* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kidneys
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
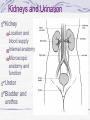
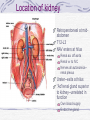
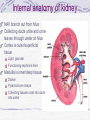
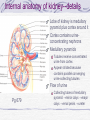
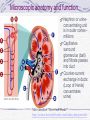
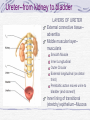
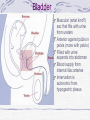
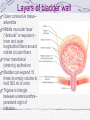
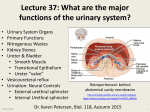
Kidneys and Urination Kidney Location and blood supply Internal anatomy Microscopic anatomy and function Ureter Bladder and urethra Location of kidney Retroperotoneal at midabdomen T12-L3 NAV enters at hilus Renal aa. off aorta Renal vv to IVC Nerves all autonomics-renal plexus Ureter--exits at hilus “Ad”renal gland superior to kidney--unrelated in function Own blood supply Endocrine gland Internal anatomy of kidney NAV branch out from hilus Collecting ducts unite and urine leaves through ureter at hilus Cortex is outer/superficial tissue Light, granular Functioning nephrons here Medulla is inner/deep tissue Darker Pyramid-cone shape Collecting tubules unite into ducts into ureter Internal anatomy of kidney--details Lobe of kidney is medullary pyramid plus cortex around it Cortex contains urineconcentrating nephrons Medullary pyramids Tubules receive concentrated urine from cortex Appear striated because contains parallel converging urine-collecting tubules Flow of urine Pg 679 Collecting tubes of medullary pyramid minor calyx major calyx renal pelvis ureter Microscopic anatomy and function Nephron or urineconcentrating unit is in outer cortex-millions Capillaries surround glomerulus (ball) and filtrate passes into duct Counter-current exchange in ducts (Loop of Henle) concentrates urine) More details at “How Stuff Works” http://science.howstuffworks.com/kidney.htm/printable Ureter--from kidney to bladder LAYERS OF URETER External connective tissue-adventitia Middle muscular layer-muscularis Smooth Muscle Inner Longitudinal Outer Circular External longitudinal (on distal third) Peristaltic action moves urine to bladder (and stones!!) Inner lining of transitional (stretchy) epithelium--Mucosa Bladder Muscular (what kind?) sac that fills with urine from ureters Anterior against pubis in pelvis (more with pelvis) Filled with urine expands into abdomen Blood supply from internal iliac arteries Innervation is autonomic from hypogastric plexus Layers of bladder wall Outer connective tissue-adventitia Middle muscular layer (“detrusal” or expulsor)-inner and outer longitudinal fibers around middle circular fibers Inner transitional (stretchy) epithelium Bladder can expand 15 times its empty volume to hold 500 ml of urine Trigone is triangle between ureters/urethra-persistent sight of infection Urethra Drains urine from bladder to outside Female = short tube Males = long tube Prostatic, Membranous, Spongy (penile) portions Also carries sperm Internal Urethral Sphincter Between bladder + urethra Thickening of detrusor (smooth muscle) External Urethral Sphincter Within urogenital diaphragm Skeletal muscle = voluntary control urination External Urethral Orifice Males = end of penile urethra Females = anterior to vaginal opening, posterior to clitoris (more later with pelvis) Micturition = Urination Emptying bladder Stretch receptors in bladder respond when bladder full Parasympathetic signals detrusor muscle to contract and internal urinary sphincter to open (also inhibits sympathetic pathways that would prevent urination) Other brain receptors can inhibit urination by relaxing detrusor, and keep external urinary sphincter closed Voluntary contraction of abdominal wall muscles increases abdominal pressure Voluntary relaxation of external urethral sphincter For nice review of kidneys and urination http://webanatomy.net/anatomy/urinary_notes.htm See pg 692, M&M Ascent of the kidney in development Kidneys from intermediate mesoderm Pronephric kidney in fetus shows segmental body plan Fish with dorsal renal tissue lateral to vertebral column for most of length In human, metanephric kidney migrates from inferior to superior Variation in kidney shape not uncommon (horseshoe kidney Ureter also from intermediate mesoderm