* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems - Demarest School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
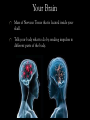
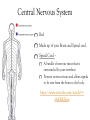
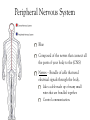
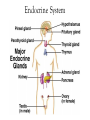
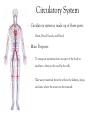
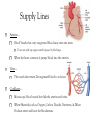
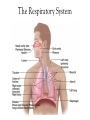
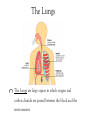
Body Systems Function and organization of the body systems https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZRFykdf4kDc Body Organization Your body is made of trillions of cells. Cells – Simplest and most basic unit of all living organisms. Tissue – A group of cells that are similar and work together to perform a specific function. Organ – Two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function. Body System – A group of organs working together for one purpose. Ex: Digestive System is made of many organs that are all working together to provide Nutrients for your body. Body Systems Work Together Each body system has a specific purpose Ex: The circulatory systems main function is to pump blood through the body. As that blood travels through the body it carries oxygen, nutrients, and chemical messages to other parts of the body. Your Body Systems Skeletal System – Provides the frame work that gives structure and supports the body. Muscular System – Works with the skeletal system to cause movement. Nervous System – Controls and coordinates the activities of the body systems. Endocrine System – Helps the nervous system control and coordinate movements of the body; Helps regulate Growth. Your Body Systems Digestive System – Breaks down food into nutrients, stores nutrients, and eliminates waste from the body. Urinary System – Filters liquid waste products from the blood and eliminates them from the body. Circulatory System – Transports and distributes gases, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body. Protects the body from disease. Respiratory System – Exchanges oxygen from the environment and carbon dioxide from the body. The Nervous System Your bodies control center Composed of: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves, and Sensory Organs. Ex: Eyes, Ears, and Taste Buds. Gathers and interoperates information about the bodies internal and external environments and generates a responds to that information. Your Brain Mass of Nervous Tissue that is located inside your skull. Tells your body what to do by sending impulses to different parts of the body. Your Brains Structure Three Parts: Cerebrum – Coordinates many of the activities of the body systems. Controls your senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, and hearing). Also controls emotions, voluntary muscle movements, consciousness, learning, and memory. Cerebellum – Muscle coordination, balance, and power. Brainstem – Part of you brain that connects to the spinal cord. Controls Heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Central Nervous System Red Made up of your Brain and Spinal cord. Spinal Cord – A bundle of nervous tissue that is surrounded by your vertebrae Protects nervous tissue and allows signals to be sent from the brain to the body. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s8yEhRZgvw Peripheral Nervous System Blue Composed of the nerves that connect all the parts of your body to the (CNS) Nerves – Bundle of cells that send electrical signals through the body. Like a cable made up of many small wires that are bundled together. Control communication. Common Problems of the Nervous System Use your computer to Look up the following… Meningitis – Rabies – Concussion – Paralysis – Epilepsy – Cerebral Palsy – Endocrine System Endocrine System Network of tissues and organs that release chemicals which control certain body functions. Composed of a system of Glands that make and release Hormones. Regulating and controlling body activity. Your Glands – Tissue or group of tissues that make and release chemicals. Endocrine System Hormones – Chemicals that travel in the blood and cause changes in different parts of the body. Used to send messages to different parts of the body which regulate your development. Helps body maintain Homeostasis – Ability of the body to maintain a constant internal state. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tN78hYn3ehc Circulatory System - Circulatory system is made up of three parts. - Heart, Blood Vessels, and Blood - Main Purposes - To transport nutrients from one part of the body to another so they can be used by the cells. - Take waste materials from the cells to the kidneys, lungs, and skin, where the waste can be removed. Heart, Blood Vessels, & Blood - The Heart is the pump that (Each beat) pushes blood through the body. - The Blood vessels are the pipes through which the blood is pumped through. - You Body has about 5 liters of blood. - Blood is a tissue that is made of liquid, cell parts and two types of cells. - 55% of your blood is a liquid called plasma. - The other 45% is made up of blood cells (RBC & WBC) and cell parts called platelets. Supply Lines Arteries – Blood Vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. Does not pick up oxygen until it passes by the lungs. When the heart contracts it pumps blood into the arteries. Veins – The vessels that return Deoxygenated blood to to heart. Capillaries – Microscopic blood vessels that link the arteries and veins. Where Materials such as Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nutrients, & Waste Products enter and leave the bloodstream. How it works https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q0s-1MC1hcE The Respiratory System The Respiratory System What is it? The Respiratory System is the body system that brings in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the body. Main components: Nose, Throat, Voice Box, Windpipe, & Lungs. The Respiratory System Why do we breath? Your cells use oxygen to function but produce carbon dioxide. These gasses are forced in an out of the body through breathing. The Path of Air Air enters the body through the Nose or Mouth. It then passes through the thought or Pharynx. The air then passes through the voice box or Larynx. The air then enters the wind pipe or Trachea. The Trachea the divides into two tubes (Bronchi) which allow air into the Lungs. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1YtXc_84A https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qGiPZf7njqY The Lungs The Lungs are large organs in which oxygen and carbon dioxide are passed between the blood and the environment. How You Breathe Alveoli Tiny air sacks located at the ends of our bronchi in the lung that help move gases when we breathe. Diaphragm Dome shaped muscle beneath the lungs. Works to move air into and out of the lungs. When the Diaphragm and other muscles in the ribs contract air enters. Air leave the lungs when these muscles relax. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hp-gCvW8PRY How You Breathe: Step by Step Step 1: Inhalation happens at the diaphragm contracts and drops, causing the lungs to fill with air. Step 2: Red Blood Cells pickup the oxygen and from the alveolus and drop off carbon dioxide. Step 3: Tissues and cells pick up oxygen from the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide. Blood travels back to the lungs where it exchanges the waste gases for oxygen. Step 4: Exhalation happens as the diaphragm relaxes and rises, which forces air out of the lungs. Common Respiratory Problems Tuberculosis Contagious infection that affects the lungs and causes chest Pain and difficulty breathing. Caused by bacteria in the air. Pneumonia Inflammation of the lungs where the alveoli become filled with a thick fluid. Bronchitis Inflammation of the bronchi that often includes a cough that bring mucus to the mouth. th 7 Grade Poster Project Students will have 2 class periods to complete. The Following must be included. The primary function of the system. The major parts of the system. The organization of the system. What influences the health of this system. How does this system help our participation in sports and activities. th 8 Grade Note Quiz Caring For Your Body Book Pg. 134-135. Read Pgs. 34 – 35 in textbook Answer Questions 1-3 in the lesson review.