* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Periodic Table notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
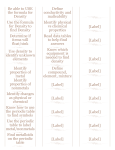
The Periodic Table Basic Arrangement -all elements are arranged according to the number of protons (positive charged particles) in one atom (atomic number) -in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (negatively charged particle) Elements can exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. The two rows below the table are pulled out to make the table fit on one page. They belong next to barium (atomic number 56) All element symbols start with a capital letter. There are 90 naturally occurring elements; the rest are man-made. Families/groups All elements in the same column on the periodic table are called families. They share common characteristics. All elements in the same family/group have the same number of valence electrons (electrons that are in the outermost shell of the atom) Example: the last column on the periodic table is known as the noble gas family. These elements do not interact with other elements and they prefer to be alone. They all have 8 valence electrons. Periods Periods are rows on the periodic table. There are 7 periods. Elements in the same period are very different. They decrease in reactivity the further to the right you go. Metals On the left side of the zig-zagged line on the periodic table (except a few known as metalloids and hydrogen) All are solids at room temperature except mercury (liquid) Most element on the periodic table are metals. They are shiny, good conductors of electricity and heat. They are ductile (they can be drawn into thin wires). They are malleable (they can be easily hammered into very thin sheets). Metalloids Elements that have characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. They are elements that touch the zig-zagged line in the periodic table. Semi-conductors and are often used in technology. Nonmetals Elements to the right of the zig-zagged line on the periodic table with the exception of Hydrogen. Hydrogen is a nonmetal but to the left of the periodic table. The nonmetals are brittle, not malleable or ductile, poor conductors of both heat and electricity, and tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions. Some nonmetals are liquids.