* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
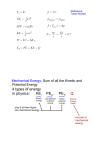
Assignment 6.2 – Conservation of Energy 1. How much energy is stored in a pole vault with a spring constant of 15 N/m if it is deflected 1.6 m? 2. One of the highest pop flies ever recorded in baseball was about 172 m. What is the gravitational potential energy of a baseball with a mass of 145 g that is hit that high into the air? 3. The women’s pole vault world record as of spring 1997 was 4.55 m, set by Emma George. What do you estimate was Emma’s speed prior to planting the pole? 4. A 2.0 kg rock is dropped off a 100-m high cliff. (a) Calculate the speed the rock is going when it gets to the bottom of the cliff. (b) Can you do this calculation if you do not know the mass of the rock? What does this imply for the speeds of falling objects when friction is not considered? 5. A bow is strung with a bowstring that has a spring constant, k, of 1500 N/m. (a) If you pull the bowstring back 25 cm, how much work have you done on it? (b) If the string is pushing against an arrow that has a mass of 0.10 kg, how fast is the arrow going when it leaves the bow? 6. A toy car with a mass of 40 g is released from rest and slides down a frictionless track 1 m high. At the bottom of the track it slides along a horizontal portion until it hits a spring with a spring constant of 18 N/m. The spring is attached to an immovable object. What is the maximum compression of the spring? 7. In an emergency stop, a 1500-kg vehicle loses 300,000 joules of energy as it comes to rest. What was the speed of the vehicle the moment the brakes were applied? 8. If a 5 kg mass is raised two meters vertically from the surface of the Earth, what will its gain in potential energy? 9. A 0.50 kg ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 35 m/s. Approximately, how high will the ball rise? 10. The starting height for a roller coaster is 25 m. Its mass with 2 passengers is 300 kg. (a) (b) (c) (d) Calculate the maximum gravitational potential energy. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy. Calculate the velocity at this maximum kinetic energy. How would the velocity change if the coaster had 4 passengers and total mass of 400 kg? 1 Assignment 6.2 – Conservation of Energy 11. A pendulum is lifted to a height of 0.75 m. (a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy at the top. (b) Find the kinetic energy of the bob at the bottom. (c) At what position of the bob will the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy be equal? 12. In the early morning, a roller-coaster train (set of cars hooked together) only has 6 passengers. In the afternoon it has 26 passengers. Will the speed of the roller coaster change with more passengers aboard? Explain your answer. 13. A spring pop-up toy with mass of 0.02 kg reaches a maximum height of 0.50 m. The compression length of the spring is 0.03 m. Find the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) Gravitational Potential Energy at the top. Spring Potential Energy before the “pop”. The spring constant k. The kinetic energy at the moment the spring toy leaves the ground. 14. A 20-kg rock is on the edge of a 100-m cliff, as shown in the diagram. (a) What potential energy does the rock possess relative to the base of the cliff? (b) The rock falls from the cliff. What is its kinetic energy just before it strikes the ground? (c) What speed does the rock have as it strikes the ground? 15. An archer puts a 0.30-kg arrow to the bowstring. An average force of 201 N is exerted to draw the string back 1.3 m. (a) Assuming that all the energy goes into the arrow, with what speed does the arrow leave the bow? (b) If the arrow is shot straight up, how high does it rise? 16. A physics book of unknown mass is dropped 4.50 m. What speed does the book have just before it hits the ground? 17. From what height would a compact car have to be dropped to have the same kinetic energy that is has when being driven at 100 𝑘𝑚⁄ℎ? 18. Hakeem throws a 10.0-g ball straight down from a height of 2.0 m. The ball strikes the floor at a speed of 7.5 m/s. What was the initial speed of the ball? 2