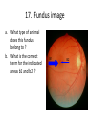
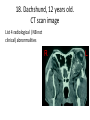
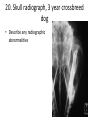
ECVO exam Slide sample questions 1. Feline eye a. List any abnormalities b. What is the correct diagnosis? c. Briefly describe the aetiopathogenesis 2. Equine fundus image a. What is the funduscopic abnormality seen? b. From which embryological layer does the affected tissue arise? 3. Turtle, 5years old This animal, housed in an aquarium and fed an insect/ meat diet, presented with bilaterally swollen and closed eyelids, and poor growth. a. What is the most likely aetiological diagnosis? b. What systemic signs may be present? c. What treatment is advised? 4. Gonioscopy, two year-old dog a. What abnormality is shown ? b. Complete an ECVO eye examination form (supplied) for this patient ECVO SLIDE EXAM: WRITE YOUR CANDIDATE NUMBER HERE: ECVO FORM FOR Q4 5. Equine fundus image In association with which equine systemic disease have these lesions been described? 6. Gonioscopy, 6yo Flat-coated retriever • What are the two major diagnoses seen in this photograph ? 7. Ultrasound image of a canine eye a. Describe any ultrasonographic abnormalities b. What is the most likely clinical diagnosis? 8. Right eye of a cat. This condition is bilateral a. State a correct term for this pupillary condition b. Which cranial nerve is affected in this condition? c. Which branch of the above nerve is affected? 9. Image of a canine fundus • What is the exact location of the indicated lesion (be precise)? 10. Histologic micrograph a. What part of the eye is shown ? b. List two major histopathological abnormalities seen? 11. Image of a Bernese mountain dog • List three systemic diseases as a possible cause for these ocular signs. 12. Clinical photograph • This pupil has been dilated with Tropicamide. List the two main intraocular clinical diagnoses 13. Slit-lamp biomicroscopy • What abnormality is identified (be specific regarding localisation) 14. Right eye of a rabbit a. List two ocular abnormalities b. What is the most likely aetiology? 15. Cytological sample, equine eye a. Describe your findings b. List two possible infectious causative agents 16. Miniature poodle, male, 3 yo, OD a. State the correct term for this ophthalmoscopic finding b. List six possible underlying systemic diseases 17. Fundus image a. What type of animal does this fundus belong to ? b. What is the correct term for the indicated areas b1 and b2 ? B1 B2 18. Dachshund, 12 years old. CT scan image List 4 radiological (NB not clinical) abnormalities R L 19. Left orbit of a canine skull • Name the three openings from the top left to the bottom right. 20. Skull radiograph, 3 year crossbreed dog • Describe any radiographic abnormalities Correct answers 1a.Shallow anterior chamber, anteriorly displaced lens 1b. Aqueous misdirection syndrome 1c. Misdirection of aqueous humour posteriorly through small breaks in the hyaloid near the vitreous base. Increased vitreous pressure causes anterior displacement of lens and a shallow AC 2a. Focal RPE hypopigmentation/ RPE coloboma 2b. Neuroectoderm 3a. Hypovitaminosis A 3b. Squamous metaplasia of renal, pancreatic, GIT and respiratory epithelia 3c. Commercial trout pellets if still eating, parenteral Vitamin A, topical antibiotics Correct answers 4a. Pectinate ligament dysplasia or goniodysgenesis 4b. Form filled correctly, box 8 and Occlusio box ticked 5. Equine motor neuron disease / Vitamin E deficiency 6a. Pectinate Ligament Dysplasia/ goniodysgenesis 6b. Limbal melanocytoma (endothelial pigmentation also accepted) 7a. Hyperechoic area adjacent to posterior lens capsule, with disruption of lens capsule 7b. Posterior lens capsule rupture Correct answers 8a. Hemidilation (reversed D-shaped pupil also acceptable) 8b. Oculomotor nerve 8c. Malar nerve 9. Pre-retinal 10a. Iridocorneal drainage angle 10b. Two of: PLD, collapsed angle, recessed angle 11. Histiocytic sarcoma/ malignant histiocytosis/ lymphosarcoma/ Leishmaniasis Correct answers 12. Cataract, microphakia 13. Crystalline opacity/ cataract located within lens nucleus 14a. Two of: Iris abscessation, iris neovascularisation, iris hyperaemia 14b. Encephalitozoon cuniculi 15a Epithelial cell with intracellular rod like bacteria visible 15b. Pseudomonas, Listeria Correct answers 16a. Lipid retinopathy/ lipaemia retinalis 16b. Six of: Hyperlipidaemia, pancreatitis, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, Cushings disease, liver disease, protein-losing nephropathy, high fat diet 17a. Primate 17b1. Macula 17b2. Fovea 18. Soft tissue density mass in left orbit; anterior displacement of left globe; indentation of posterior L globe; increased radiodensities within mass Correct answers 19. Optic foramen/ Orbital fissure/ Rostral alar foramen 20. Large radiodense mass in the right orbit (without signs of osteolysis)