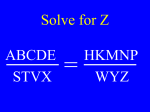* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity and Electronics Revision Questions Multiple Choice and
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electricity and Electronics Revision Questions Multiple Choice and Short Answer Please Note: These questions come from an earlier version of the syllabus. Some of these questions represent very difficult problem solving. Not all areas of the course are covered, for example there are no questions on operational amplifiers. Answers are at the end. 1. Which of the following units is equivalent to a farad? A B C D E 2. 3. A pupil sets up the circuit shown below. V C CV C V-1 V C-1 The circuit shown was used in an experiment to study the charging and discharging of a capacitor. The voltmeter has a very high resistance. If the ammeter P reads 2 A, then the voltage of the d.c. supply is A B C D E 4. The graph below was drawn using results obtained. 14 V 19 V 21 V 22 V 34 V. In the following circuits, each cell has an e.m.f. of 1.5 V and an internal resistance of 1 . Each resistor has the same value, 2 . It is a graph of A B C D E potential difference across the capacitor against time during charging current against time during charging current against potential difference across capacitor during charging potential difference across the capacitor against time during discharging current against time during discharging. If the resistance of the ammeter in each circuit is negligible, which two ammeters will show the same reading? A B C D E A1 and A4 A2 and A5 A3 and A5 A4 and A2 A5 and A1 5. The power dissipation in the resistor of fig 1 is 100 W. 7. The diagram shows a source of ions S, and a grid G beyond which is a collecting plate P. There is a potential difference V between P and G so that ions drifting into the space between P and G are accelerated to P. The whole apparatus is in an evacuated chamber. What is the power dissipation in the resistor of fig 2? A B C D E 6. 100 W 200 W 400 W 800 W 1600 W A 50 Hz a.c. source is connected to an oscilloscope. The trace obtained is shown below. Which of the following will affect the time an ion takes to go from G to P? I II III A B C D E The time-base setting is A B C D E 2.5 milliseconds per centimetre 5 milliseconds per centimetre 10 milliseconds per centimetre 12.5 milliseconds per centimetre 80 milliseconds per centimetre. the potential difference V the mass of the ion the charge on the ion I only II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 8. A four-terminal box is connected as shown to a battery and two milliammeters. The currents in the two meters are identical. 9. In the circuit diagram below, C is a 1.0 F capacitor holding a charge of 10 -5C and R is a 10 resistor. If the switch is suddenly closed, the initial current flowing in the circuit will be Which of the circuits A to E below, within the box, is the only one which will give this result? A B C D E 10. zero 10-5A 10-1A 1A 10 A. In the circuit shown the cell has an e.m.f. of 6.0 V and an internal resistance of . When the switch is closed, the reading on the ammeter is 2 A. What is the corresponding reading on the voltmeter? 11. In the circuit below, the ammeter registers 2 A. How much energy is dissipated in the resistor in 1 minute? 12. A 16-pin package contains 15 identical resistors connected together as shown. 13. When another 3.0 resistor is connected in parallel with the original one, the ammeter reading changes. What would be the two readings on the ammeter? To test these resistors, an engineer connected pins together externally and labelled them terminals P, Q, R, S and T, as shown below. When he measured the resistance between pin 16 and each of these terminals in turn, the engineer found the greatest resistance between pin 16 and A B C D E A cell of e.m.f. 4.0 V and internal resistance 1.0 is used in the following circuit. The ammeter has negligible resistance. 14. The diagram below shows an 8 V supply connected to two bulbs. terminal P terminal Q terminal R terminal S terminal T. In l6s, the electrical energy converted in the two bulbs is A B C D E 2J 4J 8J 32 J 64 J. 15. In the circuit shown below, point X can be attached to any of the points L, M, N, P or Q. 16. An alternating signal is applied to an oscilloscope which has its time-base set at “1 millisecond per centimetre”. Two complete waves appear on the screen, which is 4cm wide. To which point must X be connected to obtain a zero reading on the galvanometer G? A B C D E L M N P Q The time-base is then altered to “10 milliseconds per centimetre”, with every other control kept as before. How many waves will appear on the screen now? 17. In the following circuit, the Wheatstone Bridge is balanced. 18. Resistors R1, R2 and R3 can be connected to form the two networks shown in the diagram. Small adjustments are made to the variable resistor R3 and the corresponding current reading in the galvanometer (Ig) is noted. A graph of the current through the galvanometer is plotted against R3, the small change in the resistance of R3. Which of the following shows that graph? The total resistances between the terminals P and Q, of network 1, and X and Y, of network 2, are mainly decided by the value of one resistor in each network. These dominant resistors are 19. Bulb X in the circuit below has a rating 12 V; 24W and is operating under these conditions. R1 and R2 are of equal resistance. For balance in this Wheatstone Bridge arrangement, R3 must have a value of A B C D E 20. Which of the following circuits would be used in an experiment to illustrate the charging and discharging of a capacitor in a d.c. circuit? suitable centre—zero ammeter. A 21. is a A capacitor is connected in series with a variable resistor, a sensitive ammeter, a switch and a battery, as shown. After the switch is closed, the variable resistor R is reduced at a rate which ensures that the capacitor C has a constant charging current of 2.0 x 10-5 A for a time of 30s. During this time, the p.d. across the capacitor rises from 0 V to 12V. What is the capacitance of the capacitor? A B C D E 22. 