* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs Used to Treat Eye Disorders
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
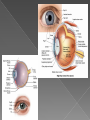
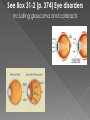
Box 31-1 The Eye: Structures and Functions: Eye has 3 layers › sclera: white of eye, outer layer › choroid: second layer, made of blood vessels, ciliary muscle and iris (give eye color), opening in middle of iris is pupil miosis: Narrowing of pupil mydriasis: dilation (widening) of pupil › retina: inner layer, has receptors for vision and nerve fibers of optic nerve light enters eye through cornea light rays pass to the lens, which lies behind pupil light then reflected to retina light is carried to brain by optic nerve aqueous chamber: separates cornea from lens, filled with fluid called aqueous humor, helps keep shape and position of cornea vitreous humor: behind lens, gelatin-like substance that supports retina and maintains eye’s shape to safely give topical ophthalmic agents see ch. 12, also follow these rules: do not use more than 1 drop (unless otherwise ordered) eye can only hold a small amount of fluid wait at least 5 mins if more than 1 drug is ordered, this prevents: › 2nd drug from washing away 1st › 2nd drug from diluting the 1st drug apply drops before ointments wait a few hours to apply drops after applying ointment provide for safety after applying ointments, they may blur vision know standard colors for ophthalmic labels and bottle caps: anti-infectives: brown or tan beta-adrenergic blocking agents: yellow, blue or both miotics: green mydriatics and cycloplegics: red (cycloplegics paralyze the ciliary muscle of the eye, used for eye exams) › non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents: grey › › › › Delegation Guidelines Drugs Used to Treat Eye Disorder: Some drugs used to treat eye disorders are given parenterally- by intramuscular or intravenous injection. Because you do NOT give parenteral dose forms, they are NOT included in this chapter. Should a nurse delegate the administration of such to you, you must: - remember that parenteral dosages are often very different from dosages other routes -Refuse the delegation. Make sure to explain why. Do NOT just ignore the request. Make sure the nurse knows that you cannot give drug and why See Box 31-2 (p. 374) Eye disorders Including glaucoma and cataracts Drug therapy for glaucoma: several drugs are used to treat glaucoma goals of therapy: › reduce intra-ocular pressure (IOP) › prevent further blindness Drug therapy for glaucoma: Osmotic Agents: cause fluid to be drawn from outside of the vascular system into the blood, this lowers amount of intra-ocular fluid, decreased IOP results Assisting With the Nursing Process Osmotic agents: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs, weight, intake/output, observe for alertness and orientation to person, time and place PLANNING: see table 31-1 for “Oral Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-1 for “Adult Dosage” EVALUATION: report and record: Thirst: changes in alertness and orientation to person, time and place; confusion; muscle cramps; nausea: may signal dehydration or electrolyte imbalance Headache: signals cerebral dehydration, person is kept in supine position Edema and signs/symptoms of heart failure (ch. 21): caused by fluid moving into blood stream Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: agents inhibit carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme inhibiting the enzyme causes decreased production of aqueous humor, IOP lowers Assisting With the Nursing Process Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs, weight, intake/output, observe for alertness and orientation to person, time and place, ask about GI signs/symptoms PLANNING: see table 31-2 for “Oral Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-2 for “Adult Dosage Range”, remove contact lenses for topical dose form, do NOT give drug if person is allergic to sulfonamide antibiotics, give oral dose forms with food/milk to lessen stomach irritation EVALUATION: report and record: Thirst: changes in alertness and orientation to person, time and place; confusion; muscle cramps; nausea: may signal dehydration or electrolyte imbalance Signs and symptoms of allergic reaction to sulfonamide antibiotics: tell nurse at once, do not give next dose unless approved by nurse Confusion: provide for safety Drowsiness: usually mild and resolves, provide for safety Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Cholinergic Agents: produce strong contractions of the iris (miosis) produce muscle contractions that allow eye to adjust to distances drugs lower IOP in persons with glaucoma by permitting the out-flow of aqueous humor they also reverse pupil dilation after eye surgery or eye exams Assisting With the Nursing Process Cholinergic Agents: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: see table 31-3 for “Topical Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-3 for “Adult Dosage” EVALUATION: report and record: problems adjusting to changes in light, problems seeing at night, blurred vision: provide for safety eye irritation, eye redness, headache: usually mild and tend to resolve pain, discomfort: may occur in bright light sweating, increased saliva, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, broncho-spasm, tremors, hypotension, dysrhythmias, bradycardia: signal person is receiving too much of a cholinergic agent Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Cholinesterase Inhibitors: cholinesterase is an enzyme that destroys acetylcholine cholinesterase inhibitors prevent the metabolism of acetylcholine within the eye cholinergic activity increases, which results in decreased IOP and miosis Assisting With the Nursing Process echothiophate iodide (Phospholine lodide): ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: Topical Dose Form is 0,125% solution IMPLEMENTATION: 1 drop is instilled 1 or 2 times/day EVALUATION: report and record: problems adjusting to changes in light, problems seeing at night, blurred vision: provide for safety eye irritation, eye redness, headache: usually mild and resolve sweating, increased saliva, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, broncho-spasm, tremors, hypotension, dysrhythmias, bradycardia: signal person is receiving too much of a cholinergic agent Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Adrenergic Agents: used for eye disorders because they cause: › pupil dilation › increased out-flow of aqueous humor › vaso-constriction › relaxation of the ciliary muscle › a decrease in formation of aqueous humor