* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4 lecture uterus gross anatomy File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
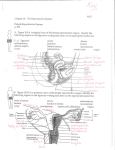
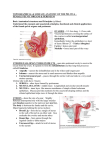
Female Reproductive Anatomy Uterine tube Ovary Uterus Urinary bladder (moved aside) Vagina Urethra Hymen Vestibule The uterus (womb) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LUtjft-8s5k Functions 1. serves to receive the sperm 2. transports sperm from site of deposition to uterine tubes for fertilization 3. provides suitable environment for: a. implantation of the embryo b. nourishment of the embryo & fetus during pregnancy 4. provides mechanical protection of the fetus 5. expels the mature fetus at the end of pregnancy The uterus: domestic animals Uterine horns Uterine horns Uterine body Cervix Vagina Vestibulum The uterus: woman Fundus of uterus Body of uterus Ureter Uterine blood vessels Isthmus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Wall of uterus • Endometrium • Myometrium • Perimetrium Internal os Cervical canal External os Lateral fornix Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Vagina The uterus: topography Rectum Peritoneum Perimetrium Bladder Uterus Round ligament Rectouterine pouch Vesicouterine pouch Rectum Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Cervix Vagina Anus Uterus configuration duplex: rat, rabbit, guinea pig bipartite: mare bicornuate: bitch, sow, cow, ewe simplex: primate, human Rabbit: duplex uterus The female rabbit has a duplex uterus. This has two separate uterine horns and no uterine body. Each horn has its own cervix, and the two cervices open into a single vagina. Cow: bicornuate uterus It is characterized by a small uterine body and two long uterine horns. Fusion of the uterine horns of the cow and ewe near the uterine body gives the impression of a larger uterine body than actually exists. Cow: bicornuate uterus It is almost totally within the abdominal cavity. The uterine horns have a ventral concavity. Ewe: bicornuate uterus It is similar to the cow uterus. Sow: bicornuate uterus The sow has long uterine horns (1m). Horns have an intestinal loop appearance. Sow: bicornuate uterus Mare: bipartite uterus The uterus of the mare is termed bipartite due to the relatively large size of the uterine body compared to the two uterine horns. This differs from that in other farm animals where the uterine horns are more predominant. The lack of a septum dividing the uterine body is also notable. Woman: simplex uterus It has a pear shaped body with no uterine horns, is characteristic of humans and other primates. Uterine horns Dorsal Face intercornual ligament Free border Mesometrial border APEX BASE Ventral Face Cow Uterine body Right margin Dorsal Face Ventral Face Left margin Cow Body: major portion Fundus: rounded superior region Isthmus: narrowed inferior region Cervix: narrow neck Body of uterus Uterine body Fundus of uterus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Wall of uterus • Endometrium • Myometrium • Perimetrium Isthmus Cervical canal Vagina Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Uterus: ligaments (woman) The ligaments of the uterus are 10 in number: one anterior (vesicouterine fold of peritoneum); one posterior (rectouterine fold of peritoneum); two lateral or broad; two uterosacral; two cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments; and two round ligaments. Anterior ligament: consists of the vesicouterine fold of peritoneum, which is reflected on to the bladder from the front of the uterus Posterior ligament: consists of the rectouterine fold of peritoneum, which is reflected from cervix on to the front of the rectum. Uterosacral ligaments: secure uterus to sacrum Suspensory ligament of ovary Peritoneum Uterine tube Ovary Uterosacral ligament Uterus Rectouterine pouch Round ligament Rectum Urinary bladder Vesicouterine pouch Pubic symphysis Cervix Vagina Anus Mons pubis Urethra Clitoris External urethral orifice © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Domestic animals rectouterine fold Rectum Bladder vesicouterine fold cardinal (lateral cervical) ligaments: from cervix and superior vagina to pelvic lateral walls Suspensory ligament of ovary Ovarian blood vessels Broad ligament • Mesosalpinx • Mesovarium • Mesometrium Ovarian ligament Body of uterus Ureter Uterine blood vessels Isthmus Uterosacral ligament Uterine (fallopian) tube Fundus of uterus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Uterine tube • Ampulla • Isthmus • Infundibulum • Fimbriae Ovary Round ligament of uterus Wall of uterus • Endometrium • Myometrium • Perimetrium Internal os Cervical canal Cardinal (lateral cervical) ligament External os Lateral fornix Vagina Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Round ligaments: bind uterus to anterior wall Broad ligaments: a fold of peritoneum which is reflected from the margin of the uterus to the lateral walls of the pelvis Mesometrium: lateral support of broad ligament Suspensory ligament of ovary Ovarian blood vessels Broad ligament • Mesosalpinx • Mesovarium • Mesometrium Ovarian ligament Body of uterus Ureter Uterine blood vessels Isthmus Uterosacral ligament Uterine (fallopian) tube Fundus of uterus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Uterine tube • Ampulla • Isthmus • Infundibulum • Fimbriae Ovary Round ligament of uterus Wall of uterus • Endometrium • Myometrium • Perimetrium Internal os Cervical canal Cardinal (lateral cervical) ligament External os Lateral fornix Vagina Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The broad ligaments in domestic animals Laterale Face Medial Face Dorsal Margin Broad ligament Cranial Margin Ventral Margin Uterus cavity Fundus of uterus Body of uterus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Wall of uterus • Endometrium • Myometrium • Perimetrium Isthmus Cervical canal Vagina Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Uterus cavity Horns Body Cervix Body Cervix Uterus cavity The body is long and does not show a septum. The uterus has endometrial folds which are parallel to the length of the uterus. mare Cervix Cervix: narrow neck, or outlet; projects into vagina Cervical canal communicates with: Vagina via external os Uterine body via internal os Cervical glands secrete mucus that blocks sperm entry except during estrus Cervix Fundus of uterus Lumen (cavity) of uterus Body of uterus Isthmus Internal os Cervical canal External os Lateral fornix Vagina Cervix Posterior view © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Cervix Posterior fornix Cervix Anterior fornix Vagina Cervix: domestic animals •The lumen of the cervix is the cervical canal. •The canal is formed by, and often almost occluded by mucosal folds. • Single fold in the queen and bitch • Multiple folds protruding into the cervical canal in the cow, ewe, sow and mare. •The cervical canal opens cranially into the body of the uterus at the internal uterine ostium. •The cervical canal opens caudally into the vagina at the external uterine ostium. Cervix: cow Internal os folds Fornix Cervical canal External os Vagina cow External os Vagina Cervix: cow Cervix: cow cow Fornix Cervix: sow Body * The body is very small (few cm). Body The cervix is very long (10 cm) And directly continous into the vagina without forming the fornix. Cervical folds form rings * ** cervical rings* that interdigitate with each other to close the cervical canal. Some useful links https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a8fgm-zEYjQ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CNRDxjMlEoQ