* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Goals
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
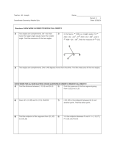
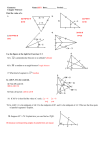
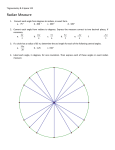
Unit 1 – Geometry Basics Specific Objectives by Section 1.2 Points, Lines, and Planes 1.3 Segments and Their Measures 9.2 Memorize and use area formulas for square, rectangle, triangle, and circle Memorize and use perimeter and circumference formulas Find area or perimeter for shapes on coordinate plane by first finding length of sides, or height of shape Circumference and Arc Length 11.5 Find the measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons. Introduction to Perimeter, Circumference, and Area 11.4 Identify vertical angles and linear pair Identify complementary and supplementary angles Calculate angle measures using definitions of above terms by setting up correct equations to represent angle relationship Angle measures in Polygons 1.7 Use properties of bisectors and midpoints to determine if a segment is a perpendicular bisector Angle Pair Relationships 11.1 Bisect an angle and segment using a compass or paper folding Find the midpoint of a segment on the coordinate plane using the midpoint formula Find angle measures using definition of angle bisector Perpendicular Bisectors 1.6 Use a protractor to correctly measure an angle by degree Classify an angle according to its measure Find angle measures using angle addition postulate Segment and Angle Bisectors 5.1 Correctly use the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance between two points on the coordinate plane Angles and Their Measures 1.5 Find the distance between two points using segment addition postulate Use the distance formula to find distance between two points on the coordinate plane Pythagorean Theorem 1.4 Understand basic undefined terms of geometry Identify and correctly use geometric symbols Sketch intersections of lines and planes Adapt the circumference formula to find length of specified circle arc Areas of Circles and Sectors Adapt the area formula of a circle to find area of a specified circle sector Vocabulary for Unit 1 – Basics of Geometry 1.2 undefined terms point line plane collinear points coplanar points segment ray opposite rays intersection 1.7 area perimeter circumference height base 11.1 polygon interior angles exterior angles 1.3 postulates or axioms congruent segments distance formula 11.4 arc arc length arc measure 9.2 Pythagorean theorem 11.5 circle sector 1.4 initial point vertex congruent angles interior of angle exterior of angle acute angle right angle obtuse angle straight angle reflex angle adjacent angles 1.5 segment bisector midpoint midpoint formula angle bisector 5.1 perpendicular bisector 1.6 vertical angles linear pair complementary angles supplementary angles