* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrangement of Fascicles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
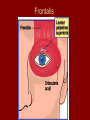
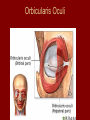
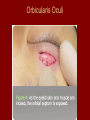
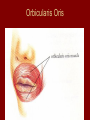
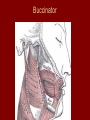
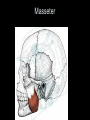
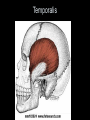
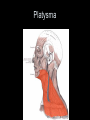
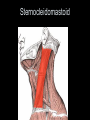
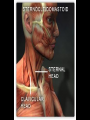
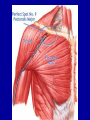
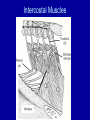
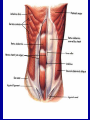
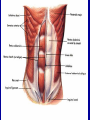
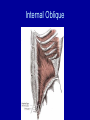
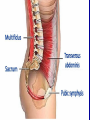
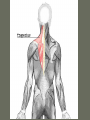
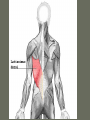
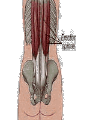
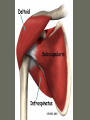
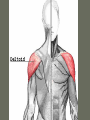
Arrangement of Fascicles Remember: a fascicle is several sheathed muscle fibers wrapped by a coarse fibrous membrane Arrangement of Fascicles • Common fascicle patterns: – Circular • When fascicles are arranged in concentric rings (sphincters) – Convergent • When the fascicles converge to a single insertion • Triangular or fan-shaped – Parallel • The length of the muscle runs parallel to the long axis of the muscle • Strap like Arrangement of Fascicles • Common fascicle patterns: – Fusiform • Modified parallel form • Has a spindle-shaped muscle • Has an expanded belly or gastor – Pennate • Short fascicles • Attach obliquely to a central tendon – Unipennate – insert into one side of the tendon – Bipennate – inserts into opposite sides of the tendon – Multipennate – inserts into multiple places of the tendon Head and Neck Muscles • Facial Muscles – Frontalis – covers the frontal bone from the cranial aponeurosis to the skin of the eyebrow • Raises the eyebrows – Occipitalis – covers the posterior aspect of the skull • Pulls the scalp – Orbicularis Oculi – fibers run in circles around the eyes • Allows eye closing, squinting, blinking and winking Frontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oculi Head and Neck Muscles • Facial Muscles – Orbicularis Oris – the circular muscle of the lips • Opens the mouth and protrudes the lips (kissing muscle) – Buccinator – fleshy, runs horizontally across the cheek • Inserts into the orbicularis oris • Flattens the cheek • Doubles as a chewing muscle Orbicularis Oris Buccinator Head and Neck Muscles • Facial Muscles – Zygomaticus – extends from the corner of the mouth to the cheek • “smiling muscle” • Raises the corners of the mouth Head and Neck Muscles • Chewing Muscles – Buccinator – already mentioned – Masseter – covers the angle of the lower jaw • Runs from the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to the mandible • Closes the jaw – Temporalis – fan-shaped, overlying the temporal bone • Inserts into the mandible and is a synergist to the masseter Masseter Temporalis Head and Neck Muscles • Neck muscles – Platysma – single sheet-like muscle • Covers the anterolateral neck • Originates from the connective tissue of the chest muscle and inserts in the area around the mouth • Pulls the corners of the mouth inferiorly – Sternocleidomastoid – paired muscle • Two headed muscles, one on each side of the neck • One head arises from the sternum, the other from the clavicle • Head fuses before insertion into the mastoid process of the temporal bone • Flex the neck Platysma Sternocleidomastoid Trunk Muscles • Divided into Anterior and Posterior muscles – Anterior • Pectoralis Major – large fan-shaped muscle covering the upper part of the chest • Origin is in the sternum, should girdle, and first 6 ribs • Insertion is on the proximal end of the humerus • Flexes the arm Trunk Muscle – Anterior Muscles • Intercostal Muscles – deep muscles of the ribs – External intercostal muscles are used in breathing » Raise the rib cage (air in) – Internal intercostal muscles deeper than the external – Used in breathing » Lower the rib cage (air out) • Muscles of the Abdominal Girdle – reinforce the body trunk – Consists of : rectus abdominis, external and internal obliques, and transverse abdominis. – Look like plywood – Muscles run in different directions Intercostal Muscles Trunk Muscle – Anterior • Rectus oblique – strap-like muscles – – – – Most superficial muscles of the abdomen Run from the pubis to the rib cage Flex the vertebral column Depress the abdomen during defecation and child birth • External oblique – paired superficial muscles – Make up the lateral walls of the abdomen – Fibers run downward and medially from the ribs to the illium – Flex the vertebral column, and rotate the trunk Trunk Muscles – Anterior • Internal oblique – paired muscles – Deep to the external obliques – Fibers run at right angles to those of the external obliques – Rise out of the iliac crest and insert into the last 3 ribs • Transversus abdominis – deepest muscle of the abdomen – Fibers run horizontally across the abdomen – Arises from the lower ribs and iliac crest – Inserts into the pubis Internal Oblique Trunk Muscles • Posterior Muscles – Trapezius • Most superficial muscles of the posterior neck and upper trunk • Together form a diamond shape • Have a broad origin – From the occipital bone of the skull to the end of the vertebral column – Flare to insert into the scapular spine and clavicle Trunk Muscles • Posterior Muscles – Latissimus Dorsi • • • • Large flat muscle pair which covers the lower back Origin is in the lower spine and ilium Inserts into the proximal end of the humerus Extends and abducts the humerus Trunk Muscle • Posterior Muscle – Erector Spinae • Back extension prime mover • Deep muscles of the back • Have 3 muscle columns – Longissimus – Iliocostalis – Spinalis » They span the entire length of the vertebral column » They are back extensors and help bending at the waist Trunk Muscles • Posterior Muscles – Deltoid • • • • • Fleshy triangular shaped Form the shoulder Origin is in the spine of the scapula to the clavicle Insertion is at the proximal end of the humerus Prime mover of arm abduction