* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
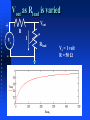
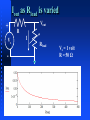
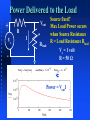
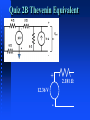
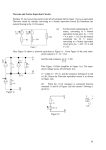
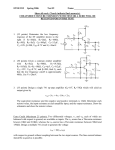
ENGS2613 Intro Electrical Science Week 7 Dr. George Scheets Read 4.13, 5.1 – 5.4 Problems 4.82, 85, & 93; m5.1, 3, &4 Quiz Friday (Find Thevenin Equivalent) Mini Design Results Hi = 10, Low = 5, Average = 9.45, Deviation = 0.85 Lowest Figure of Merit A = 0.51, B = 1.18, C = 0.24, D = 0.30 Norton Equivalent Circuits Any 2 terminal resistive circuit…. Can be replaced with … Fancy Circuit with Resistors & Voltage and/or Current sources Is … where Vs = Is R ↑ R Norton Equivalent Circuit Named after Edward Lawry Norton 1898 – 1983 American Engineer Bell Labs 1926 Proposed Current Source Equivalent of Thevenin's Theorem Also derived in 1926 by Hans Myer of Siemens Source: Wikipedia Vout as Rload is varied + Vs - Vout R I Rload Vs = 1 volt R = 50 Ω Iout as Rload is varied + Vs - Vout R I Rload Vs = 1 volt R = 50 Ω Power Delivered to the Load + Vs - Vout R I Rload Source fixed? Max Load Power occurs when Source Resistance R = Load Resistance Rload Vs = 1 volt R = 50 Ω Power = VoutI Quiz 2B Thevenin Equivalent + 12.36 V - 2.181 Ω To Maximize Power Transfer Source Resistance Fixed? Set Load Resistance = Source Resistance Source Resistance Adjustable? Want Source Resistance as small as possible Active Vs Passive Device Passive Device (Resistor) Cannot Generate Power Active Device (Voltage or Current Source) Can generate power Requires some sort physical or chemical activity Converts this to Electrical Power Efficiency < 100% OpAmp (Active Device) Absorbs power from a power supply Converts this power to another form Amplify a weak signal Act as "On – Off" electrical switch Inside a Typical OpAmp