* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download group%20work%20presentation[2] cristal
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
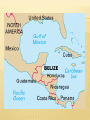
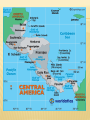
Social Studies Method University of Belize Submitted to: Mr. Kevin Tucker Submitted on: October 15th, 2011 Overview of Geography of Belize Central America and the Caribbean Done by: Abel Pop Wendy Ordonez Theryl Williams Beverly Felix Cristal Westby EXAMINE THE PICTURES? EXPLAIN WHAT IT DEPICTS? WHAT IS GEOGRAPHY? Geography is the study of the earth’s landscapes, peoples, places and environments. It is, quite simply, about the world in which we live. Geography is unique in bridging the social sciences (human geography) with the natural sciences (physical geography). OUR NATIONAL FLAG OF BELIZE BELIZE IS A COUNTRY IN CENTRAL AMERICA. Belize, a country in Central America, formerly called British Honduras. It faces the Caribbean Sea and is bordered by Mexico and Guatemala. The area is 8,867 square miles (22,965 km2). Flat, swampy lowlands cover much of northern Belize. In the south a narrow coastal plain gives way inland to the Maya Mountains, forested uplands that reach 3,681 feet (1,122 m) at Victoria Peak. Major rivers are the Belize, Hondo, and New. A barrier reef, sandy beaches, and shallow lagoons fringe the coast. The climate is tropical. Along the coast temperatures average between 75° and 85° F. (24° and 29° C.) the year round. Annual rainfall increases from 50 inches (1,270 mm) in the north to more than 160 inches (4,060 mm) in the south. Hurricanes sometimes strike the coast. FACTS IN BRIEF ABOUT BELIZE Capital: Belmopan. Official language: English. Area: 8,867 mi2 (22,966 km2). Greatest distances—north-south, 180 mi (290 km); east-west, 85 mi (137 km). Coastline—220 mi (354 km). LINKS OF BELIZE Central America, a part of North America, is a tropical isthmus that connects North America to South America. It includes (7) countries and many small offshore islands. Positioned in the planet's northern and western hemispheres the Central America isthmus is bordered in the northwest by the country of Mexico, and in the southeast by the country of Colombia. In addition, it's bordered by the Caribbean Sea, Pacific Ocean, and numerous bays, gulfs and inlets. Central American Countries Belize El Salvador Honduras Panama Costa Rica Guatemala Nicaragua FIVE THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY Theme 1: Location, Position on the Earth's Surface. Theme 2: Place, Natural and Cultural Characteristics. Theme 3: Relationships within Places, Humans and Environments. Theme 4: Movement, Humans Interacting on the Earth. Theme 5: Regions, How They Form and Change. THE SIX ELEMENTS OF GEOGRAPHY EDUCATION Element 1: The World in Spatial Terms. This element incorporates the theme of location, reminding instructors that finding places is not the only skill one uses when dealing with maps. It also identifies the variety of maps that students need to study and use. Element 2: Places and Regions. It combines two of the five themes, clarifying their meanings by pointing out that places are culturally defined by people, that they can be small or large, and that they may vary in importance over time. Element 3: Physical Systems. It serves as a reminder that the earth has patterns that are related to its physical nature, that many changes are a result of the physical processes acting on the earth, and that natural forces change Earth by moving materials. Element 4: Human Systems. This element stresses ongoing changes in human patterns related to settlements, the movement of resources, and the struggles and conflicts regarding control of the earth's surface. The inclusion of these two systems reminds teachers to include detailed considerations of both. Element 5: Environment and Society. This element shows how people, at times, adapt their behaviors to fit the environment, whereas at other times, they try to change the environment to fit their own needs and desires. This element ensures that teachers consider environmental perspectives and ask students to think about how various people view the earth. Element 6: The Uses of Geography. It encourages teachers to ask students to apply geographic knowledge to other school subjects and consider how people use geographic knowledge and skills in their jobs when making decisions. SOCIAL STUDIES BEST PRACTICES The content of this area of study has normally been organized into the specialized disciplines of sociology, political science, economics and psychology. But since human behavior and interactions take place in a physical environment and cover a wide span of time, the disciplines of geography and history also form an integral part of this area of study. STUDENT BEHAVIORS ILLUSTRATING THE FIVE GEOGRAPHIC SKILL Where is it? Why is it there? What is important about its location? How is one location related to other locations of people, places, and environments? Distinguish between geographic and non geographic questions. Locate, gather, and process information from a variety of maps and primary and secondary sources. Make and record observations of physical and human characteristics of places. Make and record direct field observations. Construct graphs, tables, and diagrams displaying geographic information. Make models of physical and cultural landscapes. Make inferences and draw conclusions. Interpret geographic information. Prepare oral and written reports that use maps and graphics. Acquire geographic information; draw conclusions; and make generalizations. Apply generalizations to solve problems and make decisions. DIFFERENT METHODOLOGY USING MAPS AND GRAPHS Using climate maps and graphs, students decide what clothing they would take if they were to travel today to a specified place. Then they decide what would be the best time for a tourist to visit that location. Using land use maps, students identify places that are home to cowboys and cowgirls, miners, and those who catch fish or raise fish. WEATHER AND CLIMATE DIFFERENT METHODOLOGY 1.Students arrange a box of crayons, a pencil, a book, and a pair of scissors on their desktop and draw a map illustrating the arrangement. 2.They remove the items and give them and their map to a partner. 3.The partner uses the map to place the items on a desktop. The mapmaker checks to see whether the arrangement is correct. 4.Young students make Me Maps. A tracing is made around the body. Then the children use previously agreed-on symbols to draw their eyes, nose, heart, knees, ears, mouth, waist, and elbows in the correct locations. MAP OF CENTRAL AMERICA 5. Students follow a map to go on treasure hunts within the school or on the school grounds. The map may be drawn by the teacher or other students. 6. Each student makes a map illustrating the route taken to school. Older students also write directions to their homes, which classmates follow to mark a route on a city or county map. MAP OF BELIZE JAMAICA GEOGRAPHY OF JAMAICA Location: Caribbean, island in the Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba Geographic coordinates: 18 15 N, 77 30 W Map references: Central America and the Caribbean Area: total: 10,991 sq km land: 10,831 sq km water: 160 sq km Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Connecticut CONCLUSION "In its simplest expression, geography asks humanities oldest, most fundamental questions: 'Where am I?' 'How do I get there?' 'What is on the other side of the mountain?' THANK YOU !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Any Questions