* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Herpes Simplex Virus
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
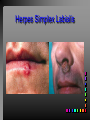
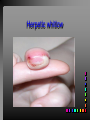
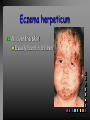
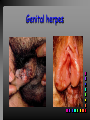
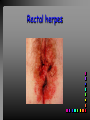
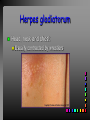
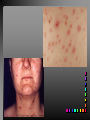
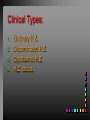
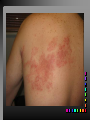
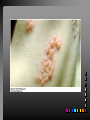
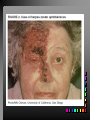
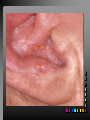
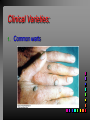
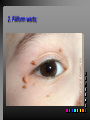
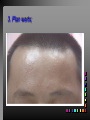
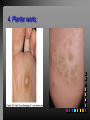
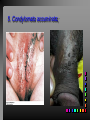
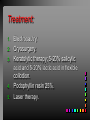
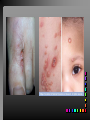
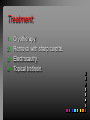
Viral Skin Diseases Herpes Simplex Virus HSV-1 & HSV-2 Frequently benign but can cause severe diseases. The clinical course is characterized by 2 stages: a primary infection and recurrent episodes. Pathophysiology The virus enters the host through either a break in the skin or intact mucus membrane. The virus invades sensory neurons and is transported to the sensory ganglia where it lies dormant. Symptoms At first there is a burning, itching, tingling sensation in the area where the lesion will form. There is also pain, fever, swollen lymph nodes and malaise. The lesion appears as vesicle 1-3 mm in diameter. The boarder around the vesicle may be red and inflamed. Fully developed lesions has a crusty cover and if there is pus under the crust that may indicate a secondary bacterial infection. The whole symptomatic process typically lasts 10-14 days and heals without scarring. Recurrence UV radiation, stress, fatigue, burn, fever, injury, menstruation, dental procedures, infectious disease and immunosuppresion. Types: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Herpes Simplex Labialis. Herpetic Gingivostomatits. Herpetic whitlow. Anorectal herpes. Genital ulcers (HSV2). Eczema herpeticum. Herpes Simplex Labialis Herpetic whitlow Eczema herpeticum All over the skin Usually found in children Genital herpes Rectal herpes Herpes gladiatorum Head, neck and chest Usually contracted by wrestlers Treatment: Acyclovir 200 mg/5 times a day for 5 days. Chickenpox Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease that causes skin lesions in children. Transmitted through direct contact with lesions and respiratory secretions. Chickenpox is caused by the varicellazoster virus (VZV). Symptoms I.P; 10-23 days Chickenpox causes a red, itchy rash on the skin that usually appears first on the abdomen or back then spreads to almost everywhere else on the body, including the scalp, mouth, nose, ears and genitals. The rash begins as multiple small, red papules that look like insect bites. They develop into vesicles filled with clear fluid. The blister wall breaks, leaving open sores, which finally crust over to become dry, brown scabs. Some kids have a fever, abdominal pain, sore throat, headache, or a vague sick feeling a day or 2 before the rash appears. Treatment: Only symptomatic. Herpes Zoster (Shingles) Herpes zoster is caused by the same virus as chicken pox (VZV). Zoster typically causes more pain and less itching than chicken pox. A person may feel burning, itching, tingling. These symptoms are typically present for 1-3 days, before a red rash appears in the same area. Then groups of vesicles appear, which generally last for 2-3 weeks. Clinical Types: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ordinary H.Z. Disseminated H.Z. Ophthalmic H.Z. H.Z. oticus. Complications 1. 2. 3. 4. Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Severe disease may show hemorrhagic, bullous and gangrenous lesions. Motor involvement: facial palsy. Ocular complications: uveitis, keratitis and conjunctivitis. Treatment: Acyclovir 800 mg/5 times a day for 7-10 days. Warts Warts are caused by human papilloma viruses (HPV). Clinical Varieties: 1. Common warts 2. Filiform warts; 3. Plan warts; 4. Plantar warts; 5. Condylomata accuminata; Treatment: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Electrocautry. Cryosurgery. Keratolytic therapy; 5-20% salicylic acid and 5-20% lactic acid in flexible collodion. Podophyllin resin 25%. Laser therapy. Molluscum Contagiosum The infecting virus is a pox virus called the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Molluscum contagiosum lesions are flesh-colored, dome-shaped, and pearly in appearance. They are often 1–5 millimeters in diameter, with a dimpled center. Treatment: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cryotherapy. Removal with sharp curette. Electrocautry. Topical tretinoin. THE END