* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4: Wheat Diseases
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
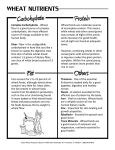
Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Rusts Three forms can affect wheat (all fungal forms) Stem rust Leaf rust Stripe rust Stem Rust Most destructive wheat disease Severe grain shriveling Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Masses of pustules on leaves & stems containing brick red spores Rust infested plants transpire much more water than normal Spores overwinter in southern U.S. Blow north w/ winds A rust epidemic in TX can produce a similar epidemic in ND (when conditions are favorable) Lush growth on high N soils are most susceptible to rust Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Rust can overwinter and/or develop on barberry bushes Dusting or spraying infested fields often not economically effective Seed-treatment also not effective because its not a seed-borne disease Only plant resistant varieties >275 stem rust biotypes (hard to maintain resistant varieties) Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Leaf Rust Many consider to be more important than stem rust Early infection can cause 42-94% yield loss Mostly due to less kernels in spike Pustules w/ orange-red spores cover leaves and some stem Resistant varieties are effective for control Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Stripe Rust Not commonly a problem in the Midwest Smuts Flag Smut Yield losses of 10-20% in susceptible varieties Dark stripes on leaves & sheathes Infected plants are often dwarfed; fail to form normal heads Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Disease can be carried on the seed and in the soil Can be controlled w/ seed treatment Many varieties are resistant Scab Caused by Fusarium spc. Fungal infection attacks head shortly after emergence Can kill or obstruct development of the spikelets Identified by pinkish-white fungal growth Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Diseased grains Shriveled White Scabby Carried on seed and crop residue Most severe when wheat follows corn Use seed treatments Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Take-All Not common for our area Has destroyed 10-50% of the wheat crop Kills plant in the heading stage to grain fill Plant can turn white May kill all plants in an area Root rot occurs & spreads damage Bottom 1-2” of stem may be black Unit 4: Wheat Diseases Fungus lives in the soil Must rotate out of wheat, oats, barley, etc. for 2-4 yrs.