* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E-Business - Computer Science and Information Systems Technical
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
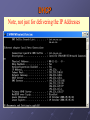
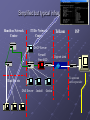
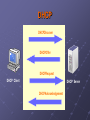
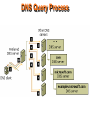
Section Outcome (TCP/IP Services) Describe four (4) services that are part of the TCP/IP protocol suite that would probably be implemented within a network centre to manage: • naming within legacy systems • automated issuing of IP Addresses • name to IP Address translation • private IP addressing Overview • • • • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Domain Name System (DNS) Windows Internet Naming System (WINS) Network Address Translation (NAT) DHCP Administering IP Address allocation - Static configuration (becomes impossible as network grows in size) - Dynamic configuration (automated system of IP address, subnet details and other network information delivery) DHCP Note, not just for delivering the IP Addresses Simplified but typical infrastructure Hamilton Network Centre IT Div Network Centre Telkom ISP DHCP Server Firewall Free BSD Diginet Link To upstream service provider East lab etc DNS Server Jackall Gecko DHCP • • • • • Static VS Dynamic IP Addressing Pool of IP Addresses known as Scopes DHCP Renewal Process DHCP Server per Segment DHCP Relay Agent DHCP DHCPDiscover DHCPOffer DHCPRequest DHCP Client DHCP Server DHCPAcknowledgement DHCP • Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) - 10.0.0.0 through 10.255.255.255 169.254.0.0 through 169.254.255.255 172.16.0.0 through 172.31.255.255 192.168.0.0 through 192.168.255.255 - Network Address Translation (NAT) • Multicast Scopes (224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255) • Scopes and Superscopes DHCP Three DHCP Implementations: • Dynamic allocation - Leased basis from available pool • Automatic allocation - Permanent allocation for duration of communication. Maintains historical list. • Static allocation - MAC/IP address allocation, one MAC address will have the same IP address all the time Network Address Translation (NAT) Office Telkom Internal IP Addresses Computer running: Network Address Translation (NAT) Diginet Link A class C IP Address Firewalling DHCP To upstream service provider ISP DNS • Host File or DNS Server • Different Levels of Domain - Root-level “.” - Top level domain (gov / com / org) - Second level (Course / Microsoft) - Subdomain (sales / marketing) DNS • Top Level - gov (U.S. government agencies) - com (Commercial organizations) - mil (U.S. military services) - edu (Educational institutions) - net (ISP’s) - org (Nonprofit organisations) DNS • Primary Name Server has DNS zone file. • Authoritative for Domain means server holds the main DNS zone file • Primary name server holds a read / write copy of zone file • Incremental Zone Transfers DNS Query Process DNS and ISP’s DNS • Win2003/7+ provides a full-featured DNS server integrated with older DNS methods such as host files • FreeBSD, UNIX etc • Primary and Secondary Zones • Can be primary server for one zone and secondary for another • Win 2003/7+ DNS supports Active Directory • Dynamic DNS, clients can create their own A records DNS • Caching-only servers • Forward lookup zones • In-addr.arpa (name given to reverse lookup zone file) • Iterative vs recursive • Secondary name servers (read only copies of zone file) • Zone transfers WINS • Used for identification in older pre-Windows 2000/3/7 Server versions. Just as DNS provides IP Addresses for host names, Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) provides IP Addresses for NETBIOS computer names. WINS Subnet 1 Subnet 2 No Broadcast Traffic Router Other Servers Other Servers WINS Server WINS Server Proxies Forward Facing Proxy Proxies • Keep machines behind it anonymous. • To speed up access to resources (using caching). • To log / audit usage • To scan transmitted content for malware before delivery. • To scan outbound content, e.g., for data loss prevention. • Access enhancement/restriction Proxies Open Proxy Allows users to conceal their IP Address Proxies Reverse Proxy Proxies 1. Security 2. Act as a firewall 3. SSL Encryption 4. Load-balancing 5. Cache static content 6. Compression 7. Spoon-feeding 8. Multiple servers on the same public IP address Firewalls Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) References: Napier, A., Judd, P., Rivers, O., and Adams, A., (2003) E-Business Technologies Thomson Course Technologies ISBN: 0-619-06319-x Panko, R (2005) Business Data Networks and Communications, 5th edition, Prentice Hall ISBN: 0-13-127315-9 Schneider E-Business, Eighth Edition ISBN-13: 978-0-324-78807-5 Hogan, F., (2005) Internet Presentation