* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Catheter Ablation for AF: Patients, Procedures, Outcomes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
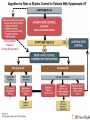
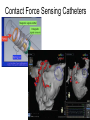
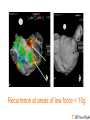
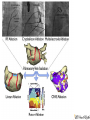
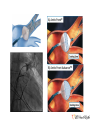
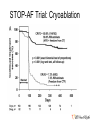
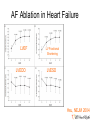
Catheter Ablation for AF: Patients, Procedures, Outcomes John Sapp Director Heart Rhythm, QEII Health Sciences Centre Professor of Medicine, Dalhousie University Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation is a pain in the rear…. What makes it so difficult? Goals of Care? Live longer and / or Live better How can AF hurt your patients? • Symptoms • Stroke/Thromboembolism • Tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy The indication for rhythm control is inadequate symptom relief with rate control How to Pick Rhythm Control • The main goal is symptomatic control Which one is better? How To Choose Rate Vs Rhythm Control? Liparus Weevil Pissodes pini Weevil The Devil you know? Rate Control Beta-blockers ++ Ca Channel Blockers Digitalis Rhythm Control AF Ablation Amiodarone, Sotalol, Flecainide, Propafenone, Dofetilide, Dronedarone Young patients? Athletes? Resting Bradycardia? ? How to rate control • Beta-blockers • Verapamil / Diltiazem • Digoxin? Not dronedarone • Sometimes pacemaker to permit drug therapy • Rarely AVN ablation How to Rate Control • Target resting HR < 100 – Sometimes a treadmill test or loop recorder is informative… • Pill in the pocket rate control and anticoagulation? Rhythm Control • Special cases for rhythm control: – Heart failure? – Young age – Highly symptomatic – Resting bradycardia / Athletes Rhythm Control • Sotalol – Avoid in elderly women, use of diuretic, renal dysfunction, hypokalemia, prolonged QT – I start at 80-120 bid…not higher than 160 bid • Flecainide – Avoid in patients with ventricular scar – I start at 50 mg bid, sometimes 100 bid, rarely 150bid • Propafenone – Avoid in patients with ventricular scar – I start at 150 bid-tid, rarely 300 tid Rhythm Control • Sotalol: Monitor renal function over time, check QTc interval intermittently, concern if >470, reduce dose if >500 • Flecainide: Watch for side-effects—QRS widening, other • Propafenone: Watch for side-effects— QRS widening, other Rhythm Control With Flecainide / Propafenone, I always use an AV node blocking agent Catheter Ablation for AF • Triggers • Substrate Who Should Have Ablation? Risks • 4.7% Complications – 1.5% vascular – 1% Perforation/Tamponade – 1% Stroke/TIA • Rarer Complications – Pulmonary vein stenosis – Phrenic nerve injury – Atrio-esophageal fistula / Death Redo Rates • Seems to be changing… – Was approximately 1 in 3 – Moving closer to 1 in 4-5…. Ablation Procedure Ablation Techniques • Radiofrequency Ablation – Double trans-septal puncture – Point-by-point ablation lesion delivery encircling the pulmonary veins and electrically isolating them Andrade et al. CJC 2014; 30 S431-S441 Contact Force Sensing Catheters TOCCASTAR Reddy et al. Circulation Sep 2015 Recurrence at areas of low force < 10g CryoAblation • Liquid-Nitrogencooled balloon • Advanced across interatrial septum, and inflated in pulmonary venous ostia STOP-AF Trial: Cryoablation Catheter Ablation for Persistent AF • Patients with persistent AF have lower success rates with catheter ablation than paroxysmal patients… Ablation for Persistent AF Trials to come… • Comparisons of Cryoablation against RF ablation • Comparison of cryoablation against antiarrhythmic drug therapy as an early intervention • Comparison of AF Ablation versus drug therapy with clinical endpoints Longer Term Outcomes • Most recurrences occur within the first year after ablation • Late recurrences: – 87% 1 year, 81% at 2 years, 63% at 5 years… – 85% at 3 years, 75% at 5 years • Focus still remains on ablation to control AF, not necessarily a cure… AF Ablation in Heart Failure LVEF LVEDD LV Fractional Shortening LVESD Hsu, NEJM 2004 Freedom from AF after AF ablation in patients with LV dysfunction Hunter (N=26) MacDonald (N=22) De Potter (N=36) Choi (N=15) Efremids (N=13) Lutomsky (N=18) Khan (N=41) Gentlesk (N=67) Chen (N=94) Hsu (N=58) 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% AF Free post-ablation 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% RAFT-AF • Hypotheses • • Key Inclusion Criteria: • • • • Catheter ablation-based AF rhythm control as compared with rate control in patients with HF of either impaired LV function (LVEF ≤ 45%) or preserved LV function (LVEF > 45%) will reduce allcause mortality or HF hospitalization High burden AF – paroxysmal, persistent, long-term persistent NYHA class II or III HF Increased NT-proBNP/BNP Intervention: • • Rhythm control arm: Rate control arm: Catheter ablation ± AAD Rest HR<80; 6MW HR <110 Conclusions • Rhythm control is still directed at symptoms • First-line therapy is still usually antiarrhythmic drug therapy • I think new technology is improving the single-procedure success rate • New trials will help us know best technology for ablation, and role for ablation in heart failure patients with AF Conclusions • AF Ablation works best for patients with: – Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation – Normal hearts • Less appropriate for – Very elderly – Longstanding persistent AF – Diseased atria, size > 50 mm…