* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brandee Oliver
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
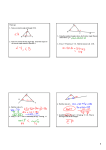
Brandee Oliver Geometry Grade 9-12 November 10, 2008 Section 4-2 Standards and Objectives: G.3. Core Content: Two- and three-dimensional figures G.3.A Know, explain, and apply basic postulates and theorems about triangles and the special lines, line segments, and rays associated with a triangle. G.7. Core Processes: Reasoning, problem solving, and communication G.7.H Use inductive reasoning to make conjectures, and use deductive reasoning to prove or disprove conjectures. Objectives: SWBAT discover the Angle Sum Theorem through the use of manipulatives. SWBAT discover the Exterior Angle Theorem through the use of manipulatives. SWBAT use the Angle Sum Theorem and the Exterior Angle Theorem to find the measurement of missing angles. Background Information: Previous Lesson: Student went over the following vocabulary: Triangle, Acute triangle, Obtuse triangle, Right triangle, Equiangular, Scalene, Isosceles, and Equilateral. They reviewed what the base, legs and vertex of a triangle are. Following Lesson: Students will learn about congruent triangles and how to label corresponding parts of congruent triangles. Instructional Plan: Entry Task: Students will be given the following problem to complete. Students must work at their seats; however, they may consult their partners in their group. Find the measure of the legs of an isosceles triangle ABC if AB = 2x + 4, BC = 3x – 1 and AC = x + 1, and the perimeter of triangle ABC = 34 inches. After finding the measure of each leg State which angles is the vertex angle of the triangle. *HINT* Draw a diagram to help you understand the problem. B P = 34 in 2x + 4 A 3x -1 x+1 C Solution: 2x + 4 + 3x – 1 + x + 1 = 34 (Add all sides to equal perimeter) 6x + 4 = 34 6x = 30 x=5 AB = 2(5) + 4 = 14 BC = 3(5) – 1 = 14 AC = 5 + 1 = 6 The vertex angle is angles B Correct Assignment: Pg 184 16-23, 30-42 OMIT 35. After we correct assignment I will ask if there are any questions on the assignment. If there are questions we will go over them, if not we will move on to the activity. Lesson: We will start out by going over a few vocabulary terms. Exterior Angle: an angle created by extending a side of a polygon Remote Interior Angles: the two interior angles of the triangle not adjacent to the given exterior angle. Students will be asked to pick one person from each group to go back and collect the material. The material person must collect the following items for each group member: a container of playdough, a ruler, and a piece of paper. After they have collected the material I will put up an instructions sheet instructing the student activity. Instruction: (will be typed up and projected on document camera) Activity 1) With your ruler draw a straight line on your piece of paper. Flatten your playdough out and cut out a triangle using the edge of your ruler. Label the angles of the triangle 1, 2, and 3. Next, use the ruler to cut off two of the angles. Carefully move your detached angles and line them up with the straight line you have drawn on your sheet of paper. With your group make a conjecture about these three angles. What do you notice? Activity 2) Flatten out your playdough and cut out another triangle and label the angles 1, 2, and 3. This time line the base of the triangle up with the line drawn on the piece of paper. Cut angles 2 and 3 off and compare them to angle 4. With your group make a conjecture about these angles. What do you notice about angle 2, 3, and 4? After students are finished with the activity we will regroup and discuss as a whole what kind of conjectures each group came up with. We will then go over the Angles Sum Theorem, Third Angle Theorem, Exterior Angle Theorem, Corollary 4.1, and Corollary 4.2. (Pick students to read them to the class) Examples: 82° 65° 46° 1 3 2 4 5 Work: m 1 = 46 + 65 = 111 180 – 111 = 69 = m 2 180 – 142 = 38 = supplement of 142 m 3 = 180 – 82 – 38 = 60 142° m 3 = m 4 = 38 180 – 38 – 69 = 73 = m 5 m 1 = 111 m 2 = 69 m 3 = 60 m 4 = 60 m 5 = 73 5 2 p 60° p // q 135° 1 3 4 q m 1 = 45 m 2 = 75 m 3 = 60 m 4 = 120 m 5 = 45 Independent Practice: Students will be assigned the 4-2 worksheet to complete before the next class period. Students must complete all of the study guide side and all of the evens. They may complete the odds for extra credit.