* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download vein - Highline Canvas
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
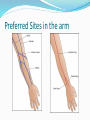
Phlebotomy: Venipuncture Phlebotomy What does it mean? Process of collecting blood Dates back to ancient Egypt Bloodletting-”bad” blood Greek translation Phlebos- vein Tome –incision Why collect blood? Diagnosis and treatment of disease Therapeutic purposes Blood donation The Medical Assistant’s Role Perform venipuncture accurately and efficiently Reliable test results Provide quality care Patient safety and confidentiality Phlebotomist safety (PPE) Anatomy and Physiology of the Circulatory System Blood forms in body’s organs and bone marrow Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste products and carbon dioxide (Review your terminology textbook Hematology and Immunology) Do you know? The difference between an artery and a vein? Circulatory System Cont’d Arteries and Veins Arteries Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart Pulse Thick walls No Valves Veins Carry deoxygenated blood to the heart No pulse Thin elastic walls Valves Circulatory System Cont’d Body contains about 6 liters of blood Forty-five percent of blood is formed elements Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes (platelets) Two mL of blood will yield about 1 mL of fluid Liquid part of blood is plasma Important Terms Fibrinogen –substance in blood Converted by the blood clotting process to fibrin Fibrin- “sticky” web like substance –traps the formed elements-result is a “blood clot” Serum- clear liquid portion of blood extracted from the “blood clot” used for many tests Important Terms Anticoagulant-used to prevent blood from clotting. Found in certain blood tubes Buffy coat-layer separating plasma from RB Centrifuge- machine which spins blood separating the RBC from the serum Anatomy and Physiology of the Circulatory System Centrifuge separates serum from blood Anticoagulant prevents blood from clotting to produce plasma specimen Buffy coat Phlebotomy Sites Order of Draw by sites Arm-Antecubital Space includes Median cubital Cephalic Basilic Veins in hand Veins in feet Preferred Sites in the arm Arteries of Arm Note locations of arteries in the arm. You DO NOT want to draw from an artery Brachial Radial Ulnar How can you distinguish an artery from a vein? Venipuncture Methods There are three main methods of drawing blood Vacuum Tube Syringe Butterfly Evacuated Tube Method This method includes: Vacutainer tube Adapter Double-pointed Needle Features of this method are: Closed system - needle stick risk low Vacuum draws blood inside the tube Safety needles meet OSHA guidelines Venipuncture Technique Butterfly collection system Combines benefits of syringe and vacuum methods Used for small or fragile veins that are difficult to draw Winged needle inserted at about 5° angle then threaded into vein Syringe method Used for small or fragile veins Control flow Venipuncture Equipment Safety needles Required Protects patient and health care worker Equipment/Supplies Needed Physician order and Lab requisition form Pen –black ink Appropriate PPE (gloves, gown, goggles) Needle holder and Needle (varying sizes) Tubes –varying sizes and types used More Equipment/Supplies Tourniquet or blood pressure cuff Constrict flow of blood in arm Make veins more prominent Alcohol or Betadine Cotton balls or gauze-(preferred) Bandages or tape Order of draw Why? Prevent carryover or contamination - Order may vary between laboratories. Basic order: Sterile- sterile specimens Light blue-sodium citrate Red or plain tubes no additives or gel SST –Serum separator tube (Red/Gray, Yellow) Green –heparin Lavender-EDTA Gray –oxalate-fluoride Venipuncture Equipment Additives, anticoagulants, and gels Thixotropic separator gel >> Separator gel tube: centrifuging process Glass particles activate clotting Venipuncture Equipment Specimen collection trays Hold all equipment necessary Carts also used Venipuncture Technique A Phlebotomist needs to use all these skills: Technical skills Prepare for the draw-equipment (spare tubes) Positioning the patient Administrative skills Note order-required tests and Complete the lab requisition Social skills Small talk (weather, pets, entertainment) Good Therapeutic Communication Assess patient comfort level Put patient at ease-show confidence Ask about past experiences Preparing the patient Identify yourself and explain the procedure Properly Identify your patient ask them to: State their name and date of birth For non-English speaking photo ID Note fasting or non-fasting Ask patient about allergies Taking blood thinners Past Experiences Remember to Wash your hands The Draw Position your patient for safety: sit lie down (note past history of fainting or loss of consciousness) Select the appropriate site and vein free of: Scars Hematomas A Pulse The Draw Cont’d Find site that will give best blood return (remember the location order) Palpate vein with tip of finger Differentiating between veins, tendons, and nerves Use the tourniquet appropriately Proper Tourniquet Technique To prevent inaccurate blood test results-do not leave on longer than one minute Tourniquet may be applied over clothing for patient comfort Remove tourniquet when blood flow is achieved or prior to inserting last tube Always remove tourniquet prior to removing needle Proper completion of draw Remove tourniquet Remove needle and apply safety device while Applying pressure to site (patient can assist) Bandage appropriately Tend to the safety of your patient Label specimen tubes in front of patient Venipuncture Technique Patient and specimen identification Computer label >> Compare lab requisition with patients information Important Tips Do Not draw from a resistant patient Do Not draw if you are not comfortable Uncooperative children must receive special care and be restrained for safety Note Patient reactions, stop if patient complains of pain-assess patient Venipuncture Technique The unsuccessful venipuncture Reposition tube and needle Rotate needle Advance further into vein Try another tube-maybe the tube is defective If you haven’t succeeded in getting blood after 2 tries ask someone else to try Venipuncture Technique Factors affecting laboratory values Incorrect specimen handling and storage Drawing procedure incorrect Alcohol in specimen Tourniquet on too long Wrong tube Tubes not filled to appropriate levels will cause inaccurate test results Patient Factors Affecting Lab Results Blood Alcohol-elevate Hemolysis-destroys RBC’s results Diurnal rhythm-RX or daily activity level Exercise-runner’s anemia, change results Fasting (not)-inaccurate results Heparin-incorrect use interferes with results Stress-Increase in WBC’s Tourniquet on too longdilution hemoconcentration Challenging Patients Pediatric The child, parents or guardians Approach-explain –get down to their level Resistant-restraints ? Geriatric Physical-skin, hearing or vision impaired Effects of disease-stroke, arthritis, Parkinson’s –tremors, Dementia-Alzheimer's Safety issues-wheelchairs, balance More Challenges Dialysis or Cancer patients -fistulas and shunts (AV-arteriovenous-permanent access for dialysis) Long-Term Care patients, Home Care, or Hospice Patients Traveling phlebotomists Problem Sites Burns, Scars, Tattoos Damaged Veins (sclerosed-thrombosed) Edema-swelling due to abnormal accumulation of fluid Hematoma-swelling or mass of blood Mastectomy-caution lymph node removal Obesity Complications or Conditions Allergies-adhesive, antiseptic, latex Excessive bleeding due to medications, hemophilia Fainting Nausea and vomiting Pain while drawing-what is normal –what is NOTstopping the draw Seizures/Convulsions-stop draw immediately-get help Comprehensive Medical Assisting 4th Edition Clinical Medical Assisting: A professional, Field Smart Approach to the Workplace, Textbook and Workbook Phlebotomy Essentials 4th Edition