* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - MsTurnbull.com
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
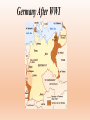
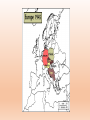
12.9 Bell work 12/9 • What Treaty ended WWI? • Treaty of Versailles • How did that treaty help start WWII? • Things Fall Apart 12/14 • Last day of school in 2 weeks! • December 18 Extra credit opportunity • Watch a film about genocide • Write about it (exact directions on front page of my website) • Up to 100 points • Due December 16 • You can only do this if you have 0 or 1 missing assignments • Remember: your final is 20% of your grade • Yes it is EVERYTHING from day 1 • 3 parts • Part A: 61 question Multiple choice (taken on finals day) • Part B: 9 question multiple choice w/reading (3 q’s per reading) • Part C: 1 essay (documents provided and need 3 paragraphs) Part A+B is 15% of your grade Part C is 5% of your grade Take out paper for WWII notes Remember: Celebration Time • Cheering the end of world war I, on Nov. 11, 1918. • The long, horrible war had taken the lives of nearly 10 million soldiers. Germany After WWI “Nature is cruel, so we may be cruel, too… I have the right to remove millions of an inferior race that breeds like vermin” -Hitler How It Began Lots of factors • WWI leftovers • Germany defeated in and had to pay cost of war. In huge economic depression • Italy victorious but wanted more territory • Japan victorious but wanted China • Outside factors… What Were These Outside Factors? • Germany reduced size • Organized League of Nations • French and Britain unsure • U.S. isolationist Immediate Causes of WW II • In Germany Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933 as a fascist dictator. • Hitler Hated the Treaty of Versailles and violated it. First he built up the German military. Then he sent troops into the Rhineland. This was a direct violation of the Treaty of Versailles, which said in 1919 that Rhineland was a demilitarized zone. Political Ideologies • Totalitarianism is a form of government that aims to control everything, including newspapers, radio, and television • Democracy a form of government in which citizens elect representatives to govern for them. Hitler • He was a totalitarian leader. • He caused millions to die, divided the country, caused countries to go to war with one another, and made people live in fear. Hitler is busy… • Gestapo Created -- April, 1933 • Jewish Boycott – April, 1933 • Jewish Books Banned & Burned – May, 1933 • 27,000 People in Camps – July, 1933 • 60,000 People in Camps – 1938 • Illegal to Leave Germany – October, 1941 Immediate Causes of WW II • Hitler wanted to conquer whoever he felt was inferior to the Germans or Aryans. He wanted “living space” for the Germans in Eastern Europe. • On September 1, 1939 Germany invaded Poland without a declaration of war. This starts World War II. German Territorial Gains • Austria – March, 1938 • Border of Czechoslovakia – Sept., 1938 • All of Czechoslovakia – March, 1939 • Poland – Sept., 1939 • By Summer of 1940, Germany Controlled Most of Europe • World shocked as France falls to Germans Immediate Causes of WW II • Britain and France declared war on Germany on September 3, 1939. • Italy declared war on France and Britain on June 10, 1940. “Blitzkrieg” • In German blitzkrieg means “lightning war”. • Hitler used blitzkrieg during his invasion of Poland. • Blitzkrieg included surprise attacks, rapid advances into enemy territory, and massive air attacks that struck and shocked the enemy. • Germany achieved most of its victories in World War II with the Blitzkrieg tactic. • A blitzkrieg consists of bombing enemy positions with airplanes, then attacking with armored forces (tanks), and finally following up with ground troops. • Germany used Blitzkrieg tactics against France. • Germany defeated France in 5 weeks. • They had done what could not be done in 4 years of WWI. Blitzkrieg Axis Powers Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance known as the Axis. Six other nations eventually joined the Axis. Alliance That Changes War • Germany “allies” with Japan • Japan was “China Hungry” • Japanese angry over U.S. support of China • Agreed to peace negotiations with U. S. Hirohito Emperor of Japan World War II War in the Pacific • Japan occupied French Indo-China. • The US responded by cutting off Japan’s supply of scrap metal and oil. • US embargo angers Japanese and is the provocation for Japan attacking Pearl Harbor • Without American oil, Japan only had a six month reserve of oil. • Japan had to act quickly or not be able to wage war. • That is when they decided to bomb Pearl Harbor. • Japan wanted the oil from the Dutch East Indies • But they knew America would go to war with them if they attacked that area. • So they decided to destroy the American fleet at Pearl Harbor in a surprise attack. Pearl Harbor Dec. 7, 1941 “Yesterday, December 7, 1941 is a date which will live in infamy. The United States Of America was suddenly and deliberately attacked by Naval and Air Forces of the Empire of Japan.” -Franklin Roosevelt The U.S. during the beginning of WWII was isolationist. Why did the United States decide to join the war? Allies United: U.S.S.R, England and The U.S. D-Day - June 6, 1944 Landing on Normandy Beach It was the largest sea borne invasion in history. The Air War During world war II the B-24 bombers were used to strike factories, railroads, and other industrial targets. Germany Surrenders May 7, 1945 Germany At The End Of WWII How did the war with Japan end? • Atomic bomb The Atomic Bomb • Atomic Bomb – was a “super weapon” because it was a single bomb with the destructive capacity of thousands of regular bombs. • Decision to drop it – President Truman decided to drop the atomic bomb on Japan because he believed it would shorten the war and save American lives. • The first bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, Japan. It destroyed the city and killed about 100,000 people. • When Japan did not respond to America’s request to surrender, the second bomb was dropped. • It was dropped on Nagasaki, Japan and killed about 60,000 people. • Japan surrendered after that. Hiroshima and Nagasaki • They were chosen as targets because… • Much of the population was military personnel • Large industrial and manufacturing facilities made both cities wealthy • Both cities were virtually undamaged by previous U.S. bombings Important Years to Remember • 1939 – German invasion of Poland starts WWII • 1941 – Germany invades Russia • 1941 – Pearl Harbor – USA enters war • 1942 – Turning points at Stalingrad and Midway • 1945 – Atomic bombs dropped on Japan • 1945 – Germany and Japan surrender Important turning points to remember • Formation of alliances • Stalin grad • D-Day