* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Internet and World Wide Web
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
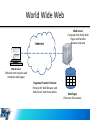
The Internet, World Wide Web, and Computer Communication The Internet • The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks.* *Wikipedia World Wide Web • A system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet* *Wikipedia History of the Internet • Began with Point-to-Point (P2P) communication between computers (later Peer-to-peer) • First version of the Internet was called ARPANET – Mainly used by universities, scientists, and government agencies to share information • Internet2 Peer-to-Peer • P2P – a network where one computer acts as a server or client for other computers • Allows sharing access to various resources such as files Centralized (Not P2P) Internet 2 The Internet • http://www.cablemap.info/ • http://maps.level3.com/default/#.UUY45xw3t 2A Internet Communications • Sold by ISPs (Internet Service Providers) – Verizon, Comcast, Cox Cable, etc. • • • • • • LAN – Local Area Network Dial-Up Broadband Wi-Fi Satellite Broadband Mobile Broadband Routers and Modems • Router – forwards data packets over computer networks to multiple computers • Modem – (modulator-demodulator) encodes and decodes transmitted information. Connects to your ISP. The Internet • Every computer or device connected to the Internet has an IP address • Instructions on where to send data and where to receive data • http://www.whatismyip.com/ VoIP, IM, Video Chat • Voice over IP • Alternative to traditional telephone • Ventrilo, Teamspeak, Raidcall • Skype, Google Hangouts, Facetime The Internet Internet users by Language Website content language Internet - Domain Names • Defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control • US Department of Justice began using a tactic of seizing domain names, based on the legal theory that domain names are part of the property used by defendants to allegedly engage in criminal activities, and thus subject to forfeiture The World Wide Web • Not exactly the same as the Internet – Internet is a system of interconnected computer networks – World Wide Web is a collection of text documents and other resources linked by hyperlinks and URLs( Uniform Resource Locator) World Wide Web Internet Web Server Computer that holds Web Pages and handles Browser requests Web Browser Software that requests and interprets web pages Hypertext Transfer Protocol Protocol for Web Browser and Web Server Communications Web Pages Electronic Documents 15 Google Data Centers Computer Communications • Information broken into packets • To avoid monopolizing a network • To recover in an event of an interruption Computer Communications • Bandwidth – the available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits per second • Latency – Time delay between communications • Ping • Speedtest Torrents • Torrent file – a computer file that contains metadata about files and folders to be distributed, and usually also a list of the network locations of trackers • Uses Peer-to-peer connections (P2P) Proxy Servers and VPN • User connects to a proxy server as an intermediary to another server – i.e. Connect to a proxy server from another country • VPN – virtual private network: allows computer to send and receive across shared or public networks as if it were directly connected to the private network Net Neutrality • The principle that Internet service providers and governments should treat all data on the Internet equally, not discriminating or charging differentially by user, content, site, platform, application, type of attached equipment, and modes of communication.