* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Shaping Transformation Unit (STU)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
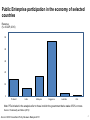
The Future of Public Enterprise Dato’ Sri Idris Jala Public Enterprises play an important catalytic role in the early stages of Economic Development 2 The role of Public Enterprises decline as economies shift to be more developed Underdeveloped Developing Developed Market Capitalisation (% of GDP) Strategic Investment, Provide Infrastructural Support, End-to-End Business, Fulfill Market Demand Strategic Investment, Provide Infrastructural Support STAGE 1 STAGE 2 STAGE 3 Development (GDP) Catalytic Facilitative 3 Public Enterprise participation in the economy of selected countries Revenue (% of GDP, 2010) 50 40 30 20 10 0 Thailand India Malaysia Singapore Australia USA Note: PEs included in the analysis refer to those in which the government had a stake of 50% or more. Source: Chakravarty and Ghee (2012) Source: OECD Investment Policy Reviews: Malaysia 2013 4 Public Enterprises remain instrumental in sectors that require Huge Infrastructural and Financial Support 5 Petroleum Refining, Utilities, Financial Services, Mining are dominant sectors among PEs / SOEs in the Fortune Global 500 Source: PWC Report on State-Owned Enterprises: Catalysts for public value creating, April 2015 6 The Future of Public Enterprise: Rationalisation 7 Public Enterprises should be rationalized to focus on the following Private Investor needs Co-Investor. Business must be owned domestically. Large growth capital, catalytic or new technology required. National Infrastructure. 8 The Malaysian Story: The GLC Transformation Programme 9 Snapshot in 2005: Malaysian Public Enterprises are major contributors to the Economy 1 Tun Abdullah Ahmad Badawi’s Keynote Speech during the GLCT Programme Launch on 14 May 2004 Source: GLC Transformational Manual, July 2005 10 The true performance of Malaysian PEs is much weaker than reported headline profits suggest Company Telekom Maybank Sime Darby Tenaga CAHB Proton MAS Golden Hope Affin Guthrie Boustead BIMB UEM World MRCB MBSB Net Profit USD million, 2004 Economic Profit USD million, 2004 692 -117 642 394 243 215 92 -778 199 60 135 50 122 1 90 6 61 -8 42 -14 31 21 23 -39 17 -39 9 8 -14 -1 *Economic Profit is an important yardstick to measure value creation to shareholders. It shows a company’s net income after deducting shareholder’s opportunity cost in investing in the firm. EP is defined as the difference between a company’s return over and above its costs of capital. [EP = (Return on invested capital – Weighted average cost of capital) x Invested capital] 11 The Malaysian GLC Transformation Progamme 15 years (2004 – 2015) Hired professional CEOs on contract with clear KPI targets 10 Guidebooks to improve performance PM chair biannual review of performance of GLCs via Putrajaya Steering Committee The performance of the GLCs improved to match / better than other private companies 12 G20 delivered strong financial performance over the past 10 years Market Capitalization (USD bil) Net Profit (USD bil) 113.8 Economic Profit (USD bil) 7.7 0.3 FY04 FY14 2.9 39.5 May ’04 July ‘15 FY04 FY14 -0.94 1. FY14 extraordinary break-up basis adjustments due to the restructuring of MAS have been excluded to provide a fair view of operational performance 2. Economic Profit started being tracked since the official launch of the GLCT Programme in FY05 Note: In G20’s TSR & market capitalisation computation, UEM Sunrise (TSR only) & UEM Edgenta (previously known as UEM Faber) are used as a proxy for UEM Group Berhad while MAS has been excluded due to its delisting 3. US-Ringgit Exchange Rate taken at 10-year average [ 1 USD = RM 3.392] Source: G20 annual reports, G20 submissions to PCG Secretariat, Bloomberg and PCG analysis 13 The GLCT Programme has provided economic and social benefits to all Stakeholders Employees Government 373,627 USD 32b Employed by G20 in 2014, of which 225,050 are Malaysians G20 dividends paid (FY04 to FY14) USD 18.5b G20 taxes paid (FY04 to FY14) USD1.2b Spent by G20 on training & development from 2004 to 2014 Note: US-Ringgit Exchange Rate taken at 10-year average [ 1 USD = RM 3.392] Source: G20 annual reports, GLICs and G20 submissions to PCG Secretariat, PCG Secretariat analysis 14 We ran an 8-week lab and identified 131 EPPs to TRANSFORM the Economy 131 USD 406 bil (2011-2020) Investments GNI USD 250 bil (2020) Gross National Income ENTRY POINT PROJECTS 3.3 mil (2011-2020) Additional Jobs • • Idris Jala – Top 10 Most Influential Policy Makers in the World (Bloomberg Market 2014) PEMANDU – Top 20 Most Innovative Government Agencies in the World (Bloomberg Philantropies and Nesta 2014) *US-Ringgit Conversion Rate at the time of the lab, 1 USD = RM3.2 15 With the Economic Transformation Programme, Private Investment in Malaysia has grown 2.2x ETP Launch 16 Malaysia is no longer stuck in the middle income trap, with worsening fiscal deficit Gross National Income 2010 USD 12,276 Fiscal Deficit (of GDP) 2015 USD 12,475 -6.6% (2009) 15% 33% USD 10,570 -3.1% USD 8,280 World Bank’s Highincome threshold (2015) Malaysia’s GNI per capita 17 Under the GLCT Programme many professional CEO’s were hired to run Malaysian PEs. I was hired from Shell to turnaround Malaysia Airlines. 