* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Date
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
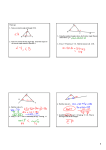
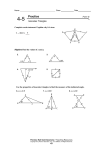
Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Do Now 32 Name: Date: Do Now 32 – Slope from Graphs Directions: draw a slope triangle and use it to find the slope of each line shown. 1. 2. 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 –5 –5 5 5 –2 –2 m= m= 3. 4. 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 –5 –5 5 5 –2 –2 –4 m= m= 5. All slope triangle are (circle one) right / acute / obtuse triangles. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 1 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Intro to Triangles Notes Name: Date: Introduction to Triangles – Guided Notes Classifying Triangles By Sides Classification Description Figure A triangle with three congruent sides. Scalene Triangle Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 2 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Intro to Triangles Notes Name: Date: Classifying Triangles by Angles Classification Description Figure Right Triangle A triangle with all acute angles. 127° Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 3 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Intro to Triangles Notes Name: Date: Triangle Sum Investigation: You probably know what the sum of the degrees in a triangle is, but you probably haven’t seen it proved. The exercise that we are about to do shows one way to understand this theorem. Materials: • • • • A sheet of colored paper. A straight edge Scissors Scotch tape Step 1: Draw a triangle on your sheet of paper. If your birthday is in January, February, March, or April, draw an acute triangle. If your birthday is in May, June, July or August, draw a right triangle. If your birthday is in September, October, November or December, draw an obtuse triangle. Step 2: Write the letters a, b, and c in the interiors of the three angles of one of the triangles, and carefully cut out the triangle. Step 3: Tear off the three angles. Arrange them so that their vertices meet at a point. (See diagram below.) How does this arrangement show the sum of the angle measures? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Step 4: Tape your corners onto this paper on the lower right-hand corner. Triangle Sum Theorem: The sum of the angles in any triangle is _____________. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 4 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Intro to Triangles Notes Name: Date: Example 1: Classify each of the triangles by sides and angles. a. b. c. d. Example 2: Use the triangle sum theorem to write an equation and solve for x in each triangle. Then find the measure of each unknown angle in the triangle. a. b. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 5 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Intro to Triangles Notes Name: Date: Triangle Sum White Board Practice Directions: Use the triangle sum or another theorem to write a true equation for each figure. Solve for x and hold up your board silently to allow the teacher to check your answer. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 6 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Homework 26 Name: Date: Homework 26 – Sides and Angles in Triangles Directions: Classify each triangle by BOTH its sides and its angles. 1. 2. 3. Directions: Find the measure of angle 1. Show your work. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Directions: For question 10, show or explain how you got your answer to each part of the question. 10. Consider triangle ABC with ∠𝐴 measures 40 degrees. a. Give possible measures of ∠𝐵 and ∠𝐶 that would make triangle ABC an acute triangle. b. Give possible measures of ∠𝐵 and ∠𝐶 that would make triangle ABC an obtuse triangle. c. Is it possible to give measures of ∠𝐵 and ∠𝐶 that would make triangle ABC an equilateral triangle? Explain why or why not. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 7 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Do Now 33 Name: Date: Do Now 33 – Classify Triangles Directions: Classify each of the triangles by their sides and angles based on the markings. Figure Classify By Sides Classify by Angles 1. R T S 2. V U W 3. E 102° 7 cm 9 cm F 13 cm D 4. O Q 114° P Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 8 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Exterior Angles Name: Date: Triangle Exterior Angle Conjecture – Guided Notes We often discover theorems _________________________, by using examples and generalizing. Today, we will derive our theorem ________________________, by using previously agreed upon facts to reach a new conclusion. Our goal is to discover a relationship between the exterior angle of a triangle and the remote interior angles of the triangle. Exterior Angle of a Triangle D ________________________________________ ________________________________________ C ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Remote Interior Angles of a Triangle A ________________________________________ B ________________________________________ ________________________________________ F ________________________________________ Name each Exterior Angle in the diagram above and name each of the remote interior angles to that angle. Exterior Angle Remote Interior Angle Remote Interior Angle Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 9 E Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Exterior Angles Name: Date: B Exterior Angle _____________ b Adjacent Interior Angle ____________ Remote Interior Angles _________ & ___________ a A y x C D Step 1: Write an equation that relates the exterior angle and the adjacent interior angle. What conjecture supports this statement? Step 2: Write an equation that relates the three interior angles of the triangle. What conjecture supports this statement? Step 3: Use substitution to combine the two equations. Step 4: Use the subtraction property of equality to eliminate the adjacent interior angle. Step 5: State the Triangle Exterior Angle Conjecture: Triangle Exterior Angle Conjecture The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to __________________________ _______________________________________________________________________. