* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Syllabus 2011
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
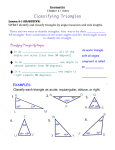
GEOMETRY Mathematics Prince George’s County Public Schools SY 2011-2012 Course Code: 343003, 343023, 343063 Prerequisites: Algebra 1 Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit Geometry provides students with the skills outlined in the Maryland Core Learning Goals for Geometry. These skills include using logic to develop arguments, working with the postulates and theorems of Euclidian geometry, applying rules for parallel and perpendicular lines, identifying congruent and similar figures, classifying polygons, measuring angles and segments, writing proofs of triangle congruence, drawing, constructing, and performing plane transformations. INTRODUCTION: Typically in a Math class, to understand the majority of the information it is necessary to continuously practice your skills. This requires a tremendous amount of effort on the student’s part. Each student should expect to dedicate approximately 1 hour of studying for every hour in class. Some hints for success in a Math class include: attending class daily, asking questions in class, and thoroughly completing all the homework problems with detailed solutions as soon as possible after each class session. INSTRUCTOR INFORMATION: Name: Dr. Rosalinda Dimamay E-Mail: [email protected] Planning: 2B Phone: 301-449-4800 ext 257 CLASS INFORMATION: COURSE NUMBER: GEOMETRY CLASS MEETS: Every other day for 85 minutes ROOM: 225 TEXT: Geometry, Prentice Hall WEB SITE: www.phschool.com/math CALCULATORS The use of a calculator is required. While participants may use any graphing calculator, the instruction in the course requires the use of scientific calculator with trigonometric functions. Knowledge and competence for use of graphing calculators will be the sole responsibility of the student. GRADING: Your grade will be computed from the following categories: class work, homework, and assessment. The following weighted average will be used to calculate your grade. Category Brief Description Grade Percentage CLASS WORK/ THIS INCLUDES ALL WORK COMPLETED IN THE CLASSROOM SETTING. INCLUDING: NOTEBOOKS , WARM-UPS, VOCABULARYWRITTEN RESPONSES TO CONSTRUCTED RESPONSES (BCR/ECR) WHERE APPLICABLE, GROUP DISCUSSION, ACTIVE PARTICIPATION IN MATH PROJECTS, COMPLETION OF ASSIGNMENTS 30% THIS INCLUDES ALL WORK COMPLETED OUTSIDE THE CLASSROOM TO BE GRADED ON ITS COMPLETION AND STUDENT’S PREPARATION FOR CLASS (MATERIALS, SUPPLIES, ETC.) ASSIGNMENTS CAN INCLUDE, BUT NOT LIMITED TO: PROBLEM OF THE WEEK, FRIDAY NIGHT HOMEWORK THIS CATEGORY ENTAILS BOTH THE TRADITIONAL (EXAMS AND QUIZZES) AND ALTERNATIVE (PRESENTATIONS, PROJECTS, PORTFOLIOS) METHODS OF ASSESSING STUDENT LEARNING. EXAMS, QUIZZES, PORTFOLIOS, RESEARCH/UNIT PROJECTS, ORAL PRESENTATIONS SUGGESTED CRITERIA FOR GRADING PRESENTATIONS, PROJECTS, PORTFOLIOS: CONCEPTS/OBJECTIVES HAVE BEEN MET COMPLETION OF PROJECT CREATIVITY, ORIGINALITY 20% GROUP PARTICIPATION HOMEWORK ASSESSMENT 50% Your grade will be determined using the following scale: 90% - 100% A 80% - 89% B 70% - 79% C 60% - 69% D 59% and below E SAT/ACT: SAT/ ACT preparation is infused into daily instruction. The curriculum is embedded with standardized test preparation activities and test-taking strategies that will help students be successful on high-stakes tests like the SAT, ACT or college entrance exams. The practice in each lesson will prepare the students for the format as well as for the content. IMPORTANT DATES: First Day of School Professional Development ½ Day Professional Development End of 1st Quarter (45 days) Grading/Teacher Planning Parent/Teacher Conferences End of 2nd Quarter (46 days) Grading/Teacher Planning Day ½ Day Professional Development Professional Development End of 3rd Quarter (46 days) Grading/Teacher Planning Last Day for Students (44 days) Last Day for Teachers Monday, August 22, 2011 Friday, September 23, 2011 Thursday, October 13, 2011 Friday, October 28, 2011 Monday, November 1, 2011 Friday, November 12, 2011 Friday, January 21, 2012 Monday, January 24, 2012 Friday, February 18, 2012 Friday, March 4, 2012 Thursday, March 31, 2012 Friday, April 1, 2012 Monday, June 13, 2012 Tuesday, June 14, 2012 First Quarter at a Glance Throughout first quarter reasoning and proof, communication, and connections in mathematics should be emphasized. As students learn the theorems, axioms, and postulates, they should be guided through deductive reasoning procedures in order to learn logical thinking processes. By the end of First Quarter