* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter4
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Broadcast television systems wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
High-frequency direction finding wikipedia , lookup
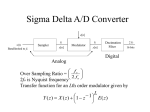
Computer Networks Digitization Transfer of an Analog Signal When analog data (voice, pictures, video) are transformed into analog electrical signal and transmitted through the media, the transmission impairments of the media change the signal. The noise is added to the signal and the result is a signal that does not look very much like the original. When the signal is amplified the noise is amplified, too. It is hard to extract the original signal. Spring 2006 Computer Networks s(t) Signal at the sender (original) t Noise Noise Signal at the receiver 2 t Why we are going digital? The receiver of the digital signal samples the received signal using the clock at the sender. It is only required that it detects whether the voltage is positive or negative. If positive it generates positive pulse If negative it generates negative pulse As a consequence the received signal is exactly the same as the one that r(t) was sent. s(t) Signal at the sender (original) Noise Signal with noise Signal at the receiver Ocasionally errors can appear, but there are methods for their detection and correction. Spring 2006 Computer Networks 3 Digital versus Analog Transmission Advantages of digital communication Regenerator receiver Original pulse Regenerated pulse Propagation distance Different kinds of digital signal are treated identically Voice Data Spring 2006 Media Computer Networks A bit is a bit! 4 Examples of Analog and Digital Transmission Analog transmission Local loop in PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) Cable television Digital Transmission Long-distance circuits in PSTN All kinds of LANs Spring 2006 Computer Networks 5 Analog-to-digital Conversion (A/D) Transformation of analog (continuous) signals into digital signals Infinite number of values of the amplitude need to be represented (coded) as a digital stream with a minimum loss of information The device that codes the analog signal into digital signal is called a coder. The device that performs the inverse operation is called a decoder. Both are usually assembled in one box called a codec. Spring 2006 Computer Networks 6 CODEC V V t Codec t CODer-DECoder Spring 2006 Computer Networks 7 Sampling the Analog Signal Nyquist Sampling Theorem Analog signal can be recovered if sampled at frequency equal or greater than its maximum frequency. In other words, If s(t) is a contnouus signal with a frequency spectum that stisfies S(f) ≤ fmax for all frequencies in S(F), then it can be recovered from a discrete signal consisting of samples taken from s(t) with frequency that is at least twice as big as fmax . Spring 2006 Computer Networks 8 Sampling – Example s(t) s1 (t) t Analog signal Spring 2006 t Samples from the analog signal Computer Networks 9 Quantization Each sample obtained by the sampling process has a different amplitude. This would require an infinite number of values to be transmitted. To reduce the size of the problem the process of quantization is used. Quantization A method dividing the range of amplitude of the samples into finite number of levels, assigning sign and magnitude to each of these values, and Coding each of the levels with a binary equivalent Spring 2006 Computer Networks 10 Quantization - Example The range of amplitude is divided into 128 negative and 128 positive levels (only some of them are shown on the diagram) The value of each sample is associated with one level Each level is translated into its seven-bit binary equivalent The sign of the level is translated into additional bit +125 +125 +110 +105 +102 +100 +88 +75 +48 +50 +38 +39 +26 +25 +24 0 -15 -25 -50 -50 -75 -80 -100 + -125 Spring 2006 Sign bit is 0 , - is 1 +024 00011000 +102 01100100 +038 00100110 +110 01101110 +048 00110000 +124 01111101 +39 00100111 +105 01101001 +26 00011010 +85 01011000 -015 10001111 -80 1101000 -50 10110010 Computer Networks 11 Quantization Error By replacing the value of the original sample with the value of the level, an intentional error called quantization error is introduced. Quantization error can be regarded as noise. The error depends on the number of levels used If 2N quantization levels are used, the number of bits per sample is N. More quantization level means lower quantization noise and more bits per sample. Spring 2006 Computer Networks 12 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) The process of sampling, quantization, binary encoding and digita-to digital encoding is known as pulse code modulation PCM is usually used to transform voice signals. Voice data (phone conversation) is limited to below 4000Hz Require 8000 sample per second Each analog sample is assigned a digital value of 8 bits. Therefore the speed of a digitized voice channel is 64 Kbps Spring 2006 Computer Networks 13 Look at this presentation created by one of the former students. You can read more about how the voice is digitized and try the animation that shows the steps in the process of transforming the voice into a digital signal. Sampling the Voice Spring 2006 Computer Networks 14