2.0 x I0-4 F 2.4 x 10-4 F 5.0 x I0-5 F 8.0 x 10-6 F 1.7 x 10-6 F When a 12V, 50Hz a.c. supply is connected to an oscilloscope the following trace is obtained. The time base control of the oscilloscope is set to move the spot across the screen at A B C D E 1 division per 1/600 th of a second 1 division per 1/500 th of a second 1 division per 1/400 th of a second 1 division per 1/200 th of a second 1 division per 1/50 th of a second. 23. An immersion heater is used to heat water in an insulated container. An a.c. supply and a d.c. supply are available which produce the same rate of heating from the heater. If the a.c. supply has a peak value of 10V, then the p.d. of the d.c. supply must be 26. A 20 V supply, connected to a set of resistors in series as shown, can be used to provide a selection of output voltages by suitable choice of connecting points. The resistance of each resistor is as shown in the diagram. Between which two points does the voltmeter read 8V? 24. Four resistors are connected to a 6 V supply as shown. A B C D E 27. LN MO KL KN LO A low resistance ammeter and a high resistance voltmeter are used to measure resistance R. The resistance of the voltmeter is known to be about the value of R. Initially circuit I is used, then circuit II. What is the potential difference between points X and Y? 25. The circuit below shows two 4 resistors in parallel across a 6 V constant voltage supply. What changes are there in the meter readings when circuit II is used? Calculate the total power developed in this circuit. 28. A particular wire wound resistor has a resistance of 100 when used at a room temperature of 200C. 30. In the circuit below, S is a two-way switch and A is a centre-zero ammeter. Using wire of the same metal, another resistor is constructed. Which of the following combinations of factors would be certain to give a resistance greater than l00 ? The switch contact is moved to X then very quickly to Y. Which of the graphs shows how the current I in the ammeter varies with time? 29. When a capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a supply of potential difference V, it stores a charge Q. Which of the following expressions correctly gives the energy stored in the capacitor? 31. In the following circuit, the supply maintains a constant d.c. voltage. When the switch S is closed, the power delivered to the circuit by the supply is 30W. What power is delivered to the circuit by the supply when the switch is open? 32. On setting up the following bridge circuit, a pupil finds that no current flows in the galvanometer. What is the resistance of the unknown resistor R? 33. An immersion heater is connected to a constant voltage supply. It is found that 2000J of energy is required to supply a current of 2 A for 4s through the immersion heater. What is the potential difference between the ends of the heater, in volts? 34. The circuit below is set up in the laboratory during some practical work in electricity, using a power supply which has no internal resistance. What reading is recorded on the ammeter, assuming it has no resistance? A B C D E 0.05A 0.125A 0.25A 0.50A 1.25A 35. The diagram shows a circuit used to determine the e.m.f. E and the internal resistance r of a cell. Which graph correctly shows how the potential difference V across the terminals of the cell varies with the current I drawn from it? 36. In the Wheatstone Bridge circuit below, the variable resistor R is initially set at 50.0 . The value of R is then increased in 0.1 steps up to 51 and the corresponding values of galvanometer current I are noted. A graph of galvanometer current I against change in resistance X from the initial value is of the form 37. In the following circuit, the p.d. across the 16 ohm resistor is 40 volts when switch S is open. What is the p.d. across the 16 ohm resistor when the switch S is closed? 38. Each cell in the circuit below has an e.m.f. of 2 V and an internal resistance of 1 . Calculate the current in this circuit. 39. The diagram shows two charged parallel plates in a vacuum. The electric field between the plates is shown by the dashed lines. An electron starts from rest at G and moves along one of the paths GH or GI. Which entry in the table below describes the motion of the electron, if gravitational effects are neglected? 40. The diagram below shows a charged capacitor C in a circuit with a resistor R and a switch S. Which one of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of current I with time t in the above circuit after S is closed? 41. The diagram illustrates an experiment to compare the a.c. and d.c. voltages which will produce the same brightness in the lamp. 43. The circuit diagram below shows a cell of e.m.f. E and internal resistance r in series with a resistor R. Which of the following statements about this circuit is/are always true? The circuit is adjusted until the lamp brightness is the same with either a.c. or d.c. voltages across it. The pieces of apparatus marked W, X, Y and Z are I II III A B C D E 44. 