* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Mathematical modelling then to do with
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
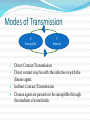
By Prof. J. B. Shukla International Internet University for Research in Science and Technology, HQ Kanpur Website : www.iiurst.org Formerly, IIT Kanpur Email: [email protected] Introduction From where shall I begin. Let us begin from the very beginning What is research? Research is to discover some new characteristics about a system/situations which has not been explored before. “The greatest force on earth is the human soul (mind) on fire” …Forsyth “People see things and ask why. I see thinks that are not and ask why not” …George Bernard Shaw Researchers therefore must have that kind of vision and mind for quality research Introduction contd. CHIT JAL PAWAK GAGAN SAMIRA PANCH TATVA SE BANA SHARIRA ...Tulsidas The survival of all living beings depends upon the following FIVE Tatvas (Resources) Air Water Earth Fire (Energy) Space(Environment in the Universe) Therefore, our research must be directed towards conservation and preservation of these resources by using modern science and technology The role of research should therefore be to preserve these resources provided by nature and not used them to the extend so that they do not remain available for future generation Mathematical Model “An equation for me has no meaning unless it expresses the thought of God.” S. Ramanujan Thought of God Nature Nature includes any thing and every thing in this universe including planet earth. As mentioned before research must be focussed on nature and society. Mathematical Model contd. Mathematics has permeated in all sciences. Physical Science, Environmental, Biological Sciences, Social Sciences. Systems Math Models • Unknown and known variables Mathematical relations among the variables and parameters All systems are governed by some laws, principles and hypothesis. Mathematical Model Cont. Models predicts the future. The future can not be experimented upon. Model predicts the system’s future behaviour on the basis of what is known today. Mathematical models are complex and non linear O.D.Es/PDEJ etc. Solution are difficult, as no. of unknown variables are large. They can be analysed using both quantitative techniques as well as qualitative methods. Stability analysis Validations is needed. Math. Model Solution System validation interpretation Infection Diseases These are diseases which are transmitted by infection. Factors affecting the spread of such diseases: • • • • • • • • • No. of susceptibles No. of infectives No of exposed persons No. of removed persons Rate of contact Incubation period Rates of removal Genetic and immunological factors Nature of diseases Other Factors i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. Demographic (Human) Environmental Ecological Societal/Economic Growth of Vector, Carrier, Bacteria population. Diffusion of population in the habitat Convective effect caused by motion of the medium Migration between two habitats Not better Better Some More Factors a) Isolation b) Nutrition c) Sanitation d) Medication Religion, Caste Creed. Social interaction Professional Interactions Interactions at work place. Modes of Transmission X Susceptible Y Infective Direct Contact/Transmission • Direct contact may be with the infective or with the disease agent. ii. Indirect Contact/Transmission Disease agent are passed on the susceptible through the medium of some kinds. i. Direct Transmission Type Pathway for transmission Diseases Direct Contact Skin to skin mucosa to mucosa, sexual STD, AIDS, Leprosy, Eye infection Droplet infection Spray of droplets of Common old, T.B. saliva, other secretions by coughing, sneezing, spitting etc Contact with soil, etc. Direct contact of susceptible with disease agent in soil etc. Hookworm Larvae, tetanus Indirect Transmission Type Pathway for Transmission Diseases Vector, Carrier, borne Vectors transmit infection by biting or by depositing infective material on food skin etc. Malaria, Dysentery ,Typhoid fever by House fly, Cholera Medium Borne Through the agency of food, water, ice, blood, serum, tissues, injection, cloths, soil, etc. Typhoid fever (TB) Air borne bacteria, viruses, Droplets, Infected Dust Small droplets in the air may evaporate leave behind viruses bacterial which remain in the air and can get to susceptibles, Sneezing and spitting on the ground wall etc. Chicken Pox, Measles, Influenza, H1N1, TB, etc Aims/ Objectives of Study 1) How fast a disease is spreading? 2) How much of the total population has been infected? 3) How of much of the remaining will be infected at a particular time/ location 4) What are the causes and factors for the spread of a particular disease 5) What is the effect of control measures, if any other the spread etc. A General Epidemic model X: Susceptible Y = Infective dX A XY dX Y Z k1 X dt dY XY dX Y Y 1Y dt dZ 1Y dZ Z dt dZ1 k1 X dZ1 dt N X Y Z Z1 dN A dN Y dt Z = Removed Z1 = Isolation Some Ideas 1. Non mixing models for the spread of infections diseases 1. Effects of sanitation II. Effect of nutrition III. Effects of medication IV. Effects of awareness I. Effects of environmental and ecological factors on the spread of infections diseases 3. Effect of diffusion (Movement of population) 4. Effects of movement of convection effects on the spread of infection diseases. 2. Non mixing model β-Interaction coefficient, rate of contracts. It should dependent upon the following i. Space ii. Social factors such as going together to Churches, Temples, Dargahs, Malls, Fairs, Feats And Parties iii. Office factors such as working in the same office, department, building etc sitting on the same table. iv. Professional factors such as doing research together v. Travel factors such as going to together in same vehicle vocation doing the office vacation vi. Awareness of the disease Non Mixing Models contd… Effect of Space X 2Y A X Y d 2 t s 2 X dX d1 2 s Y 2Y 2Y X Y d 2 dY d 2 2 t s s Effect of Sanitation S = Sanitation variable B = Bacteria dX A ( S )Y dX dt dY ( S )Y dX dt dB Y 0 B 1 BS dt dS B 0 ( S S0 ) 1 BS dt Effect of Medication M= Variable for Medical support dX A ( M )Y dX dt dY ( M )Y dX dt dM Y 0 ( M M 0 ) 1 BM dt Where B(M) to be defined suitably Effect of Nutrition H= Healthy Population Nu = Variable for nutrition dH A0 dH 1 XN dt dX A ( Nu )Y dX 1 XN dt dY ( Nu )Y dX Y dt dNu Y 0 ( Nu Nu0 ) dt N X Y H dN A0 A dN Y dt Effect of Media Awareness Me=Variable for Awareness dX A ( M e ) XY dX dt dY ( M e ) XY dX dt dM e Y 0 ( M e M e 0 ) dt How to Consider Environmental/Ecological Effects First we consider the changes in environmental/ecological factors Then their effect on e human / agent (vector, bacteria carriers etc). dE E E 1 0 E 1 EN dT Em dT Q(N) Q0 T dt Q( N ) Q0 QN N – Is the total human population E – Ecological density (biomass density) T – Density (Environmental factor) How to consider spatial effects A simple case with convection and diffusion X X 2Y 2 X U A x Y d 2 dX d 2 t s s s Y Y 2Y 2Y U x Y d 2 dY d 2 2 t s s s