* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IV Therapy and Blood Administration
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
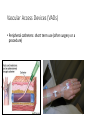
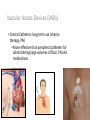
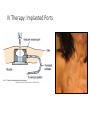
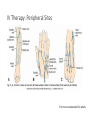
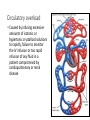
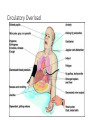
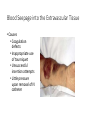
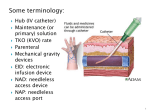
IV Therapy Vema Sweitzer, MN,RN 1 Vascular Access Devices (VADs) • Peripheral catheters: short term use (after surgery or a procedure) 2 Vascular Access Devices (VADs) • Central Catheters: long-term use (chemo therapy, PN) • More effective than peripheral catheters for administering large volumes of fluid, PN and medications 3 IV Therapy: Implanted Ports Vascular Access Devices (VADs) • Central Catheters: long-term use (chemo therapy, PN) • PICC: Peripherally inserted central catheters 5 IV Therapy: Peripheral Sites Feet not recommended for adults IV Therapy: Starting an IV • Review order • Get supplies • Explain to patient • Find best vein • Start distally • Perform venipuncture, secure, start fluids • Document • Dressing should be transparent Complications of Intravenous Therapy Circulatory overload • Caused by infusing excessive amounts of isotonic or hypertonic crystalloid solutions to rapidly, failure to monitor the IV infusion or too rapid infusion of any fluid in a patient compromised by cardiopulmonary or renal disease Circulatory Overload Circulatory Overload • NI/Treatment • Plan ahead if patient is to receive a lot of fluid • Stop the fluids and contact the HCP immediately for new orders. • Continue to monitor the patient and anticipate doctor’s orders: • Oxygen • Diuretics Infiltration • Occurs with IV becomes dislodged or a vein ruptures and IV fluids enter subcutaneous tissue • Nursing Assessment: Infiltration NI/Treatment Prevention • Remove the IV catheter • Apply warm soaks to aid in absorption (check hospital’s policy) • Elevate the limb • Notify the HCP if severe • Assess circulation • Restart the infusion in the other arm • Document the patient’s condition and your interventions • Check the IV site frequently • Don’t obscure area above site with tape • Teach the patient to report discomfort, pain swelling Documentation Infiltration Scale Extravasation • The inadvertent administration of a vesicant solution into surrounding tissue • Signs/symptoms Extravasation NI/Treatment • Immediately stop the infusion and remove the device • Elevate the affected limb • Apply cold compress to decrease edema and pain • Apply moist heat to facilitate the absorption of fluid at grossly infiltrated site Prevention • Check the IV site frequently • Don’t obscure area above site with tape • Teach the patient to report discomfort, pain swelling • Drugs that can cause Necrosis • Calcium chloride • Calcium gluconate • Vancomycin • Cancer Chemotherapy drugs Phlebitis • An inflammation of the vein in which the endothelia cells of the venous wall become irritated and cells roughen, allowing platelets to adhere and predispose the vein to inflammationinduced phlebitis • Causes • Injury during venipuncture • Prolonged use of the same IV site • Irritation/incompatible IV additives • Use of vein that is too small for the flow rate • Use of needle size too large for the vein size Phlebitis Signs/symptoms: NI/Treatment • Upon assessment of phlebitis, remove the needle • Avoid multiple insertion attempts • Application of warm compress • Continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs Documentation Phlebitis Scale Local Infection • Caused by poor aseptic technique during catheter insertion • Signs/symptoms Hematoma at the IV Site • Hematoma: formations resulting from the infiltration of blood into the tissues at the venipuncture site • Causes: nicking the vein during an unsuccessful venipuncture attempt, discontinuing the I.V. cannula or needle without pressure, applying a tourniquet too tightly above a previously attempted venipuncture site Hematoma at the IV Site • Signs/symptoms: • Discoloration • Site swelling and discomfort • Prevention and treatment Blood Seepage into the Extravascular Tissue • Causes • Coagulation defects • Inappropriate use of tourniquet • Unsuccessful insertion attempts • Little pressure upon removal of IV catheter