* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient India notes
Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Daṇḍa (Hindu punishment) wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Dayananda Saraswati wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
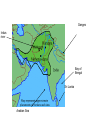
Ancient India Geography • Subcontinent – a large land mass that is smaller than a continent and is separated by physical features from a continent. • Himalayas –Mountain range in North of India that separate it from the rest of Asia. • Early civilization developed along the Indus River. Climate • Hot and Humid • Monsoons – heavy seasonal rains that occur in India. Ganges Indus river Bay of Bengal Sri Lanka Arabian Sea Harappan Civilization • Harrapan civilization – the civilization that grew along the Indus river. • Grew as irrigation and agriculture improved. • Harappa – main city • Mohejo- Daro – other main city • Well planned Harappan Achievements • • • • Indoor plumbing Excellent pottery Cotton clothing Jewelry • http://www.harappa.com/indus/1.html http://www.mohenjodaro.net/index.html http://www.mohenjodaro.net/index.html Aryan Civilization • Invaded from central Asia • Took control of the entire Indus river valley. • Vedas- collection of poems hymns and myths written by Aryan Priest. • Nomads – traveled • Lived in small communities. • Each community had its own leader • Raja- leader of small communities in Aryan Society. • Villagers worked for Raja. • Aryan language - Sanskrit Section 2 • • • • • Aryan Society became divided into groups. Four main groups: Brahmins- Priest Kshatriyas – rulers and warriors Vaisyas – Farmers, craftspeople, and Traders • Sudras –labors and non - Aryans The Caste System • Divided Indian Society based on a persons wealth, birth or occupation. • The four main groups were divided into thousands of subgroups. • Their was no movement from group to group but the status of a group could change. Caste rules • People could not marry outside of their caste • Couldn’t eat with a person from another caste. • If you broke the rules you became an untouchable Untouchables • Not members of any group • Seen as unclean and outcast • Non untouchables were forbidden contact with them. Brahminism • Aryan Religion was called Brahminism • Based on the Vedas • Vedas – contain sacred Hymns and Poems Vedas • Rig Veda – the oldest Hymns and praise to the Gods • Vedic Text –religious rituals • Vedic text – contains secret rituals that only certain people could perform • Upanishads- Reflections on the Vedas by students and teachers. Hinduism • The Ideas of Brahmanism and the Vedas blended with the ideas of other cultures and became Hinduism. Hindu Beliefs • Polytheistic • Three Major Gods: – Brahma – the creator – Vishnu the preserver – Siva the destroyer Brahman- the supreme universal spirit that flows through all things. Brahma Vishnu Siva Life and rebirth • Karma – the effects a good or bad actions have on your soul. • Atman – soul • Based on how well a person follows Caste rules they are born up or down the Caste rank. • How you are born is based on your Karma. • The ultimate goal is to have no further rebirths and to have your atman become one with Brahman. • This world is an illusion. Hinduism • You must accept your place in the world without complaint. • Women are inferior to men Jainism • Based on the Teachings of Mahavira • Beliefs – Injure no life – Tell the truth – Do not steal – Own no property Ahimsa – practice non violence Buddhism • Siddhartha Gautama – 505 B.C. – Prince who founded Buddhism • Buddha – means Enlightened one • Buddhism – religion based on the teachings of Buddha • Was a prince • Sought the answer to the question ; Why is there so much pain and suffering in the world? • Legend has that he meditated for 40 day and fasted on a single grain of rice. • The Answer : Because of Selfish Desires • Wanting what we like but do not have • Wanting to keep what we like and already have • Not wanting what we dislike but have 4 truths • 1. Suffering are part of life • 2. Suffering comes from our desires for pleasure and material goods. • 3. People can overcome desire and reach Nirvana ( a state of Spiritual peace) • 4. Follow an 8 fold path 8 fold path • • • • • • • • Think right Right intent Right speed Right Action Right livelihood Right effort Right mindfulness Right concentration Mauryan Empire • Mauryan empire – founded by Chandragupta Mayura. • Lasted 150 years • Added central India • Asoka- added most of India- became Buddhist monk and rejected war Gupta Empire • United northern and central India • Hindu becomes India’s Religion also supported Buddhism and Janism. • Chandra Gupta II – Ruled during India’s highest point. Supported the Caste System. India’s Achievements • Built great Temples • Stupas – domed roofs meant to house sacred items. • Writing – Kalidasa – Playwrite – Ponchatantra- book of stories with moral lessons • Science – – Metallurgy – work with metals – Alloys – mixed two or more metals Math Hindu Arabic – numbers we use today Idea of Zero • Medicine – Inoculation – give you small doses of virus to build up your immunity • Astronomy – Study of plants and stars – Knew the sun was a star and planets evolved around it. – Predicted eclipses of moon and sun.