* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Lesson 31
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
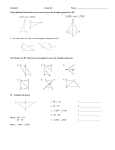
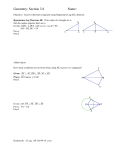
Name: __________________________ Geometry Lesson 31 Date: ________________________ Objective: TSW use flow chart and paragraph proofs. Period: ______________________ Flowchart Proof - A style of proof that uses boxes and arrows to show the structure of the proof. A flowchart proof should be read from left to right or from top to bottom. Each part of the proof appears in a _____, while the justification for each step is written __________ the box. The arrows show the progression of the proof’s steps. Example 1 Interpreting a Flowchart Proof Use the given flowchart proof to write a two-column proof. Given: ∠1 and ∠3 are congruent. ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary. Prove: ∠2 and ∠3 are supplementary. SOLUTION Statements Reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Flowchart proofs are useful when a proof has two different ________________ that could be performed at the same time, rather than in sequence with one another. Whenever a proof does not proceed linearly from one step to another, a flowchart proof should be considered. Example 2 Writing a Flowchart Proof Prove the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Given: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 Prove: m∠1 + m∠2 + m∠3 = 180° SOLUTION 1 2 Paragraph Proof - A style of proof in which statements and reasons are presented in paragraph form. In a paragraph proof, every step of the proof must be explained by a sentence in the paragraph. Each sentence contains a _____________________ and a _______________________________. Example 3 Reading a Paragraph Proof Use the given paragraph proof to write a two-column proof. Given: ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary. Prove: ∠3 and ∠4 are complementary. ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary, so m∠1 + m∠2 = 90° by the definition of complementary angles. Angle 1 is congruent to ∠4, and ∠2 is congruent to ∠3, by the Vertical Angles Theorem. So m∠1 = m∠4, and m∠2 = m∠3. By substitution, m∠4 + m∠3 = 90°. Therefore, ∠3 and ∠4 are complementary by the definition of complementary angles. SOLUTION Statements Reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A paragraph proof is good for ____________ proofs where each step follows logically from the one before. Paragraph proofs are usually more compact than two-column proofs. Example 4 Writing a Paragraph Proof Prove Theorem 10-1: If two lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate interior angles are congruent. Given: Lines p and q are parallel. Prove: ∠2 ≅ ∠3 SOLUTION You Try! b. Prove the Vertical Angles Theorem using a flowchart proof. Given: a and b are intersecting lines. Prove: ∠1 and ∠3 are congruent. d. Prove Theorem 5-4: If two lines are perpendicular, then they form congruent adjacent angles. Given: Lines s and t are perpendicular. Prove: Angles 1 and 2 are congruent adjacent angles.