* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparative analysis of different Current mirror using
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
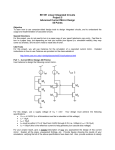
ISSN: 2277 – 9043 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJARCSEE) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014 Comparative analysis of different Current mirror using 0.35µm and its Application Rashmi Sharma#1, Mr. Neeraj Gupta #2 , Mr. Ashok kumar #3 #1 #2,#3 M.Tech (ECE), Amity University Gurgaon Lecturer, Amity University Haryana (gurgaon),India Abstract— Current mode circuits have come to knowledge as compared to voltage mode circuits in recent days because of their properties like low voltage requirement, high slew rate and wider bandwidth The circuit made by current mode technique uses small area, consumes less power dissipation and achieves high operation speed. Current mirrors are the main structures of almost all analog circuits. Current mirror provides high performance, low voltage and low power consumption to its circuits. In the first section of this paper we will analyze and compare the performance parameters of different current mirrors in 350 nm technology in Xilinx xmanager (mentor graphics) tool and in the other section we will show its application in analog circuits. The performance parameters are output impedance, power dissipation, threshold voltage and Trans conductance. Keywords— Current mirror, current mode circuits, input the input current constant regardless of drive conditions. Under ideal conditions, the current-mirror gain is independent of input frequency, and the output current is independent of the voltage between the output and common terminals. The transistors used must be identical and the gate to source voltage should be equal and transistors should work in saturation region. When used as a load element in transistor amplifiers, the high incremental resistance of the current mirror results in high voltage gain at low power supply voltages[1]. and output compliance voltage. Output compliance voltage To keep output transistor in saturation, the minimum voltage that is required is called output compliance voltage. This value can be different for different current mirror structures. For a simple current mirror 1. Introduction Current mirrors made by using active devices have come to be widely used in analog integrated circuits both as biasing elements and as load devices for amplifier stages. The circuit made by current mode technique uses small area, consumes less power dissipation and achieves high operation speed. The current mode circuits uses current signal both at input and output. When the current mirror is used as a load element in amplifiers, the high incremental resistance of current mirror provides high voltage gain at very low supply voltage. The current mirror uses the principle that if the gatesource potentials of two identical MOS transistors are equal, then the current flown through their Drain terminals should be the same[15]. The use of current mirrors in biasing can result in superior insensitivity of circuit performance to variations in power supply and temperature [1]. 2. Current Mirror A current mirror is a two terminal circuit in which the input current is mirrored or copied from the input terminal to output terminal and this output current is independent of the voltage applied to the output terminals. An important feature of the current mirror is its high output resistance which keeps the output current constant regardless of load conditions. Another feature of the current mirror is its low input resistance which keeps The common application of current mirrors are as active load, as biasing element, current amplifier, operational amplifier, analog to digital converters, digital to analog converter and current conveyor etc[3]. There are many current mirrors available, following are the performance parameters of a current mirror: minimum voltage required is Vds2 (sat). Input and output impedance CM should have zero input and infinite output resistance so that the input voltage will not vary with the input currents and the output currents will not depend on the applied output voltage. Output resistance is very important parameter for a current mirror. [12] Device matching It requires perfect matching of the mirroring transistors Ml and M2 (Fig. 1) for accurate mirroring of the signal current. Current transfer ratio (CTR) is precisely set by the (W/L) ratios.[12] Input linear range The total input current must be in the range where both transistors (Ml and M2) operate saturations. DC balance The drain source voltage of the mirror transistors MI and M2 should be equal. The error due to the mismatch in drain to source voltages is λ(Vds2- 317 All Rights Reserved © 2014 IJARCSEE ISSN: 2277 – 9043 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJARCSEE) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014 Vds1), where λ is the channel length modulation coefficient. 3. Different current mirrors 1.Simple current mirror: Figure 2 shows an MOS version of the simple current mirror. The drain-gate voltage of M2 is zero; therefore, the channel does not exist at the drain, and the transistor operates in the saturation or active region if the threshold is positive. Although the principle of operation for MOS transistors does not involve forward biasing any diodes, M2 is said to be diode connected in an analogy to the bipolar case. Assume that M1 also operates in the active region and Fig 2: Simulated wave for simple current mirror that both transistors have infinite output resistance. Then 2.Cascode current mirror: ID1 is controlled by VGS1, which is equal to VGS2 by KVL. resistance is a good measure of the perfection of the A KVL equation is at the heart of the operation of all current mirror[cm1]. Higher performance current mirrors current mirrors. If the transistors are identical, (W/L)2 = try to increase the value of Rout. To increase the output (W/L)1, and therefore resistance the approach used is Cascode structure. The small signal output IOut = ID1 = ID2 Cascode CM shown in Fig 4 is a good choice for The above equation shows that the current that flows in increasing output resistance. The small-signal output the drain of M2 is mirrored to the drain of M1. Since βF resistance is →∞ for MOS transistors, and KCL at the drain of M2 yield Ro = ro2[1 + (gm2 + gmb2)ro1] + ro1 