goals of therapy: › dilate the pupils (mydriasis) for eye exams › reduce IOP › reduce redness of the eyes from irritation Assisting With the Nursing Process adrenergic agents: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: see table 31-4 for “Topical Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-4 for “Adult Dosage” EVALUATION: report and record: sensitivity to bright light: sunglasses help reduce brightness, provide for safety eye irritation, tearing: tend to be mild and resolve palpitations, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, hypertension, faintness, trembling, sweating: signal over-dose or excessive amounts of an adrenergic agent Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Beta-Adrenergic Blocking Agents: used to reduce elevated IOP agents are thought to reduce production of aqueous humor Assisting With the Nursing Process Beta-adrenergic blocking agents: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: see table 31-5 (p. 380) for “Topical Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-5 for “Initial Adult Dosage” EVALUATION: report and record: eye irritation, tearing: tend to be mild and resolve bradycardia, dysrhythmias, hypotension, faintness, broncho-spasm: dosage may need adjustment Drug therapy for glaucoma cont…. Prostaglandin Agonists: reduce IOP by increasing the out-flow of aqueous humor used to reduce IOP in persons who have not responded well to other IOP-lowering agents Assisting With the Nursing Process prostaglandin agonists: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: see table 31-6 (p. 380) for “Topical Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-6 for “Adult Dosage Range” EVALUATION: report and record: eye irritation, burning and stinging, tearing: tend to be mild and resolve changes in eye color: eye color may gradually change, amount of brown pigment in eye may gradually increase, may take several months or years and is permanent; eyelids may develop color changes. Eyelashes may increase in growth Other ophthalmic Agents: there are many other drug classes used to treat eye disorders: › anti-cholinergic agents › anti-fungal agents › anti-viral agents › anti-bacterial agents › cortico-steroids › ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents › antihistamines › anti-allergic agents › artificial tear solutions Anti-Cholinergic Agents: cause relaxation of certain eye muscles, as a result pupils dilate this allows: › examination of interior of eye › resting of the eye during uveitis- inflammation of the uveal tract (middle coat of eye) › measurement of lens strength for eyeglasses (refraction) Assisting With the Nursing Process anti-cholinergic agents: ASSESSMENT: measure vital signs PLANNING: see table 31-7 for “Topical Dose Forms” IMPLEMENTATION: see table 31-7 (p. 381) for “Adult Dosage” EVALUATION: report and record: sensitivity to bright light (dilated pupils let more light in): sunglasses help reduce brightness, provide for safety eye irritation, tearing: tend to be mild and resolve flushing, dry skin, dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, urinary hesitancy and retention, vaso-dilation, constipation: signal overdose or excessive administration Anti-Fungal Agents used to treat fungal infections in the eye Assisting With the Nursing Process natamycin (Natacyn): ASSESSMENT: ask about eye symptoms, ask about the amount and type of visual impairment PLANNING: topical dose form is a 5% suspension IMPLEMENTATION: 1 drop in the eye at 1 or 2 hour intervals for the first 3-4 days. dosage may be reduced to 1 drop every 3-4 hours, therapy is continued 14-21 days EVALUATION: report and record: sensitivity to bright light (dilated pupils let more light in): sunglasses help reduce brightness, provide for safety blurred vision, tearing, redness: tend to be mild and resolve, provide for safety, remind person not to forcefully rub eyes eye pain: person needs medical attention worsening of symptoms: person need medical attention if symptoms worsen or do not improve after several days Anti-Viral Agents agents inhibit the virus from reproducing used to treat herpes infections of the eye Assisting With the Nursing Process trifluridine (Viroptic) ASSESSMENT: ask about eye symptoms, ask about the amount and type of visual impairment PLANNING: topical dose form is a 1% solution in 7.5mL IMPLEMENTATION: 1 drop onto cornea of affected eye every 2 hours while awake. dosage should NOT exceed 9 drops/day, continue for 7 more days after healing to prevent recurrence1 drop every 4 hours (at least 5 drops daily) EVALUATION: report and record: visual haze, tearing, redness, burning: usually mild, tend to resolve, provide for safety sensitivity to bright light (dilated pupils let more light in): sunglasses help reduce brightness, provide for safety allergic reaction: person needs medical attention Opthalmic antibiotics: used to treat superficial eye infections prolonged or frequent use of topical antibiotics should be avoided because of these risks: hyper-sensitivity reactions › development of resistant organisms, including fungi › see table 38-1 Cortico-Steroids: used for allergic reactions of the eye used for acute non-infectious inflammatory conditions of the eye prolonged therapy may cause glaucoma and cataracts see table 39-1 Ophthalmic Anti-inflammatory Agents: the following are used before and after cataract surgery: › flurbiprofen (Ocufen): 1 drop in eye every 30mins beginning 2 hours before surgery, a total of 4 drops are given › suprofen (Profenal): 2 drops in eye 3 hours, 2 hours and 1 hour before surgery › diclofenac(Voltaren): 1 drop in eye 4x a day beginning 24 hours after surgery. Drug is continued for 2 weeks the following is used to relieve eye itching from seasonal allergies: › ketorolac(Acular): 1 drop in each eye 4x a day Antihistamines: used to relieve signs/symptoms associated with allergic conjunctivitis prevent itching for best results should be instilled before exposure to allergens see table 31-10 pg. 384 Anti-Allergic Agents: inhibit the release of histamine used to treat allergic eye disorders cromolyn (Crolom, Opticrom): 1 or 2 drops in each eye 4-6x/day at regular intervals lodoxamide (Alomide): 1 or 2 drops in each affected eye 4x/day pemirolast (Almast): 1 or 2 drops in each affected eye 4x/day nedocromil (Alocril): 1 or 2 drops in each eye 2x/day at regular intervals Artificial Tear Solutions: they are like natural eye secretions lubricate dry eyes may be used as lubricant for artificial eyes the dosage is 1-3 drops in each eye 3-4x/day as needed products include: › Isopto Plain › Teargen › Tears Naturale › Murine › Liquifilm Tears