18 Flash back... 19 Most routes are losing money NIAT Unprofitable routes 3 Americas China 9 Middle East 9 North Asia (Japan, Korea, Taiwan) 10 12 Europe South Asia 6 Australia & New Zealand 7 Domestic +163 24 7 -100 4 -84 4 -120 0 -561 -63 6 -317 3 66 114 RM millions -305 0 10 ASEAN International Profitable routes 48 4 -1.3b Relentless Daily Monitoring of P&L and Cash Balance 21 MAS Profit & Loss 2005 – 2010 USD P&L 300,000 247,910 200,000 Global financial crisis Record high oil price 144,998 83,148 78,025 100,000 0 2005 -22,009 -100,000 -200,000 -300,000 -400,000 2006 -363,486 2007 2008 2009 2010 What we did at MAS Cut loss making routes Implemented dynamic pricing to improve yield Reduce manpower by 3000 staff Sold HQ building to raise cash for operation Implemented structural cost reduction exercise Started a new subsidiary airline (Firefly) for non-trunk domestic routes 23 Future of Public Enterprises Only where the private sector DOES NOT do a better job Hire the best talents Set tough targets and insist on delivery Reward and Consequence Management 24 THANK YOU 25 APPENDIX 26 Governments around the world have beautiful plans and promises. However, the main difficulty is the failure to deliver. 30,000 ft High Level Policy / Framework Big Disconnect 3 ft On the ground realities of implementation Implementation: Problems differ depending on countries, sector, companies etc There is a big disconnect between high level decision making and ground level implementation Organizing for Implementation: The 8-Step BFR Methodology Planning / Thinking (10%) • Strategies, Key Activities & Responsibilities • Organizing • Communication & Engagement Implementation / Doing (90%) • Monitoring • Recursive Problem Solving • Assessment / Validation • Reporting We ran an 8-week lab and identified 131 EPPs to TRANSFORM the Economy 131 USD 406 bil (2011-2020) Investments GNI USD 250 bil (2020) Gross National Income ENTRY POINT PROJECTS 3.3 mil (2011-2020) Additional Jobs • • Idris Jala – Top 10 Most Influential Policy Makers in the World (Bloomberg Market 2014) PEMANDU – Top 20 Most Innovative Government Agencies in the World (Bloomberg Philantropies and Nesta 2014) *US-Ringgit Conversion Rate at the time of the lab, 1 USD = RM3.2 29 Malaysia is no longer “stuck in the middle income trap, with worsening fiscal deficit” Gross National Income 2010 USD 12,276 Fiscal Deficit (of GDP) 2015 USD 12,475 -6.6% (2009) 15% 33% USD 10,570 -3.1% USD 8,280 World Bank’s Highincome threshold Malaysia’s GNI per capita (2015) 2.2X growth in Private Investment ETP Launch We promised to create 3.3 million jobs in 10 years To date, 1.8 mil Jobs have been created We implemented inclusive measures for rural folks 5,286 kilometers rural roads completed 3.5 334,593 rural houses have access to clean water 6 million 1,681,330 Rural people benefited from rural infrastructure projects 144,025 rural houses have access to reliable electricity 720,125 people people 79,137 rural houses built and restored 412,360 people We implemented inclusive measures for low income people 6.8 million Low income households and individuals benefited from BR1M (cash transfer) 198,943 Individuals participate in the 1AZAM programme 2.9 million Lifted out of poverty due to minimum wage policy TUKAR is a grass root and touch point project for Rakyat Modernising the traditional sundry shops (TUKAR) An initiative to assist small retailers in modernising their business and remain competitive This initiative is a collaboration between the Government and the hypermarket operators in growing the retail business RM 5.6 512,500 billion GNI Impact 35 Jobs Created The Amazing Transformation – GST ready and better pricing options BEFORE AFTER 36 The Amazing Transformation – GST ready and better pricing options BEFORE AFTER 37 Internationally recognised as the 1st in the world 38 The Government’s Fiscal Sustainability Malaysia is in the fiscal “safe zone” Note: All figures are as of 2015 est. // Countries markers are masked and coded for confidentiality Source: MOF; BNM; CIA World Factbook; PEMANDU Analysis International recognition of PEMANDU • World’s Best national transformation programme (3G Award by Cambridge IF, 2016) • Top 20 Most innovative Government Agencies in the World (Bloomberg Philantropies and Nesta, 2014) Top 10 • Idris Jala: Most influential policy makers / top 50 influential person in the World (Bloomberg Market, 2014) • PEMANDU / BFRI providing consultancy to other countries Tanzania BRN achieved remarkable results only after 3 years in implementation Tanzania Big Results Now! 6.58 million rural population have gained access to clean water Almost 400,000 households have been electrified Ship turnaround time halved from 7 Days to 2.92 Days at Dar es Salaam port Budget deficit slashed by 64% Maize and rice production increase by 500,000 MT and 166,000 MT respectively BFR Andhra Pradesh Lab Wave 1 & 2 Outcome Renewable Energy MOU Signed Worth Biodiesel Retail USD 3 billion 8000 direct jobs Water and Sewerage Food & Beverage Water Treatment Biotechnology & Vector Control