* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BE LAB
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
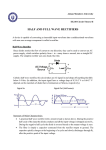
BASIC ELECTRONICS (BE) LAB VIVA QUESTIONS Course code: 15EC02P 1. Define Resistor? The component which offers resistance is called as resistor. It is measured by ‘R’ measured in ohms (Ω) Resistance is the property of the material which offers opposition to the flow of the current. 2. Define electric current? The flow of free electrons from higher pressure(density) to lower pressure(density) is called Current. it is represented by ’I’ and measured in amphere(A) 3. Define EMF? Electro motive force is the force is the force which sets up the flow of the electric current in the circuit. It is represented by ‘emf’ and measured in volts(v) 4. Define ohm’s law? Ohm’s law states that “The Electric current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the conductor and inversely proportional to the potential difference across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor at constant temperature”. 5. State Kirchhoff’s current law? Kirchhoff’s current law states that “the Algebraic sum of current meeting at the point or node is zero” OR Incoming current is equal to outgoing current at a node or a point. 6. State Kirchhoff’s Voltage law? Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that “in a closed circuit the algebraic sum of emf is equal to the sum of product of current and resistance”. 7. What are active components? Active components are the components which amplify and process the signal are called active components Ex: transistor, diode, FET, AFG etc. 8. What are passive components? Passive components are the components which are not capable of amplifying or processing are called as passive components Ex: Resisters, capacitors, inductor 9. What is capacitor? Capacitor are the electronic(passive)components which are capable of storing electronic charges blocks dc and passes ac. it is represented by c and measured in farads(f) Different types of capacitors are? Capacitor Fixed variable Gang capacitor trimmers and paddlers Electrolytic Non Electrolytic ceramic aluminum tantalum Paper Mica Plastic 10. What is Inductors? Inductors are the passive electronic components which opposes any change in the flow of electric current. Types of Inductors are: Inductors Fixed Air core iron core Variable Ferrite core RFC AFC 11.What is diode? Diode is a semi-conductor diode which converts AC into pulsating DC. Diode is a single junction,two layered,two terminal device. 12.What is a zener diode? Heavily doped in the reverse bias semi-conductor diode is called zener diode. zenerdiode has two layers single junction and two terminal device. 13.what is a transistor? Transistor is a three terminal, two junctions and three layered device, which strengthens the weak signal. There are 2 types of transistor NPN and PNP. Emitter is the terminal which emitts charge carriers,heavily doped region collector is the terminal which collects the charge carries and moderately doped region or terminal. Base is the region through which charge carriers passes and thinly doped region. 14.what is doping? Adding impurities to the semi-conducting material is called doping. Semi-conducting material doped with trivalent element is called as P type material Semi-conducting material doped with pentavalent element is called as N type material 15.what is rectification? Rectification is the process of converting AC into pulsating DC is called rectification. Diode is used as rectifier. 16.what is amplification? The process of strengthening the weak signal is called as amplification. Transistor is used as amplifier. 17.what is BJT? Bipolar junction transistor is called as BJT.NPN and PNP are called BJT’s.the conduction current takes place by both type of charge carriers In PNP current conduction takes place by holes(majority carriers) In NPN transistors current conductor takes place by electrons(majority carriers) Hence BJT’s are current controlled device. 18.what is FET? The field effect transistor is a semi-conductor device. Its operation based on the control of current takes place by an electric field(voltage). Hence FET is a voltage controlled device 19.what is JFET’S and MOSFET’S? Field effect transistors are called as JFET’S. FET”S are of two types 1)J FET’S a)N channel JFET’S b)P channel JFET”S 2)MOSFET’S or IGFET’S Metal oxide semi-conductor field effect transistor or insulated gate field effect transistors are of two types: FET”S are unipolar device in which current conduction takes place by means of one type of charge carriers.FET’S have high input impedence. 20.What is uni-junction transistor? Single junction transistor, which has emitter,base 1and base 2 terminals. it operates in negative resistance region.UJT acts as a switch. 21.What is an SCR? Silicon controlled rectifier is a semi conductor device which converts AC into DC and controls the power to external loads. SCR is a four layered three junction and three terminal device, which is also known as thyristor. 22.what is a op-amp? It is a linear integrated circuit which has high gain direct coupled amplifier capable of amplifying both DC and AC signals. 23. What are the Characteristics of ideal Opamp?. An ideal opamp would exhibits the following electrical characteristics: 1) Infinite voltage gain A. 2) Infinite input resistance. 3) Zero output resistance. 4) Infinite Bandwitdh. 5) Infinite common mode rejection ratio. 6) Infinite slew rate. 24. What are the applications of Opamps ? Modern opamps are used 1) In ac and dc signal amplification 2) In active filters 3) In oscillators 4) In comparators, regulators 5) In performing mathematical operation such as adder, integrator 6) ,differentiator 7) In voltage followers 25.What is CMRR? Common mode rejection ratio is the ratio of differential voltage gain to the common mode voltage gain. 26 .what is slew rate? It is defined as the maximum rate of change of the output voltage per unit time is expressed in volts per micro seconds. 23.what is ripple factor? The AC components present in pulsating DC of a rectifier is called as ripple factor Ripple factor of full wave and bridge rectifier is 0.48. ripple factor of half wave rectifier is 1.21 24.what is the output frequency of half wave,full wave and bridge rectifier? In half wave fo=fin In full wave fo=2fin In bridge rectifier output frequency fo=2fin 25.what is the efficiency of half wave, full wave and bridge rectifier? The efficiency of half wave rectifier is 40.6% The efficiency of full wave rectifier is 81.2% The efficiency of bridge full wave rectifier is 81.2% 26.what are filters? Filter is an electronic circuit which removes AC components(ripples)in the rectified output. Filter are connected with rectifiers are called passive filters which consists of passive components like inductor,capacitor. There are 4 types of filters. 1)inductor filter 2)capacitor filter 3)LC filter 4)pie type filter.