Geometry students should be able to: PRE ASSESSMENT Find the distance between two points on the coordinate plane Find the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment in the coordinate plane Find perimeter and area of rectangles and squares Find circumference and area of circles Graph lines given their equations Relate slope of parallel and perpendicular lines Write ratios and solve proportions Tools of Geometry Use inductive reasoning Make conjectures Understand basic terms and postulates Identify segments, rays, and parallel lines Find the length of segments and the measures of angles Reasoning and Proof Justify steps of a logical argument Prove and apply theorems about angles and converses Properties of Parallel Lines Identify angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal Use a transversal in order to prove that lines are parallel Triangle Relationships and Angle Sums Classify triangles by angles and sides Find the triangle angle sum and polygon angle sums Second Quarter at a Glance Throughout second quarter reasoning and proof, communication, and connections in mathematics should be emphasized. As students learn the theorems, axioms, and postulates, they should be guided through deductive reasoning procedures in order to learn logical thinking processes. By the end of Second Quarter Geometry students should be able to: Congruent Triangles Recognize congruent figures and their corresponding parts Prove two triangles congruent Use and apply properties of isosceles triangles Use congruent triangles in proofs Relationships within Triangles Apply midsegments theorem in problem solving Use perpendicular and angle bisectors Identify properties of perpendicular and angle bisectors, medians and altitudes Use inequalities involving sides and angles Quadrilaterals Define and classify special types of quadrilaterals Use relationships of diagonals, sides, and angles that are present in special quadrilaterals Prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, and kite Area Find the Area of parallelograms Use the Pythagorean Theorem Use properties of special right triangles Find the area of trapezoids, rhombuses, and kites Third Quarter at a Glance Throughout third quarter measurement and connections should be emphasized. As students learn discover different geometric figures, the relationship of the properties of area, surface area, circumference and individual measurements should be highlighted. By the end of Third Quarter Geometry students should be able to: Similarity Identify and apply similar polygons Prove triangles similar Find and use relationships in similar right triangles Right Angle Trigonometry Use tangent, sine, and cosine ratios Use trigonometry to find area of triangles Use angles of elevation and depression to solve problems Surface Area and Volume Find the number of faces, edges, and vertices of a three dimensional figure Find the surface area and lateral area of prisms, cylinders, pyramids and cones Find the volume prisms, cylinders, pyramids, and cubes Find the surface area and volume of a sphere Find the ratios between area and volumes of similar figures Fourth Quarter at a Glance Throughout fourth quarter measurement and connections should be emphasized. As students learn the equations of different types of figures, the relationships to prior knowledge should be highlighted in order to assist the student’s construction of knowledge. By the end of fourth Quarter Geometry students should be able to: Circles Find the measures of central angles, arcs and arc length Use the radius and tangent relationship to investigate circles Use congruent chords, arcs, and central angles Recognize properties of lines through the center of a circle Find the measure of an inscribed angle Find the measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a chord Find angle measures and segment lengths of a circle Write an equation of a circle Find the center and radius of a circle Transformations Identify isometries Find reflection images Describe translations using vectors Find translation images using matrix and vector sums Logical Reasoning Write bi-conditionals and definitions Write the negation, contrapositive, and inverse of a conditional statement Use the law of detachment and syllogism Recognize conditional statements and write converses Constructions Perform Basic Constructions Constructing Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Enrichment Areas of regular polygon Areas of sectors and segments of circles Reflect and translate figures using matrices Use the side splitter and angle bisector theorem Describe and add vectors