The bipolar Cascode current mirror cannot realize an IOUT = ID1 = IIN output resistance larger than β0ro/2 because β0 is finite and nonzero small-signal base current flows in the Cascode transistor. In contrast, the MOS Cascode is capable of realizing high output resistance by increasing the number of stacked Cascode devices because β0→∞ for MOS transistors. However, the MOS substrate leakage current can create a resistive shunt to ground from the output node, which can dominate the output resistance for VOUT > VOUT (min). Fig 1: Simple current mirror circuit Simulation Results of Basic Current Mirror: Fig 3: Cascode current mirror circuit 318 All Rights Reserved © 2014 IJARCSEE ISSN: 2277 – 9043 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJARCSEE) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014 Simulation Results of Basic Current Mirror: Fig 4: Simulated result for Cascode current mirror 3.Wilson current mirror: Wilson current mirror use Shunt-series negative feedback technique to improve the output impedance and stabilize the output drain current [10]. The process for Wilson current mirror design involves matched identical transistor M1& M3 to achieve same drain current. Simulation Results of Wilson Current Mirror: Fig 6: Simulated result for Wilson current mirror 4. Simulated results The following table shows the simulated and calculated parameters of the different current mirror: Table 1: Comparison of different current mirrors Parameter Simple Cascode Wilson CM CM CM Slew rate 5.1706u 58.874u 104.82u Maximum 61.00u 49.721u 44.903u Power 38.1050u 139.5324u 15.1295u dissipation W W W Threshold 350.96mV 325.60mV 380.50mV 414kΩ 2.40MΩ 4.50MΩ 99.50u 90.40u 310.50u 5v 1.8v 5v 0.35um 0.35um 0.35um 2 4 3 voltage Output impedance Trans conductance Supply voltage Simulation Fig 5: Wilson current mirror circuit The drain current curve with respect to output is much more flat than that for Cascode and simple current mirror. Thus provides better linearity to the output response. Output impedance is higher thus provides better mirror efficiency[9]. technology Number of transistors From the above table it is clear that performance wise the Wilson current is best than the other two current mirrors because the power dissipation is very small and other parameters are also high as compare to others. 319 All Rights Reserved © 2014 IJARCSEE ISSN: 2277 – 9043 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJARCSEE) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014 6. Application Many configurations of current mirror are discussed and used for many applications. Especially Wilson current mirror which is one of the main building blocks of analog and mixed signal integrated circuits for low voltage design circuit and high speed application. The Wilson current mirror can be used for application to Linear Voltage-to-Current Converter Used for Two-Stage Operational Amplifier[14]. Fig 8. Shows the circuit of voltage to current converter used for Op amp application: 7. Conclusion In this article we have simulated and analyzed the different types of current mirrors and successfully measured the parameters of current mirrors using DC analysis. Any one of them can be selected as per their requirement. We have compared the performance of simple CM, Cascode CM and Wilson CM. It is concluded from the table that the Wilson current mirror is best among them because of its medium output compliance voltage and high output resistance. Wilson current mirror can be used as a low biasing circuit. Circuit diagram: REFERENCE [1] Paul.R.Gray, Paul.J.Hurst, Stephen.H.Lewis and Robert.G.Meyer, “Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits”, by John Wiley & sons, Inc 1984. [2] E. SACKINGER and W. GUGGENBUHL, “A versatile building block: the CMOS differential difference amplifier,” IEEE J., 1987, SC-22, (2), pp. 287294. [3] B. Razavi, “Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits,” New York: Tata McGraw-Hill 2002. [4] P. E. Allen and D. R. Holberg, “CMOS analog circuit design,” New York: Oxford University Press, 2002. [5] S.S. Rajput and S.S. Jamuar, “Low voltage analog circuit design techniques”, IEEE circuits systems Magazine 2, pp-24-42, 2002. [6] S.S. Rajput and S.S. Jamuar, “A current mirror for low voltage, high performance Analog Circuits.” In Proc.Analog integrated Circuits & Signal, Kluwer Academic Publications,36, pp. 221-233, 2003. Fig 7: Circuit of voltage to current converter Simulation result: [7] B. Minch, “Low-Voltage Wilson Current Mirrors in CMOS,” in IEEE ISCAS, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007, pp. 2220–2223. [8] Cyril Mechkov, “Equalizing the Currents in Wilson Current Mirror”, International Scientific Conference Computer Science,2008 [9] Neeraj gupta, nutan, taru tewatia “Characterization & Analysis of Various Current Mirrors using 180Nano Technology”, 2009 [10] Mei-Ping Pua, “The Design of A Precision Current Mirror Using A High-Gain Current Amplifier, Published M S Thesis ,The University of Texas at Arington, ,December 2008. [11] Hassan Faraji Baghtash, Khalil Monfaredi, and Ahmad Ayatollahi, “Very Low Power, Low Voltage, High Accuracy, and High Performance Current Mirror”, JOURNAL OF ELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 9, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2011 Fig 8: DC characteristics for V-I converter for different value of resistance. [12] Bajrang Bansal, “Current Mirror Circuits With Improved Performance”, International Journal Of 320 All Rights Reserved © 2014 IJARCSEE ISSN: 2277 – 9043 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Electronics Engineering (IJARCSEE) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014 Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Vol-I , Issue – II,2011. [13] Hitesh, anuj goyal, “Advancement in Current Mirror Techniques”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, volume 2, issue 1, january 2012 [14] Radwene Laajimi, Mohamed Masmoudi, “HighPerformance CMOS Current Mirrors: Application to Linear Voltage-to-Current Converter Used for TwoStage Operational Amplifier”, scientific research, vol-3, page:311-316, year 2012 [15] ajay kumar, arjun singh yadav, C. M roy, “A New CMOS Voltage Divider Based Current Mirror,Compared with the Basic and Cascode Current Mirrors”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, Volume 3, Issue 4, April 2013 321 All Rights Reserved © 2014 IJARCSEE