* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tutorial 2 - Controller, Sensors and Motors
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Rotary encoder wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
PID controller wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
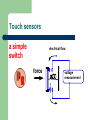
Tutorial 1, UGB 230N Controller, Sensors and Motors Ding Ke 2009-10-12 How to control your robot? For Vex, we have two ways, – – Remote Control Programming Logic Controller The Vex Controller The Vex Controller Board The Vex Controller is the brain of the Robot. All of your inputs and outputs go through this controller. Remote Control Remote Control Signal Reception The vex RF Receiver Module allow the robot to receive transmitted signals. Reception begins when a radio signal reaches the receiver’s antenna. Remote Control The Vex Micro Controller coordinates the flow of information and power on the robot. All other electronic system components must be connected to the Micro Controller in order to function. Control Configurations Programming Logic Easy C – – Easy C is a programming language that you will use to tell your robot what to do. In Easy C, programs are written using icon-based code, but the interface includes a window that displays the program in a text-based format as well. Sensors Why does a robot need sensors? – – – The controller need additional information in order to make right decisions The sensors are used to get these information. There are different kinds of sensors, for example, touch sensors, light sensors, line follower sensors, optical shaft encoder, ultrasonic sensors What makes a machine a robot? Sensing information about the environment where is the truck? where should I dig? Planning Acting action on the environment Touch sensors a simple switch electrical flow force voltage measurement Sensors defined Sensors convert physical phenomena into readable electric signals. Also known as “transducers.” Vex Sensors Bumper switch sensor Limit switch sensor Application Motors Motors get their power from the batteries. motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy Connected to the controller. Vex Motors Motor spinning either forward or backward at a controlled speed. Servo Motor Can be directed to turn to face a specific direction, rather than just spin forward or backward. Application