* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT: Waveforms 2
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Curry–Howard correspondence wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
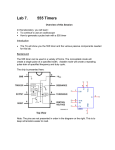
Basic Digital Waveforms 2 Measurement Paul Godin Updated October 2009 Waveform 2.1 Measurement Tools ◊ Several instruments are used to analyze Digital Electronic circuits, including: ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ Logic Probes Oscilloscopes Logic Analyzers Tracers Function generators Waveform 2.2 Logic Probes ◊ Logic Probes display static logic states at specific points on a digital logic circuit. These states include: ◊ High ◊ Low ◊ Float ◊ Logic probes are easy to use. Waveform 2.3 Logic Probes ◊ Logic Probes are usually connected to the power supply of the circuit under test. ◊ Some logic probes can also detect the presence of an oscillation. ◊ Related to probes are: ◊ Current tracers, used to detect the location of a short circuit in digital circuits. Works with induction. ◊ Pulsers, used to inject an oscillation into the circuit to trace its route. Waveform 2.4 Logic Probes - Limitations ◊ Logic probes are designed to measure active circuits only. ◊ Logic probes provide the static logic states and cannot measure: ◊ Oscillation values (time high / time low) ◊ Voltages ◊ Transients (short-lived problems) Waveform 2.5 Oscilloscope ◊ Oscilloscopes are a common electronics instrument used to measure voltage and frequency. ◊ Oscilloscopes can also be used to compare signals. Most oscilloscopes have at least 2 channels. Waveform 2.6 Oscilloscope ◊ Oscilloscopes work best with periodic signals. ◊ Some more advanced oscilloscopes can: ◊ measure aperiodic signals ◊ retain measured values in memory ◊ have advanced analysis capabilities Waveform 2.7 Oscilloscope - Limitations ◊ Oscilloscopes measure active circuits only ◊ Expensive ◊ Most are not very portable and require an AC power source ◊ Requires training and practice to use properly Waveform 2.8 Waveform Measurement Period (T) Pulse Separation Pulse Width Ps Pw 90% Amplitude 50% 10% Rise Time Fall Time (tR) (tF) Rise and fall times are typically measured in nanoseconds (ηs) Waveform 2.9 Oscilloscope Measurement ◊ Measuring with a scope – Static logic state Probe 5V Circuit Ground 1 1 1 Set input to DC Waveform 2.10 Oscilloscope Measurement ◊ Measuring with a scope - Oscillation Probe 5V Circuit Ground 1 1 Set input to DC Waveform 2.11 Oscilloscope Measurement ◊ Several controls need to be adjusted when measuring with the scope: ◊ Volts/Division: controls the displayed voltage ◊ Time/Division: controls the displayed time ◊ Trigger: controls the trigger point for a periodic signal. Must be set within the signal’s amplitude. ◊ Coupling: should be set to DC (Direct Coupled) when measuring digital values ◊ Horizontal and Vertical position: used to set the position of the ground reference on the display Waveform 2.12 EWB Oscilloscope Semi-expanded view Connections correspond to Normal View Ground must be connected Normal View with 4 connections Waveform 2.13 EWB Oscilloscope – Expanded View Cursors used for measurement. Values between cursors in box below Position of Red Cursor Position of Blue Cursor Adjustable Settings Waveform 2.14 Exercise: EWB Oscilloscope Class activity: ◊ Open the EWB file titled scope1 on the site. ◊ Use the scope in EWB to measure the output waveforms and complete the worksheet on the next slide. Waveform 2.15 Oscilloscope Worksheet Signal A: Signal B: ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ Period: ___________ TH (time high):_____ TL (time low):_______ Duty Cycle: ________ Period: ___________ TH (time high):_____ TL (time low):_______ Duty Cycle: ________ Signal C: ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ Period: ___________ TH (time high):_____ TL (time low):_______ Duty Cycle: ________ TR (rise time): ______ TF (fall time): ______ Waveform 2.16 Logic Analyzer ◊ Logic analyzers display multiple dynamic (changing) logic states in a format that resembles a timing diagram. Very useful for analyzing more complex digital circuits. ◊ Typical analyzers have 8 or 16 channels. Waveform 2.17 Logic Analyzers - Limitations ◊ Logic analyzers display logic states, not voltage values. They may not display poor edges or other similar electrical faults. ◊ Expensive ◊ Most are not very portable and require an AC power source ◊ Requires training to use properly Waveform 2.18 EWB Logic Analyzer Circuit connections Expanded view Red Cursor Blue Cursor Cursor Position Internal Clock Set Waveform 2.19 Exercise: EWB Logic Analyzer ◊ Class activity: ◊ Open the EWB file titled analyze1 on the site. ◊ Use the Logic Analyzer in EWB to measure the PW of the 3 waveforms and record below. Signal A PW: _________ Signal B PW: _________ Signal C PW: _________ Waveform 2.20 Function Generators ◊ Function Generators generate AC voltages, with control over output: ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ Frequency AC voltage DC offset voltage Wave shape (typically Sine, Triangle, Square) Duty Cycle ◊ Some function generators have more features or are more specialized. Example includes generating RF frequency and waveforms. Waveform 2.21 Function Generator Use ◊ Function Generators are used to inject signals into circuits to analyze their function. ◊ Failure to configure the output of the function generator before connecting it to the circuit will likely result in circuit damage. Check: ◊ Output AC voltage ◊ Output DC offset voltage (no negative voltage) Most ICs will be damaged if negative voltage is applied. Waveform 2.22 Ohmmeters ◊ Most ohmmeters produce a high enough voltage to damage logic circuits and should never be used in a digital electronics environment. Waveform 2.23 END Waveform 2.24