* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypothyroidism
Survey
Document related concepts
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Osteoporosis wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
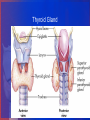
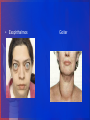
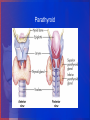
Endocrine: Thyroid and Parathyroid Created by: D.Losicki, MSN, RN Adapted by: C.Perez, MSN,RN. Thyroid Gland Functions of thyroid hormone in Adults • Control metabolic rate of cells • Promote sufficient pituitary secretion of growth hormone and gonadotropins • Regulate protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism • Exert effects on heart rate and contractility • Increase red blood cell production • Affect respiratory rate and drive • Increase bone formation and decrease bone resorption of calcium • Act as insulin antagonist Collaborative Assessment Thyroid Studies • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) (thyrotrophic) Reference interval: 4.6-11.0 mcg/dL (59-142 nmol/L) • Free thyroxine (FT4) Reference interval: 0.8-2.7 ng/dL (10-35 pmol/L • Triiodothyronine (T3), total Ages 20-50: 70-204 ng/dL (1.08-3.14 nmol/L) Ages >50: 40-181 ng/dL (0.62-2.79 nmol/L) Diagnostics • Thyroid scan: • RAIU uptake test: Thyroid Function Test Hyperthyroidism • T3, T4, Free T4, T3 are all increased • TSH is high • TRSH stimulation test: little or no TSH response Thyroid Function Test Hypothyroidism • T3, T4, Free T4, T3 are all decreased • TSH is high in primary, low in secondary hypothyroidism • TRSH stimulation test: Elevated 2 or more times the normal in primary hypothyroidism Affects of Aging Thyroid Spectrum Common Assessment Abnormalities • Hypothyroidism: Cool, Pale dry scaly skin, Decreased hair growth, poor wound healing, Depression, Paranoia, Withdrawal, Weight gain (IE, Eeyore) Hyperthyroidism: Warm, smooth, moist skin T Thinning of scalp hair, HTN, Tachycardia, weight loss, Restlessness ( IE, Tigger) Thyroid Conditions • Hashimotos thyroiditis: Autoimmune hypothyroidism • Graves Disease: Autoimmune, most common form of hyperthyroidism • Exophthalmos Goiter Collaborative Care Hyperthyroidism: 1. Antithyroid medications (Chart 66-3) a. propylthiouracil (PTU) b. methimazole (Tapazole) c. Lithium( Eskalith) 2. Radioactive iodine therapy [RAI]: 3. Sub total thyroidectomy 4. Nutritional Therapy a. High-calorie diet [4,000-5,000cal/day] b. High-protein diet [1-2g/kg ideal body weight] c. Frequent meals Safety Precautions of Patients receiving radioactive isotope • • • • • Use toilet that no one else uses for 2 weeks, men need to sit to urinate, If urine is somewhere other than toilet, clean up, and bag cleaning supplies and take to hospital radiation department for disposal. Wash laundry separate from family , then after run washer for one cycle to clean it. Stay away from pregnant women and young children. Do not share toothbrushes, paper/plastic eating utensils Chart 66-4 HYPERthyroid Care Plan: • Activity intolerance: r/t fatigue, exhaustion, and heat intolerance 2nd to hypermetabolism AEB: complaints of weakness, inability to perform usual activities, short attention span, memory lapses, dyspnea, tachycardia • Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements r/t hypermetabolism and inadequate food intake AEB: complaints of weight loss; less than optimal body weight Post Thyroidectomy 1.Assess: every 2 hours for 24 hours • irregular breathing, neck swelling, frequent swallowing, sensations of fullness at the incision site, choking, and blood on the anterior or posterior dressings. VS, tetany 2. Treat: Place in a semi-Fowler's position • support the head with pillows, • avoid flexion of the neck and any tension on the suture lines. • Pain management • Ambulate [if no complications • Fluids as soon as tolerated and soft diet the next day Thyrotoxicosis/Thyroid Storm • Nursing management: • Assess: cardiac dysrhythmias, decompensation • Treat: