* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations and Human Populations Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
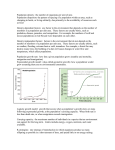
What is a population? Agenda for Monday Jan 30th 1. Populations notes 2. Population worksheet • Why study populations? – Learn how organisms change over time, problems in an environment, and relationships between organisms – Population has group and not individual characteristics • Basic characteristics of a population: • • • • Density (no/area; no/vol) Size (numbers) Age Structure (based on age distribution) Dispersion (the spread of individuals in relation to one another) What causes populations to change? 1. Birth Rate 2. Death Rate 3. Number of individuals that enter and/or leave 1. Immigration – into 2. Emigration – out (Birth rate + immigration) – (death rate + emmigration) Survivorship Curves Exponential Growth Rate • Ideal conditions • More individuals = faster growth • Rarely happens – WHY? – Limiting factors Logistical Growth Rate • Populations go through different growth phases – Lag Phase – slow growth – Exponential growth – rapid growth, few die, many reproduce – Population growth slows down – Steady state – population levels, birth rate = death rate Carrying Capacity • Maximum number of individuals that an environment can support – Measured in winter Questions • The human population is currently growing at an exponential rate. What does this mean about our birth and death rates? • The Mantled Howler Monkey is currently considered an endangered species. What does this mean about its birth and death rates? Population Density • # of organisms per area • Dispersion – pattern of spacing of populations – 3 types • Uniform • Clumped • Random Dispersion Pattern: Uniform Dispersion Pattern: Clumped Dispersion Pattern: Random Population Ranges • Species are limited to where they may exist • Abiotic conditions Temperature Rainfall • Biotic conditions Predators Competitors parasites Humidity Sunlight Limiting Factors… • Tolerance – ability of an organism to survive when subjected to limiting factors – Upper and lower limit = range Density independent factors • affects the size of a population regardless of the population density – Abiotic • Weather, Water, Fire, Sunlight, temperature • Humans – dams, pollution Density Dependent Factors • A factor whose effects on the size or growth of population vary with the population density – Biotic factors • Predation, disease/parasites, competition • Food, water, shelter (resources) Disease/Parasites • Outbreaks of disease tend to occur when population size has increased – Disease is transmitted faster – True for humans as well as animals • Parasites increase at higher densities Questions Imagine a population of skunks. Imagine that the skunks are reproducing at a very high rate, and the skunk population is growing rapidly. a) List a possible density-independent factor that could stop the skunk population’s growth. b) List a possible density-dependent factor that would limit the skunk population’s growth. Reproductive strategies R-strategy (rate strategists) • Reproduce quickly with many offspring – Little energy in raising young – Short life span – Small in size K-strategists (carrying capacity strategy) • Few offspring – Expend a lot of energy raising young – Long life span – Larger organisms • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RBOsqm BQBQk Human Population Growth http://www.census.gov/popclock/ • It took all of human history up to the early 1800s for world population to reach 1 billion people • until 1960 to reach 3 billion • Today, the world gains 1 billion people every 11 years • The current population is almost 8.5 times larger than the population of 760 million at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution • At current growth rates, the world population could double in as little as 58 years What’s Behind Population Growth • Animal Domestication and Agriculture – Provided for a few to feed many Leads to Increased Fertility Lower Infant Mortality Increased Longevity • Industrial Revolution – Growth of Cities and Infrastructure • Water • Energy • Transportation – – – – Increased Productivity Nutrition Sanitation Medicine Human Carrying Capacity •Technology has allowed us to raise Earth’s carrying capacity •Tool-making, agriculture, and industrialization each enabled humans to sustain greater populations • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ozDskXx mdDI • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VcSX4ytE fcE Human Population Growth • Zero population growth – birth rate + immigration rate = death rate + emigration rate • Age structure – # of males and females in three age groups • Pre-reproductive (0-19), reproductive (20-44), and post –reproductive (45-80+) Having many individuals in young age groups results in high reproduction and rapid population growth Why do some countries have a growing population while other countries have a declining population? Male Female Expanding Rapidly Guatemala Nigeria Saudi Arabia Prereproductive ages 0–14 Male Female Expanding Slowly United States Australia China Reproductive ages 15–44 Male Female Stable Japan Italy Greece Postreproductive ages 45–85+ Male Female Declining Germany Bulgaria Russia Four Stages of Demographic Transition Water consumption Carbon emissions Resource Consumption Our ‘Commons’ are in Danger • • • • • • Atmospheric pollution and climate change Water pollution, including ground aquifers Deforestation and loss of oxygenation The oceans, coral reefs and their bounty National parks, wildernesses and wetlands Nonrenewable natural resource depletion – Fossil fuels, mineral ores, topsoil….. Biodiversity is in Danger • Humanity has spawned a species extinction to rival the 5 great extinctions – Recovery times took 10’s of millions of years • Biodiversity is essential to life on Earth and holds untold treasures for the future • An ecological ethic is emerging Concept Web • write the “7 Billion People and Growing” in the middle • draw arrows to any of the other concepts that form a cause and effect relationship • Social, economic, envt impacts • Positive, neutral, neg impacts on more people Why do developing countries have a growing population while developed countries have a stable population? Agenda for Friday Nov 4th 1. Population questions 2. Go over populations worksheet 3. Biodiversity Quick Questions 1. What is a density independent factor? 1. List 1 example 2. What is a density dependent factor? 1. List 1 example 3. Why do populations rarely exhibit an exponential growth rate? 4. When populations level out in logistical growth rate, what is it called when they level out? 5. 5. A population is at carrying capacity. What does that mean about its birth rates and death rates? 6. The Mantled Howler Monkey is currently considered an endangered species. What does this mean about its birth and death rates? 7. What are some limiting factors that would put a population at its carrying capacity? 8. What type of growth are humans experiencing? 9. What major factors (3) have contributed to human population growth? 10. What is a characteristic of an r-strategy reproducing organism?