* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organ_Systems_of_the_Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
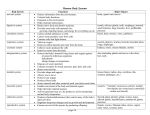
Definitions and Concepts Organ: a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissue; organized to perform more complex function(s) than any tissue alone Organ system: a group of organs arranged to perform a more complex function than can any organ alone A knowledge of individual organs and how they are organized into groups makes it easier to understand how a particular organ system functions as a whole Organ Systems Integumentary system Structure Skin Hair Nails Sense receptors Sweat glands Oil glands Functions Protection Regulation of body temperature Synthesis of chemicals Sense organ Skeletal system Structure Bones Joints Functions Support Movement (with joints and muscles) Storage of minerals Blood cell formation Muscular system Structure Muscles Voluntary (striated) Involuntary (smooth) Cardiac Functions Movement Maintenance of body posture Production of heat Nervous system Structure Brain Spinal cord Nerves Sense organs Functions Communication Integration Control Recognition of sensory stimuli This system functions through the production of nerve impulses caused by stimuli of various types Control is fast-acting and of short duration Endocrine system Structure Pituitary gland Pineal gland Hypothalamus Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Thymus gland Adrenal glands Pancreas Ovaries (female) Testes (male) Organ Systems Endocrine system Functions This system functions through the secretion of special substances called hormones directly into the blood Its purpose is the same as the nervous system: communication, integration, and control; Control is slow and of long duration Examples of hormone regulation Growth Metabolism Reproduction Fluid and electrolyte balance Cardiovascular (circulatory) system Structure Heart Blood vessels Functions Transportation Regulation of body temperature Immunity (body defense) Lymphatic system Structure Lymph nodes Lymphatic vessels Thymus Spleen Functions Transportation Immunity Immune system Structure Unique cells Phagocytes Secretory cells Specialized protein compounds Antibodies Complement Functions Phagocytosis of bacteria Chemical reactions to provide protection Respiratory system Structure Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Lungs Functions Exchange of waste gas (carbon dioxide) for oxygen in the lungs Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli Filtration of irritants from inspired air Regulation of acid-base balance Digestive system Structure Primary organs Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anal canal Accessory organs Teeth Salivary glands Tongue Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Appendix Functions Mechanical and chemical breakdown (digestion) of food Absorption of nutrients Elimination of undigested waste as feces The vermiform appendix is a structural but not a functional part of the digestive system Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis Urinary system Structure Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions “Clearing” or cleaning blood of waste products; wastes are excreted in urine Electrolyte balance Water balance Acid-base balance In the male, the urethra has urinary and reproductive functions Reproductive systems Structure Female Gonads: the ovaries Accessory organs: the uterus, uterine (fallopian) tubes, and the vagina Supporting structures: the genitalia (vulva) and the mammary glands (breasts) Male Gonads: the testes Genital ducts: the vas deferens and the urethra Accessory organ: the prostate gland Supporting structures: the genitalia (penis and scrotum) Functions Survival of the species Production of sex cells (male: sperm; female: ova) Transfer and fertilization of sex cells Development and birth of offspring Nourishment of offspring Production of sex hormones Integration of the Body Organ System Functions No one body system functions entirely independently of other systems All body systems are structurally and functionally interrelated and interdependent