* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a Network? - ITCK
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
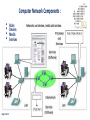
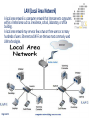
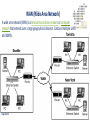
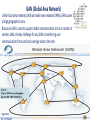
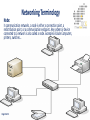
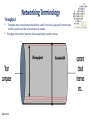
ITCK Information Technology Center Of Kabul University Networking Basics Introducing Basic Network Concepts “In the beginning, there were no networks. Life was bad.” —MIKE MEYERS Mohammad Ferdous(ehsan) “safi” Date: 21 / Sep / 2016 [email protected] In this Lecture, you will learn : • Networking History • Identify Human and Computer Networks • Describe The Benefits of Networks (Advantages/Disadvantages) • Computer Network Components • Network Types (PAN,CAN,LAN,MAN,WAN,GAN) • Networking Terminologies Date: 21 / Sep / 2016 History of Networks : • • • • • Page 1 of 22 In the late 1950s early networks of computers included the military radar system Semi-Automatic Ground Environments (SAGE). In 1960 the commercial airline reservation system Semi-Automatic Business Research Environment (SABRE) went online with two connected mainframes. Throughout the 1960s, Leonard Kleinrock, Paul Baran, and Donald Davis independently developed network systems that used packets to transfer information between computers over a network. In 1965, Thomas Marill and Lawrence G. Roberts created the first wide area network (WAN). This was an immediate precursor to the ARPANET, of which Roberts became program manager. In 1969 the University of California at Los Angeles, the Stanford Research Institute, the University of California at Santa Barbara, and the University of Utah became connected as the beginning of the ARPANET network. What is a Network? Generally a Network is : • • • • Page 2 of 22 A group or system of interconnected people or things. Nowadays a person might make a phone call, watch a television show, listen to the radio, look up something on the Internet, or even play a video game with someone in country. All of these activities depend on a network. So network is the way to connect people no matter where they are in the world. What is a Human Network? A Human Network is : • In its broadest sense, a network consists of two or more entities, or objects , sharing resources and information. • Those networks are everywhere. You have grown accustomed to working with them, possibly without even knowing it. For example: You or Your Father, Mother, Sister, Brother. • The humans on network may be linked by relations. Page 3 of 22 Human Network Page 4 of 22 What is a Computer Network? A Computer Network is : • A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows computers to exchange data. • In computer networks, networked computing devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. • The computers on a network may be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites, or infrared light beams. Page 5 of 22 Computer Network Page 6 of 22 Networks are Used to : • • • • • Page 7 of 22 Facilitate communication via email, video conferencing, instant messaging, etc. Enable multiple users to share a single hardware device like a printer or scanner. Enable file sharing across the network. Allow for the sharing of software or operating programs on remote systems. Make information easier to access and maintain among network users. Networks are Used to : Page 8 of 22 Advantages of Network : • • • • • • • • Page 9 of 22 Software and resources can be centrally managed. Expensive devices such as laser printers or scanners can be shared. Users can access their files from any workstation Files can easily be shared between users. Network users can communicate by email and instant messenger. It enhances communication and availability of information. It allows for more convenient resource sharing. It boosts storage capacity. Disadvantages of Network : • • • • • Page 10 of 22 It lacks independence. It poses security difficulties. It allows for more presence of computer viruses and malware. Its light policing usage promotes negative acts. The main disadvantage of networks is that users become dependent upon them. For example, if a network file server develops a fault, then many users may not be able to run application programs and get access to shared data. Different Networks Page 11 of 22 Computer Network Components : • • • • Page 12 of 22 Rules Devices Media Services There are many types of networks, including: Page 13 of 22 Local Area Networks (LAN) Personal Area Networks (PAN) Home Area Networks (HAN) Wide Area Networks (WAN) Campus Networks Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN) Enterprise Private Networks Internetworks Backbone Networks (BBN) Global Area Networks (GAN) The Internet PAN (Personal Area Network) A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for data transmission amongst devices such as computers, telephones, tablets and personal digital assistants. Page 14 of 22 CAN (Campus Area Network) A campus network, campus area network, corporate area network or CAN is a computer network made up of an interconnection of local area networks (LANs) within a limited geographical area. Page 15 of 22 LAN (Local Area Network) A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, or office building. A local area network may serve as few as two or three users or as many hundreds of users. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most commonly used LAN technologies. Page 16 of 22 MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) It interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic area or region larger than that covered by even a large local area network (LAN) but smaller than the area covered by a wide area network (WAN). Page 17 of 22 WAN (Wide Area Network) A wide area network (WAN) is a telecommunications network or computer network that extends over a large geographical distance. Contains Multiple LAN’s and MAN’s. Page 18 of 22 GAN (Global Area Network) Unlike local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN), GANs cover a large geographical area. Because a GAN is used to support mobile communication across a number of wireless LANs, the key challenge for any GAN is transferring user communications from one local coverage area to the next. Page 19 of 22 Networking Terminology Node: In communication networks, a node is either a connection point, a redistribution point, or a communication endpoint. Any system or device connected to a network is also called a node. Examples include Computers, printers, switches… Page 20 of 22 Bandwidth: Networking Terminology Bandwidth is defined as the amount of information that can flow through a network connection in a given period of time. Bandwidth is like the width of a pipe. Or the number of lanes on a highway. Bandwidth is measured using: • • • • Bps Kbps Mbps Gbps Page 21 of 22 Networking Terminology Throughput: • Throughput refers to actual measured bandwidth at a specific time of day, using specific Internet routes, • and while a specific set of data is transmitted on the network. Throughput is the amount of material or items passing through a system or process. Page 22 of 22 References : • Lammle, T. (2007). Cisco Certified Network Associate. Study Guide. 6th Ed. Wiley Publishing: Indianapolis, Indiana. • Warner, K. (2003). Cisco Networking Academy Program. Companion Guide.3rd Ed. Ciscopress: Cisco Systems Inc. • More resources are available at: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/25597/computer-network https://www.tutorialspoint.com/ https://www.searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition https://www.omnisecu.com/cisco-certified.../unicast-multicastbroadcast.php