* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHY_211_ADDITIONAL_REVISION_QUESTION_
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Relative density wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
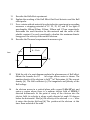
PHY 211 ADDITIONAL REVISION QUESTIONS Useful constants: Electronic charge, 𝑒 = 1.6 × 10−19 𝐶, mass of electron 𝑚 = 9.1 × 10−31 𝑘𝑔. Data for questions 1 Material n p Silicon Germanium GaAs 0.135 0.39 1.1 .05 0.19 0.05 Intrinsic Atom carrier density density in 3 m 1.7 × 1016 5 × 1028 2.4 × 1019 4.41 × 1028 1.4 × 1012 4.43 × 1028 1. A germanium rod has diameter 2mm and length 50cm. Calculate its resistance before it is doped. Find also its resistance after it is doped with (a) trivalent atoms and (b) pentavalent atoms. (see data above for the parameters needed). Assume a doping ratio of 1:107. 2. In a CRT, VA = 1135, l= 2cm, d = 1cm, L = 25cm. The p.d. across the yplates is 10V, calculate the velocity of the electron on leaving the electron gun and the total deflection in the vertical direction when it arrives at the screen. 3 Describe the structure and mode of operation of the cathode ray tube. State four applications of the C.R.O (b) The screen of a cathode ray tube measures 15cmx15cm. The final anode voltage is 1135V. The electron beam is to be magnetically deflected. The deflecting coil is 25mm long and its distance to the screen is 28cm. calculate (i) the velocity of the electrons on leaving the final anode (ii) the flux density required to deflect the spot of light to the edge of the screen. 4 A cathode-ray tube has an accelerating potential of 2kV. It is fitted with two pairs of deflecting plates, the pair being mutually perpendicular. Each plate is 1.5cm long, the spacing between the plates being 1cm. Assume that the centres of the pairs coincide calculate the lengths of the line produced if the input signals are Vy = 50V rms, and Vx = 30V rms. From the centre of the deflection plates to the screen is 38 cm. 5 A 15cm cathode-ray tube is to be magnetically deflected. The final Anode voltage is 2kV, the deflecting coil is 2.5cm long and the distance from its centre to the screen is 38 cm. find the flux density required to defect the beam to the edge of the screen. Through what angle is the beam deflected. 6 Describe the Thomson’s experiment to measure q/m. 7 Explain in detail how to determine the variation thermoemf of a copper – constantan thermocouple with temperature In a copper/iron thermocouple, the EMF generated at temperature θoC is given by the table below. Deduce the constants a and b in the expression for the thermo-emf θ0 C 50 100 150 200 200 emf(mV) 0.65 1.20 1.65 2.0 2.25 8 Describe the construction of a practical light dependent resistor. Explain its use in street light switching. 9 Describe the operation of the photo-electric tachometer 10 (a) (b) Explain the electron-gas model of a metal. Calculate the end-to-end resistance of a rectangular bar of intrinsic GaAs crystal at 3000K. Take w=2mm, t= 1mm, and l= 10cm. Intrinsic carrier density = 1.4x1012/m3 GaAs number density = 4.43x1028atoms/m3 µn=1.10, µp= 0.05 . If the doping ratio is 1: 108, find the resistances of a p-type GaAs bar and an n-type GaAs bar 11 12 13 14 Describe the Hall effect experiment. Explain the working of the Hall Effect fluid level detector and the Hall effect probe For a certain cathode material in a photoelectric experiment a resending measures a stopping potential of 1V. 2V, 3V, 4V, and 5V for light of wavelengths 400nm,300nm, 240nm, 200nm and 171nm respectively. Determine the work function for this material and the value of the plank’s constant. For each wavelength, calculate the maximum kinetic energy and the velocity of the emitted electron. Describe the Thomson’s experiment to measure q/m. B = ITesla 1mm 1mm 10A 2mm 1cm 15 With the aid of a neat diagram explain the phenomenon of Hall effect. Obtain the formula for VH. An n-type silicon water is shown. The number density of the electron is 4x1020/m3 Determine (a) The current density (b) The Hall coefficient (c) The magnitude and polarity of the Hall voltage 16 An electron moves in a vertical plane with a speed 1.41x107m/s and enters a region where there is a uniform electric field of 3500N/C directed downwards. At the point of entry of the electron into the electric field, its velocity is along a path directed at angle 30 degrees below the horizontal. Find (a) the velocity of the electron 5 10 8 s after it enters the electric field and (b) The position at the electron at this time. Draw a sketch of the orbit 17 A proton q 1.60 10 19 and m 1.67 10 27 kg is moving in a magnetic field of intensity 1.5T directed along the x axis. The initial velocity of the proton has components u x 2.5 10 5 m / s, u y 0 and u z 2.0 105 m / s Calculate (a) the force on the proton and the acceleration at time t 0 (b) the radius of the helical path (c) the angular speed of the proton (d) The pitch of the helix (the distance travelled along the axis of the helix per revolution Draw a sketch of the orbit








![The unit of the magnetic field B (the Tesla) A] is the same as the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001468224_1-294f0433f2fee7d3418b8d831b35e9d0-150x150.png)