administer antithyroid medications IV fluids and electrolyte replacement Calm, quiet room Ensure rest • Teach: Encourage exercise involving large muscle groups self medication management food selections Thyroid Storm/Thyroid Crisis • Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism and occurs often with Graves’ disease • Triggered by : trauma, infection, DKA, and pregnancy • Caused by excessive thyroid hormone released • S&S: Fever, Tachycardia, and systolic hypertension • As Thyroid storm continues: Anxious, tremors, restless, confused psychotic and seizures, leading to a coma. And even death. *** When caring for a pt with hyperthyroidism, even after a partial thyroidectomy, immediately report a temp increased even 1 degree, it may indicate impending thyroid crisis Care during Thyroid Storm • Maintain Airway • Give antithyroid med • Give sodium iodide • Give propranolol • Give glucocorticoids • Monitor for dysrhythmias( Vitals every 30 mins) • Correct dehydration with NS infusion • Apply cooling blankets/ice packs to reduce fever ** Table 66-5 Myxedema Hypothyroid: Collaborative Care • Thyroid hormone replacement (e.g., levothyroxine) (lifelong) • Teach pt and families to take drug exactly and not change the dose without talking to provider. Also, do not change brands because the response to a different drug brands can vary. • Monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust dosage (if needed) • Nutritional therapy to promote weight loss • Patient and caregiver teaching Hypothyroid Care Plan • Imbalanced nutrition: more than body requirements r/t calorie intake in excess of metabolic rate AEB: weight gain 2nd hypometabolism • Constipation r/t gastrointestinal hypomotility as evidenced by irregular, hard stools • Impaired memory r/t hypometabolism AEB: forgetfulness, memory loss, somnolence, and personality changes Parathyroid Function of Parathyroid Glands • Regulates Calcium • Regulates Phosphorus • Excretes Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) • Increases bone resorption Parathyroid Disorders • Hyperparathyroidism: • Increased secretion of PTH • over secretion of PTH is associated with increased serum calcium levels, and low Phosphate • Diagnostic Studies: • Elevated serum PTH • Elevated serum calcium • Decreased phosphorus • Bone Dexa Scan • TABLE 66-3 CAUSES PARATHYROID DYSFUNCTION Collaborative Assessment: Parathyroid Studies Vitamin D • 15-60 ng/mL Phosphate • 3.0-4.5 mg/dL Calcium Ionized • 4.64-5.28 mg/dL Calcium (total) • 9-10.5 mg/dL Magnesium • 1.3-2.1 mEq/L Parathyroid hormone (PTH) • 50-330 pg/mL *** Look over chart 66-10 VERY GOOD TO KNOW! Parathyroid Disorders • Hyperparathyroidism: Uncommon Manifestations • Hypocalcemia • Decreased PTH • Increased phosphorus • Tetany: tingling lips, extremities, tonic spasms dysphagia, laryngospasm Hyperparathyroidism: Collaborative Care • Surgical Therapy • Most effective • Causes rapid serum calcium reductions every 4 hour calcium lab until stabilized • Check for Chvostek’s sign and Trousseau’s sign. • Criteria serum calcium > 12mg/dl • Decreased bone density • Non Surgical Therapy • Does not met criteria for surgery [labs, elderly] • Annual exam, labs, bone density, urinary calcium • Mobility must be maintained • Medications: bisphosphonates, calcimimetic agents Nursing Management • Post parathyroidectomy: • Assess: bleeding, fluid, electrolyte imbalance Tetany: early post op to several days, Trousseau’s and Chvostek’s sign Labs: calcium, potassium, phosphate, magnesium Treat: Ambulation Collaborative Care • Treat acute complications: • Tetany: IV calcium chloride, calcium gluconate • Cardiac monitoring • Rebreathing Long Term management - Replacement therapy - PTH, Oral calcium, Vit D, Ergocalciferol Hyperparathyroidism • Very rare • Hypocalcemia • Treatment: correcting hypocalcemia, vit D deficiency and hypomagnesaemia. • Teach: eat foods high in calcium and low in phosphorus, milk, yogurt and processed cheeses are avoided.