* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congruency and Similarity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
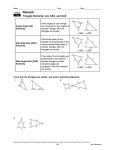
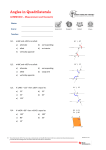
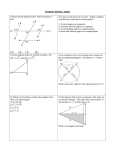
3 LESSON 36 Congruency and Similarity MPM2D | MCR3U IB MYP 5 MATHEMATICS EXTENDED Pearson IB CONTENTS 11.02 Similar Triangles 11.03 Using Scales Factors to Find Unknown Sides Geometry and Trigonometry LESSON PLAN D ONTARIO EXPECTATIONS E F I 11.04 Similar Triangle Proofs N I T I O N S Congruent MPM2D Trigonometry Prepared by Dr. Benedict Hung TEXTBOOK Pearson Pg. 294 – Pg. 313 T H O R E M In an isosceles triangle the base angles are equal the line joining the apex to the midpoint of the base bisects the vertical angle and meets the base at right angles Converses of the isosceles triangle theorem if a triangle has two equal angles then it is isosceles the angle bisector of the apex of an isosceles triangle bisects the base at right angles the perpendicular bisector of the base of an isosceles triangle passes through its apex A KEY TERMS congruency, similarity, isosceles triangle theorem, scale factor E FORMULAE & STATEMENTS N O T E B S The symbol for congruency is To say that ABC DEF means that AB DE A D E C F B E and BC EF D C F AC DF The order that the triangles are listed is important. It lets you know what angles and sides are equal. There are three different conditions for congruent triangles: Side-Side-Side Congruence ( SSS ) Side-Angle-Side Congruence ( SAS ) Angle-Side-Angle Congruence ( ASA ) The symbol for similarity is ~ A To say that ABC ~ DEF means that B D A D C AB BC AC B E and E DE EF DF C F The order that the triangles are listed is important. It lets you knowF what angles are equal and what sides are proportional. There are three different conditions for congruent triangles: Side-Side-Side Similarity ( SSS ~ ) Side-Angle-Side Similarity ( SAS ~ ) Angle-Angle Similarity ( AA ~ ) · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · C A N A D I A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S C H O O L O F H O N G K O N G AB BC AC n , n is the scale factor. DE EF DF the length of any side of ABC n (length of the corresponding side of DEF ) the length of the altitude of ABC n (length of the corresponding altitude of DEF ) perimeter of ABC n (perimeter of DEF ) area of ABC n 2 (area of DEF ) If ABC ~ DEF , then E X A M P L E For ABC ~ KLM . AB 8cm and KL 10m . The area of KLM is 40cm2 . Find the area of ABC . K A 10cm 8cm B X A M P L E C L 2 RST ~ PQW . Find the unknown side lengths. P R 24cm 12cm 14cm W T 36cm S M Q ASSIGNMENT Pearson Pg. 295 # 2, 5, 6, Pg. 298 # 6 – 8 Pg. 306 # 2 – 4, 6, 7, Pg. 311 # 1, 2, 4, 6, 7bc 2 IB MYP 5 Mathematics Extended MPM2D MCR3U Unit 3 – Coordinate Geometry Prepared by Dr. Benedict Hung E 1