* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-3 to 4-5 Student Notes (No HL)-DMW
Survey
Document related concepts
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
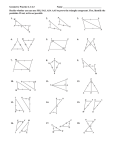
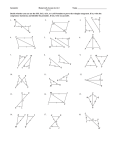
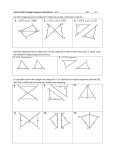
Geometry C Name:______________________ Date: ___________ Section 4.3/4.4/4.5: Proving Triangles Congruent DO NOW 1. What are sides AC and BC called? Side AB? 2. Which side is in between A and C? Objectives of Lesson: Use properties of congruent triangles. Prove triangles congruent by using the definition of congruence. Apply SSS, SAS, ASA, and AAS to construct triangles and solve problems. Prove triangles congruent using SSS, SAS, ASA, and AAS Corresponding angles and corresponding sides are in the same position in polygons with an equal number of sides. Properties of Congruent Polygons Diagram Corresponding Angles Corresponding Sides Helpful Hint: To name a polygon, write the vertices in consecutive order. 2 Side-Side-Side Congruence (SSS) Postulate Figure If three sides of one triangle are congruent to three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Example 1: Using SSS to Prove Triangle Congruence Use SSS to explain why ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐷𝐵𝐶. Example 2 Use SSS to explain why ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐶𝐷𝐴. An included angle is an angle formed by two adjacent sides of a polygon. B is the ̅̅̅̅ . included angle between sides ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 and 𝐵𝐶 Conclusion 3 Side-Angle-Side Congruence (SAS) Postulate Figure Conclusion If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. CAUTION: The letters SAS are written in that order because the congruent angles MUST be between pairs of congruent corresponding sides. Example 3: Engineering Application The diagram shows part of the support structure for a tower. Use SAS to explain why ∆𝑋𝑌𝑍 ≅ ∆𝑉𝑊𝑍. Example 4 Use SAS to explain why ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐷𝐵𝐶. 4 Example 5: Verifying Triangle Congruence Show that the triangles are congruent for the given value of the variable. ∆𝑀𝑁𝑂 ≅ ∆𝑃𝑄𝑅, when x = 5. Example 6: Proving Triangles Congruent Statements Reasons 5 Example 7: Proving Triangles Congruent Statements Reasons An included side is the common side to two consecutive angles in a polygon. Angle-Side-Angle Congruence (ASA) Postulate If two angles and the included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the included side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Figure Conclusion 6 Example 8: Applying ASA Congruence Determine if you can use ASA to prove the triangles congruent. Explain. Example 9 Determine if you can use ASA to prove NKL LMN. Explain. Angle-Angle-Side Congruence (AAS) Postulate Figure If two angles and a nonincluded side of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding angles and nonincluded side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Example 10: Using AAS to Prove Triangles Congruent Given: X V, YZW YWZ, XY VY Prove: XYZ VYW Conclusion