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 10 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Exterior Angles Name: Date: Examples: Using the Triangle Exterior Angle Conjecture Directions: Use the triangle exterior angle conjecture to find the measure of the angle marked with a question mark. Directions: Use the triangle exterior angle conjecture to solve for x. 3) 4) Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 11 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Exterior Angles Name: Date: Triangle Exterior Angle Conjecture Independent Practice Directions: Use the triangle exterior angle conjecture to find the measure of the angle marked with a question mark. Use an answer card from a teacher to check your work at the end of each section. Section A 1) 2) 3) 4) 6) 5) Section B Directions: Use the triangle exterior angle conjecture to solve for x. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 12 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Exterior Angles Name: Date: 7) 8) 9) Section C Directions: Find the measure of the angle indicated. 10) 11) 12) 13) Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 13 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Homework 27 Name: Date: Homework 27 – Triangle Exterior Angles Directions: Find the measure of angle 3 using the triangle exterior angle theorem. 1. 2. 3. Directions: Write a true equation and solve it to find the value of the variable. You must show the equation and a value for the variable to earn full credit. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Fernando drew triangle ABC and an exterior ∠CBD. a. Draw and correctly label Fernando’s triangle. b. Name the alternate interior angles to ∠CBD. c. Fernando measured ∠ABC and found that it was 52° . What must the measure of ∠CBD be? Show or explain how you got your answer. d. Fernando measured ∠C and found it to be 30° . Is this possible? Explain why or why not. e. If Fernando’s measurement of ∠𝐵 is possible, use it to find ∠A. If not, suggest an alternate measurement for ∠𝐵 and use it to find ∠A. Show or explain how you got your answer. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 14 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Do Now 34 Name: Date: Do Now 34 – Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem Directions: Use the triangle exterior angle theorem to find the measure of the angle marked with a question mark. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 15 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Isosceles and Equilateral Tri. Name: Date: Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles – Investigation and Practice Parts of an Isosceles Triangle: B Vertex angle Legs Base angles A C Base Vertex Angle of an Isosceles Triangle ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Legs of an Isosceles Triangle ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Base Angles of an Isosceles Triangle _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Base of an Isosceles Triangle ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 16 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Isosceles and Equilateral Tri. Name: Date: Investigation: Base Angles in an Isosceles Triangle Group Roles: Facilitator ____________________ Materials Manager _____________________ Reader ______________________ Technician __________________________ Materials: ● patty paper ● a straightedge ● a protractor Let’s examine the angles of an isosceles triangle. Each person in your group should draw a different angle for this investigation. Your group should have at least one acute angle and one obtuse angle. Step 1: Draw an angle on patty paper. Label it ∠C. This angle will be the vertex angle of your isosceles triangle. Step 2: Place a point A on one ray. Fold your patty paper so that the two rays match up. Trace point A onto the other ray. Step 3: Label the point on the other ray point B. Draw 𝐴𝐵. You have constructed an isosceles triangle. a. How do your know that it is isosceles? b. Name the base and the base angles of the triangle you created. Base _________ Base angles (there are 2) ______________ Step 4: Use your protractor to compare the measures of the base angles. What relationship do you notice? How can you fold the paper to confirm your conclusion? Step 5: Compare results in your group. Was the relationship you noticed the same for each isosceles triangle? State your observations as your next theorem. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 17 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Isosceles and Equilateral Tri. Name: Date: The Isosceles Triangle Theorem Verbal If: Then: Pictorial H H I I G G Symbolic If: Then: The Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem Verbal If: Then: Pictorial H H I G Symbolic If: I G Then: Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 18 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Isosceles and Equilateral Tri. Name: Date: Equilateral Equiangular Triangle Theorem A triangle is equilateral if and only if it is equiangular. Stated as a conditional, Verbal If: Then: Pictorial E D E F Symbolic If: D F Then: And the converse of the conditional. Verbal If: Then: Pictorial E D Symbolic If: E F D F Then: Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 19 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Isosceles and Equilateral Tri. Name: Date: Isosceles and Equilateral Independent Practice Directions: Find the measure of each angle marked with an x. 1. 2. 43° x° x° 41° 3. 4. 99° x° 66° 5. x° 6. x° 40° 7. x° 8. x° x° 54° 46° Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 20 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Homework 28 Name: Date: Homework 28 – Properties of Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles 16. Shanice drew triangle PQR on the coordinate plane with coordinates P (5, -2), Q (5, 2), and R (1, 2). a. Plot and label Shanice’s triangle ON GRAPH PAPER. b. Classify Shanice’s triangle by its sides. Show or explain how you know your answer is correct. c. Classify Shanice’s triangle by its angles. Show or explain how you know your answer is correct. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 21 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Do Now 35 Name: Date: Do Now 35 – Angles and Theorems Use your theorems to find each of the lettered angles. Name the theorem that you use for each angle. Theorem Bank Linear Pair Theorem Vertical Angles Theorem Triangle Sum Theorem Alternate Interior Angles Alternate Exterior Angles Corresponding Angles Isosceles Triangle Theorem Equilateral/Equiangular Triangle Theorem • • • • • • • • Angle Measure Theorem Name a b c d e f g h k n p Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 22 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Side Investigation Name: Date: Triangle Side Length Investigation Group Roles Facilitator _________________ in charge of making sure the group completes the task in a timely manner and that all group members are involved and understand Reader/Recorder _______________ responsible for reading each direction out loud. Also responsible for recording the results of each trial and making sure that all other group members also record the data Materials Manager _______________ collects all material (see list below) from the table and returns it at the end of the investigation Technician ________________ responsible for directing and/or performing the triangle trials Materials • • • • • 3 1-inch straws 2 2-inch straws 2 3-inch straws 2 4-inch straws 1 5-inch straw Investigation For each set of three lengths, use your straws to determine whether it is possible to make a triangle with those three lengths. Record whether or not it is possible and draw an example or counterexample (a picture that shows why the triangle is or is not possible.) Side Lengths 1,1, and 2 Possible (P) or Impossible (I) Example or Counterexample 1, 2, and 3 Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 23 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Side Investigation Name: Date: 2, 2, and 3 2, 3, and 4 3, 3 and 4 1, 3 and 4 3, 3 and 4 3, 4, and 5 Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 24 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Side Investigation Name: Date: 2, 2, and 4 1, 4, and 5 Use what you have determined in the investigation so far to create your own, different set of side lengths. Create 2 sets that you think will make a triangle and 2 sets that will not. Then use your straws to test your sets. Record the results below. Side Lengths Possible (P) or Impossible (I) Example or Counterexample Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 25 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Triangle Side Investigation Name: Date: Triangle Inequality Theorem: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is _________________________ the length of the third side. Extra Credit Challenge: Given the two side lengths and the possibility or impossibility, find a possible third length and draw an example or counterexample. Side Lengths 1.5, 2.7, and Possible (P) or Impossible (I) Possible Example or Counterexample ______ Impossible 3 13 , 4 34 , and ______ Examples: Determine whether each of the following sets of lengths could be the side lengths of triangles. Write yes or no. If the triangle is possible, classify it as scalene, isosceles, or equilateral. 1) 3 cm, 4 cm, 4 cm 2) 5 miles, 5 miles, 3 3) 5 in, 5 in, 5 in 4) 4.5 yds, 5 yds, 9 yds miles Possible: Possible: Possible: Possible: Classify (if possible): Classify (if possible): Classify (if possible): Classify (if possible): Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 26 Geometry Level 2 Ms. Sheppard-Brick 617-596-4133 Homework 29 Name: Date: Homework 29 – Triangle Side Lengths You may complete this assignment on this sheet of paper. 13. Desirae has a triangle which has one side that is 5 m and one side that is 9 m. She wonders what the possible lengths are for the third side. a) Which of the following side lengths are possible third sides for Desirae’s triangle? Circle the ones that are. 3m 4m 5m 13 m 15 m 16 m b) What is the smallest integer value that the third side could have? Explain how you know your answer is correct. c) What is the largest integer value that the third side could have? Explain how you know your answer is correct d) Write an inequality that shows all the possible values, x, that the third side could have. Geometry Week 12 Packet Page 27