* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
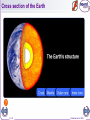
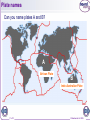
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kg_UBLF UpYQ 1 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 2 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Learning objectives How old is the Earth? What is the Earth made from? What is Plate Tectonics? What happens at the different types of plate boundary? 3 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 How old is the Earth? The Earth is… 2 million years old 100 million years old 4600 million years old 30 million years old 4 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 History of the Earth Mark the following events on your time line. What do you notice? India collides with Asia – 50 m First flowers appear – 100 m Man (Homo sapiens) inhabits the Earth – 0.1 m Formation of the Alps – 30 m Dinosaur extinction – 65 m You were born! – 0.000013 m Industrial Revolution (UK) - 0.00015 m (figures are in ‘million years ago’) 4,600 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 today million years ago 5 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 History of the Earth People (Homo sapiens) only appeared 100,000 years ago! Big Bang! 6 of 31 Dinosaurs Men-like apes Homo sapiens die out © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Learning objectives How old is the Earth? What is the Earth made from? What is Plate Tectonics? What happens at the different types of plate boundary? 7 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Cross section of the Earth 8 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Cross section of the Earth 9 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Learning objectives How old is the Earth? What is the Earth made from? What is Plate Tectonics? What happens at the different types of plate boundary? 10 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 What is continental drift? In 1912, a German scientist called Alfred Wegener proposed that South America and Africa were once joined together and had subsequently moved apart. He believed that all the continents were once joined together as one big land mass called Pangaea and this was intact until about 200 million years ago. The idea that continents are slowly shifting their positions is called continental drift. 11 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Evidence for continental drift Study of fossils Similar fossils are found on different continents. This is evidence that these regions were once very close or joined together. Pattern of rocks Similar pattern of rock layers on different continents is evidence that the rocks were once close together or joined. Shapes of continents Some continents fit together like a jigsaw. Africa South America 12 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Continental drift 13 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 What is plate tectonics? Wegener knew the continents had drifted but he couldn't explain how they drifted. It wasn't until the 1960's that geologists used ocean surveys to explain continental drift with the theory of Plate Tectonics. What is Plate Tectonics? The Earth's surface is made up of a number of large plates (like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle) that are in constant, slow motion. The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. At the edges of these plates (plate boundaries) earthquakes and volcanoes occur. Convection currents in the mantle move the plates. The source of heat driving the convection currents is radioactive decay which is happening deep in the Earth. 14 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Why do the plates move? 15 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Plate names North American Eurasian Pacific Pacific African Nazca South American Indo-Australian Plate Antarctic 16 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Plate names Can you name plates A and B? A African Plate B Indo-Australian Plate 17 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Plate names 18 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Learning objectives How old is the Earth? What is the Earth made from? What is Plate Tectonics? What happens at the different types of plate boundary? 19 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundary At a constructive plate boundary, two plates move apart. As the two plates move apart, magma rises up to fill the gap. This causes volcanoes. However, since the magma can escape easily at the surface the volcano does not erupt with much force. Earthquakes are also found at constructive boundaries. An example of a constructive boundary is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. 20 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundary 21 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Mid-Atlantic ridge Sea Floor Spreading! Did you know that the ocean floor in the Atlantic is growing by 3cm per year? Which of the following pairs of continents are moving further away from each other? 1)Europe and Africa 2)Europe and North America 3)South America and North America 22 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 How fast do plates move? Tectonic plates move at different rates. The Nazca and Pacific plates are moving apart at a rate of 18cm per year while the Eurasian and North American plates are moving apart at a rate of 3cm per year. To the nearest metre, how far will the Nazca and Pacific plates have moved over the next 200 years? 6 metres 23 of 31 36 metres 200 metres 928 metres © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundaries mid-ocean ridge B A ocean mantle Where would you find older rocks – at A or at B? 24 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary A destructive plate boundary is found where a continental plate meets an oceanic plate. The oceanic plate descends under the continental plate because it is denser. As the plate descends it starts to melt due to the friction caused by the movement between the plates. This melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 25 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary 26 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Collision plate boundary Collision boundaries occur when two plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a continental plate). This causes the material between them to buckle and rise up, forming fold mountains. The Himalayas are an example of a chain of fold mountains. They have been formed by the African plate colliding into the Eurasian plate. 27 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Collision plate boundary 28 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Conservative plate boundary Conservative plate boundaries exist where two plates do not directly collide but slide past each other along a fault (weakness). No volcanoes are found along these plate boundaries, but earthquakes do occur. An example of such a boundary is the San Andreas Fault in California. 29 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Conservative plate boundary 30 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary Match the labels to the letters. F E A B D 1.oceanic plate 2. The oceanic crust sinks under the less dense continental crust. 4. continental crust 31 of 31 C 5. explosive volcanoes 3. The oceanic crust melts and rises. 6. mantle © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Plate definitions - PLENARY 32 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 33 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005