* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of Organisms
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
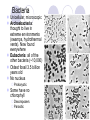
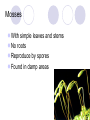
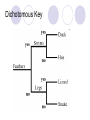
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification of organisms The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms Carol Linnaeus 1707 – 1778 Created the classification system we use today based on similarities that reveal relationships Ex: Bat is considered a mammal because it has hair and provides milk for their young and not a bird because of the wings Classification of Organisms Kingdom Phylum / Division Class Order Family Genus Species Genus/Species Binomial nomenclature: two word naming system where the first word identifies the genus (a similar group) and the second identifies the species (a characteristic) Ex: Scientific name of modern humans is Homo sapiens. Notice that the genus is capitalized and the species is lowercase Brown Squirrel Kingdom: Animalia (animal) Phylum: Chordata (has a backbone) Class: Mammalia (has a backbone and nurses its young) Order: Rodentia (has a backbone, nurses its young, and has long, sharp front teeth) Family: Scuridae (has a backbone, nurses its young, has long, sharp front teeth, and has a bushy tail) Genus: Tamiasciurus (has a backbone, nurses its young, has long, sharp front teeth, has a bushy tail, and climbs trees) Species: hudsonicus (has a backbone, nurses its young, has long, sharp front teeth, has a bushy tail, and has brown fur on its back and white fur on its underparts) Classification of two animals Bobcat Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Lynx rufus Lynx Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Lynx canadensis Five Kingdom System Bacteria Protists Fungi Animals Plants Bacteria Unicellular, microscopic Archaebacteria: thought to live in extreme environments (swamps, hydrothermal vents). Now found everywhere Eubacteria: all of the other bacteria (~10,000) Oldest fossil 3.5 billion years old No nucleus Prokaryotic Some have no chlorophyll Decomposers Parasitic Protists Unicellular or multicellular; microscopic Nucleus present, but lacks complex organ systems Eukaryotic Autotrophic or heterotrophic Lives in moist environments Found in fossils up to 2 billion years ago Red, Green and brown algae are plant-like protists Fungi Eukaryotic Either unicellular or multicellular No root, stem and leaf No chlorophyll decomposer or parasitic Reproduce by forming spores First appeared in the fossil record 400 million years ago ~100,000 known species Animals Eukaryotic, multicellular Heterotrophs Oldest animal fossil 600 million years old Divided into two groups according to the presence or absence of backbone: Invertebrates : without backbone Vertebrates : with backbone Invertebrates Invertebrates Invertebrates Vertebrates Divided into 5 groups: Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Fish Aquatic Cold-blooded Body covered with wet and slimy scales Streamlined body for easy movement through water Fins for balance and to control movement Gills for breathing External fertilization Amphibians Cold-blooded Moist, scale-less skin Limbs present Larvae (tadpoles) use gills for breathing; adults use lungs External fertilization Reptiles Cold-blooded Body covered with dry, hard scales Live on land Breathe with lungs Internal fertilization; lay shelled eggs Birds Warm-blooded With feathers With wings Beak for feeding Lungs for breathing Internal fertilization; lay shelled eggs Mammals Warm-blooded Hair on skin Females have mammary glands for producing milk for their offspring Lungs for breathing Internal fertilization; embryos develop inside mothers’ bodies Plants Most plants contain photosynthetic pigments (e.g. chlorophyll) for photosynthesis Autotrophic Can be divided into two groups: Non-flowering plants Flowering plants Oldest fossil 400 million years old Roughly 500,000 known species Non-flowering plants 4 groups: Algae Mosses Ferns Gymnosperms Algae Aquatic Simple multicellular plants No root, stem or leaf Contain photosynthetic pigments (e.g. chlorophyll) for photosynthesis Mosses With simple leaves and stems No roots Reproduce by spores Found in damp areas Ferns With true roots, stems, leaves and vascular tissues Reproduce by spores Live in damp places Gymnosperms Reproduction by producing seeds Seeds develop in cones, not enclosed by fruits naked seeds Needle-shaped leaves to reduce water loss Angiosperms (Flowering plants) With flowers for reproduction Seeds are produced inside the fruit (matured ovary) Dichotomous Key Your Mission Biology book page 474 & 475 Make a dichotomous key using beetles Follow the procedure and answer questions 1-3