42. The potential divider PQ is set up as shown below. The p.d. across the terminals of the cell is less than the e.m.f. of the cell. The current in R is less than that in r. The p.d. across R is less than the voltage “lost” across r. I only I and II only I and III only III only II and III only In the following circuit, VC is the p.d. across the capacitor and VR is the p.d. across the resistor. When the capacitor is fully charged, which of the following statements is/are true? I II III The potential difference across the load resistor XY is A B C D E 3V 5V 9V 13 V 15 V. A B C D E VR has reached its maximum value. VC has reached its maximum value. The current from the cell has reached its maximum value. I only II only III only I and II only I,II and III 45. A manufacturer constructs a capacitor of parallel metal plates separated by a thin layer of plastic dielectric. He states that “it has a maximum working voltage of l0 V”. Which of the following statements is/are correct? I II III A B C D E 46. 48. Which of the following circuits has the lowest resistance between terminals X and Y? 49. Four resistors, each of resistance 8 , are connected across a 60 V supply of negligible internal resistance, as shown below. A potential difference greater than 10 V may cause the dielectric to break down. Above 10 V, the capacitor will still work but its capacitance will increase. The capacitor can only be charged by a supply of e.m.f. 10 V. I only II only III only I and II only I and III only A 20V, 0.5A bulb is connected to a 6V d.c. supply as shown. The supply has negligible internal resistance. If the bulb is to operate at its correct rating, what must be the value of the resistor R? 47. The circuit shown consists of a battery of e.m.f. 10 V and internal resistance 2 connected to a resistor of value 3 and a high resistance voltmeter. What is the power produced in the 3 resistor? The p.d. across LM is A B C D E 12 V 15 V 20 V 24 V 30 V. 50. A battery is tested in the following circuit. 52. An a.c. voltage is applied across the input of an oscilloscope and the following trace is seen. The grid lines on the screen are 1 cm apart. The corresponding readings of voltage and current are taken at various settings of the variable resistor and a graph is plotted as shown below. If the Y-gain control of the oscilloscope is set at 5 Vcm-1, the r.m.s. value of the a.c. voltage is What is the e.m.f. and the internal resistance of this battery? 51. A battery of e.m.f. 12V and internal resistance 2 is connected to a 4 resistor as shown. The readings on the ammeter and voltmeter are noted. The 4 resistor is replaced by a 2 resistor. Which of the following three statements is/are correct? I II III A B C D E The ammeter reading increases. The voltmeter reading increases. The power developed in the resistor increases I and II only I and III only II and III only III only I,II and III 53. In the following diagram, R is a variable resistor. It is set at 8000 to balance the Wheatstone bridge. R is increased gradually from 8000 to 8010. Which one of the following graphs correctly illustrates how the current I through the sensitive meter G varies as the resistance of R is increased? 54. A pupil uses a transformer to step down mains voltage to light a lamp. The currents and voltages at various places in the circuit are indicated below. What is the percentage efficiency of the transformer in this circuit? 55. The electron shown in the diagram below is emitted from an electron gun and then moves between two charged plates. The direction of the electric field between these plates is as indicated. Assuming that the effects of gravity may be ignored, which of the following diagrams correctly indicates the motion of the electron as it passes through the electric field? 56. A pupil tries out various arrangements of three 1 resistors between the terminals X and Y of the following circuit. 57. In the circuit shown, the resistors are identical, the battery has negligible internal resistance and the voltmeter draws negligible current. Select from the table below a possible correct set of results for the readings on the voltmeter. One arrangement gives full-scale deflection on the ammeter. All the other arrangements give deflections less than the full-scale deflection. Which arrangement gives full-scale deflection on the ammeter? 58. A signal generator is connected to the Y-plates of an oscilloscope and the following trace is seen on the screen. Each small square on the screen measures 1 cm by 1 cm. What is the frequency and the peak voltage of the a.c. signal? 59. The graph below shows the relationship between the charge stored on a parallel plate capacitor and the p.d. across its plates while it is being charged up to a final voltage. Which of the following could not be calculated from the information given on the graph? A B C D E 60. The capacitance of the capacitor The final charge stored on the capacitor The final energy stored on the capacitor The final electric field strength between the plates The final voltage across its plates A charged particle is fired between a pair of charged parallel plates as shown in the diagram. While passing between the plates, the electric field deflects it sideways by 1 unit. A different charged particle, which has double the charge and four times the mass of the first particle, is fired with the same velocity between these plates. The electric field will deflect it by A B C D E ¼ unit ½ unit 1 unit 2 units 4 units 61. In the potential divider circuit shown below, the variable resistor allows the potential difference between X and Y to be varied. For the values given, what is the maximum potential difference which can be obtained across XY? Answers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 D A B A D B E B D 4V 720 J A B E D 20 E D B C C C B 6V 18 W B E E E B 15 W 200 250 V D C B 48 V 1A B A D A A B A 8 12 W C A D B A A 75 % C A E E D D 8V