* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz Review
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
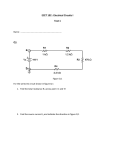
Complete Quiz You have 10 minutes to complete the quiz The Quiz is Open-Book (use it) Get help from your neighbor Quiz Review 1) Open Circuit d) A circuit with the switch turned to off or a circuit with any break A circuit (a circle) must be complete for the switch to be “on” if there is any break or open spot, it is an “open circuit”. 2) Closed Circuit f) A circuit with the switched turned on, or a completed circuit. A circuit (a circle) must be complete for the switch to be “on” if there are no breaks, it is a closed circle, or “closed circuit” 3) Battery a) A device using chemical energy to push current in a circuit. A battery acts as a pump to push electrons through a circuit. In the last unit, we learned that a battery is a source of potential (stored) electrical enerergy. 4) Resistance e) The ability to resist current flow. This is a property of materials that resists current flow, much like a kink in a hose or a bottle neck resists the flow of water. A resistor reduces the pressure (voltage) of the water flowing through it. 5) Resistor h) In a circuit diagram, an object that uses electrical energy is usually represented by one of these. Any object, a bulb, a toaster, a piece of electronics can be a resistor. 6) Ohm’s Law c) The mathematical relationship between current, voltage and resistance. Ohm’s law is represented by the equation: V = I x R, or I=V/R, or R = V/I 7) Conductor g) An object through which electricity passes easily Any passage of electricity is said to be conduction. If it is easy, then the object or material is a conductor. 8) Insulator b) An object that conducts electricity poorly Any passage of electricity is said to be conduction. If it does NOT conduct electricity easily, then it is an INSULATOR. Question 9 • A microwave uses a current of 4 amps to heat Mr. Franz’s coffee, The voltage in the wall outlet is 120 volts. Calculate the resistance of the microwave. • • • • Look at what we want, R R= V/I R=120 V / 4 A R=30 (ohms) Question 10 • A light bulb needs 2 amps to produce light. If the resistance of the bulb is 3 ohms, how many 1.5 volt batteries do you need to make it light? • • • • • Look at what we want, V V=I x R V = 2A x 3 V=6V If each battery is 1.5 V, then we need 4 of them Question 11/12 • The diagram below pictures three identical light bulbs, each with a resistance of 1 ohm, which are connected by resistance-free wires. A 9-volt battery supplies energy to the circuit. • The total resistance for the circuit shown in the figure is: • Look at what we want, R • For a series circuit, we just add the resistance • RT = R1+R2+R3 = 1 +1 +1 = 3 Question 13/14 • The current for the circuit shown is: • The voltage drop across each light bulb above is ____ volt(s). Question 15 • Suppose you connect more and more light bulbs in series to a battery. What happens to the brightness of each bulb as you add more bulbs? Question 16 • The current in a series circuit: Question 17 • The current in a series circuit ( is always the same / may be different ) in different parts of the circuit. Question 18 • The voltage in a series circuit ( is always the same / may be different ) in different parts of the circuit. Question 19 • The current in a parallel circuit ( is always the same / may be different ) in different branches of the circuit. Question 20 • The voltage in a parallel circuit ( is always the same / may be different ) in different branches of the circuit. Question 21 If each resistor is 2-ohms, what is the voltage drop across each resistor in the diagram below: What are we looking for? Question 22 • The voltage drop across each resistor in the circuit below is ____ volt(s). What are we looking for? Question 23 • The current in each resistor in the circuit is ____ ampere(s). The total current is ____ amps. What are we looking for? I = V/R This is a parallel circuit, so V is the same everywhere. Question 24 What is the voltage drop across each resistor? What are we looking for? V This is a parallel circuit, so V is the same everywhere.