* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Task: Disease Maintenance Summarization
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Forensic epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Compartmental models in epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
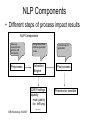
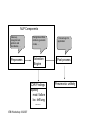
Challenges in Evaluating Natural Language Processing Systems for Military Health Records Carol Friedman, PhD Columbia University/MedLEE Applications Technologies Lawrence Fagan, MD, PhD Stanford University/MedLEE Applications Technologies IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Outline • NLP evaluation issues • Ideal evaluation of NLP output requires consideration of the context of the applications • Catalog of common NLP applications in biomedicine and the implication for evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Outline • NLP evaluation issues • Ideal evaluation of NLP output requires consideration of the context of the applications • Catalog of common NLP applications in biomedicine and the implication for evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Different Evaluation Objectives • Different NLP communities have different objectives and traditions Improvement of: – – – – – Science of NLP Science of biomedical NLP Biological research Clinical research Clinical care IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Evaluation Objectives Determine • Evaluation design • NLP requirements – Type of information needed • Medical terms with/without modifiers • Clinical & other external knowledge – End product • Codes, facts, yes/no categories IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Evaluation to Improve Clinical Research and Care Issues to Consider IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 • Need to start with a concrete clinical goal – Detect potential case of tuberculosis in chest x-ray report for isolation – Detect positive mammography reports for follow up – Find new adverse events to find ways to avoid them IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Type of Task: Broad vs. Narrow • Very specific application – Identify reports of patients who smoke – Identify x-ray reports positive for pneumonia • General application – Data mining & knowledge discovery – Generate patient problem list IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Application Requires NLP + External Knowledge • Structural knowledge – Extract diagnoses from Diagnosis Section of Discharge Summaries 486 (pneumonia) • Coding knowledge for infiltrate in cxr – ICD-9 coding of x-ray reports for billing • Clinical knowledge – Identifying x-ray reports indicating pneumonia • ~ 38 different combinations of findings & modifiers IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 NLP Components • Different steps of process impact results NLP Components Clean-up, recognize text portions and boundaries, … Preprocess IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Recognize entities, relations, generate codes, … Extraction Engine CXR Findings opacity mod: patchy loc: left lung ........ Clinical logic for application Post-process Pneumonia: possible NLP Components Clean-up, recognize text portions and boundaries, … Preprocess Recognize entities, relations, generate codes, … Extraction Engine CXR Findings opacity mod: 5x5cm loc: left lung ........ IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Clinical logic for application Post-process Pneumonia: unlikely Use of Experts • • • • • Need guidelines and examples How much to train Inter-annotator agreement & resolution Borderline cases confound results Granularity issues Fever (mod: persistent) – Comparability IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Persistent fever SNOMED codes: persistent fever chronic persistent fever prolonged fever fever (mod: persistent) Document Heterogeneity & Complexity of Text • Chief complaints (‘well baby 3 mo’, ‘c/f/h’) • Discharge summaries, radiology reports • Reports with structured & unstructured information • Telegraphic notes • Special templates IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 “Well-Structured” Reports: Chest Radiology Report CLINICAL INFORMATION: F/U. IMPRESSION: MODERATE PULMONARY VASCULAR CONGESTION AND INTERSTITIAL EDEMA SHOWS NO SIGNIFICANT CHANGE FROM 3/25 THROUGH 3/27/95. SIDE HOLE OF THE NG TUBE IS NEAR THE EG JUNCTION. DEVELOPMENT OF RIGHT BASILAR ATELECTASIS ON 3/27/95. DESCRIPTION: A series of portable chest x-rays demonstrate worsening but stable vascular congestion and interstitial edema from 3/25 through 3/27/95. The NG tube side hole is seen near the EG junction. A duo- tube is seen extending into the stomach, but its distal tip is not seen. A tracheostomy is seen in good position. …………………………………………………….. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Mixed Structure: Catheterization Report IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Poorly Structured Report: Telegraphic Note Admit 10/23 71 yo woman h/o DM, HTN, Dilated CM/CHF, Afib s/p embolic event, chronic diarrhea, admitted with SOB. CXR pulm edema. Rx’d Lasix. All: none Meds Lasix 40mg IVP bid, ASA, Coumadin 5, Prinivil 10, glucophage 850 bid, glipizide 10 bid, immodium prn Hospitalist=Smith PMD=Jones Full Code, Cx>101 IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Reducing Potential Bias NLP developers should avoid – Designing study – Being involved in choice or determination of reference standard – Correcting bugs – Changing system – Performing actual evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Analyzing Results & Errors • Determine effect of components on performance – – – – NLP vs. domain knowledge Document characteristics/quirks Frequency of adding/updating clinical terms Type of NLP task: classification/information extraction/specialized – Borderline situations • Report degree of complexity needed to correct errors • Determine if performance is adequate for task • Report on confidence intervals IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Other Issues: Clinical Environment • Heterogeneity – Systems – Document formats – Document types – Clinical Domain • Working with physicians • Clinical evaluation tradition • Workflow issues IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Patient Documents • Lack of access to patient records – Significant bottleneck for NLP progress • Difficult to get permission to share from health care institutions • Large scale effort needed to establish scrubbed document sets for development and evaluation • Individual efforts beneficial but limited and scattered IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Outline • NLP Evaluation Issues • Ideal evaluation of NLP output requires consideration of the context of the applications • Catalog of common NLP applications in biomedicine and the implication for evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation: Example Record • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • Subjective: 8 year-old girl with past history of moderate persistent asthma while living in Alaska until 2 years ago • The primary triggers for her asthma have been viral colds and irritant exposure, and she had particular difficulty with the forest fire smoke in central Alaska. • She also has a history of a low serum IgA. Her last IgA determination was August 2004, which showed an IgA level of 29 mg/dl, with the lower limit of normal for a child her age being 33. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • Subjective: 8 year-old girl with past history of moderate persistent asthma while living in Alaska until 2 years ago • Tasks: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • Subjective: 8 year-old girl with past history of moderate persistent asthma while living in Alaska until 2 years ago • Tasks: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • … • The primary triggers for her asthma have been viral colds and irritant exposure, and she had particular difficulty with the forest fire smoke in central Alaska. • … • Tasks: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • … • The primary triggers for her asthma have been viral colds and irritant exposure, and she had particular difficulty with the forest fire smoke in central Alaska. • … • Tasks: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • … • She also has a history of a low serum IgA. Her last IgA determination was August 2004, which showed an IgA level of 29 mg/dl, with the lower limit of normal for a child her age being 33. • Task: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Context-based Evaluation • Chief Complaint: Asthma re-evaluation. • … • She also has a history of a low serum IgA. Her last IgA determination was August 2004, which showed an IgA level of 29 mg/dl, with the lower limit of normal for a child her age being 33. • Task: Disease Maintenance Summarization • vs. Infectious Disease Reporting IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Outline • NLP evaluation issues • Ideal evaluation of NLP output requires consideration of the context of the applications • Catalog of common NLP applications in biomedicine and the implication for evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Potential NLP Applications • • • • • • • Health reporting requirements Known disease surveillance Unknown disease surveillance Recognizing adverse drug reaction Quality assurance/avoiding clinical errors Charge capture Recognizing scientific relations in text databases IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Health Reporting Requirements • Example: Reporting new TB cases • Task description: Governmental requirements that certain disease states must be identified within a period after the original information (typically diagnosis) is identified. • Task requirements: Text may be confined to one or more sections of record. May require inference to identify disease state. May be easier to get the “right” answer than other apps. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Known Disease Surveillance • Example: Locating Hospital Acquired (nosocomial) infections • Task description: Looking at a set of fixed reports for specific findings or combination of findings that suggest disease state • Task requirements: Need to combine free text with structured text such as lab reports, and existing codes (e.g., ICD-9 coding on discharge) IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 “Unknown” Disease Surveillance • Example: Looking for the next “gulf war syndrome.” • Task description: By far, the most difficult task because it is not clear what is being searched for. Looking for a pattern of signs, symptoms, lab tests, time course, etc, not explained by known patterns • Task requirements: Every concept is potentially relevant plus need significant inference to determine novelty of problem. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Recognizing Adverse Drug Reactions • Example: Searching for known (and possibly unknown) side effects of treatments • Task description: Side effect profiles are known for many drugs/regimens. Early recognition of onset of those side effects important to decreasing morbidity • Task requirements: Temporal relationship between treatment and possible side effects important to glean from narrative. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Quality Assurance/Avoiding Clinical Errors • Example: Flagging contra-indicated treatments due to a drug allergy • Task description: Extract from narrative signs/symptoms/lab tests that suggest unanticipated response to prior treatment. • Task requirements: combining concepts from narrative with structured parts of records and comparing to guidelines/protocols IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Charge Capture • Example: Locating clinic/hospital charges that have not been otherwise captured • Task description: Scan narrative for suggestion of procedures performed or supplies used that have not been billed • Task requirements: Inferring actions from narrative and comparing with billing codes. Concepts are well defined and can be enumerated. IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Recognizing scientific relations in text databases • Example: Finding protein-protein interactions in pubmed database • Task description: Scan abstracts to identify protein names and description of relationships • Task requirements: Requires understanding of naming schemes in biology and ability to handle naming issues. Inference to identify correctly the relationship described in the text IEBI Workshop-10/23/07 Summary • Overview of evaluation issues • Key point: evaluation requires consideration of the context of the applications • Catalog of common NLP applications in biomedicine and the implication for evaluation IEBI Workshop-10/23/07