* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Boundaries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
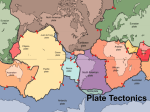
Plate Boundaries Convergent Boundaries 2 plates move toward each other Destructive plate margins Old plate material is being recycled Oceanic crust is being pushed back into the mantle at the subduction zone 3 types of Convergent Boundaries 1. Oceanic – Continental When oceanic crust is subducted under continental crust Occurs because oceanic crust is more dense As oceanic crust subducts into the mantle it melts Melted oceanic crust rise and forms mountains and volcanoes (ex. Andes Mts.) – called continental volcanic arc 1. Oceanic – Oceanic When 2 oceanic plates collide One oceanic plate subducts the other Causes volcanic activity under water (similar to oceanic – continental) Forms a volcanic island arc (ex. The Aleutian Island) 1. Continental – Continental When 2 continental plates collide Only part of one continent subducts Causes folded mountains to form (ex. Himalayas) Mts are folded along the margins Composed of metamorphosed sedimentary rock Other examples Alps, Urals, Appalachians 1. Transform Boundary (Fault) 2 plates grind (slide) past each other No destruction of lithosphere Ex. San Andreas fault Divergent Boundaries The separation of 2 plates Constructive plate margins – formation of new lithosphere Plates move away from a ridge margin New molten material wells up from the mantle Molten material cools-new crust is formed Continuous process Features Formed: Continental Rifts – Splitting of continental crust (ex: East African Rift Valley an d Rhine Valley) Continental crust is being stretched in opposite directions due to upwarping Formation of mountains and volcanoes (ex: Mt. Kenya and Mt. Kilimanjaro) Eventually a rift valley will form followed by a sea Oceanic Ridges An underwater mountain chain 70,000 miles long Formed by the upwarping of the crust – over time rift valley fills with water and forms an ocean Sea-floor spreading – spreading of the ocean floor Process where new lithosphere is formed Average rate of 5 cm/yr