* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Full-Text Support in a Database Semantic File System
Survey
Document related concepts
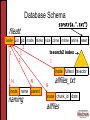
Transcript
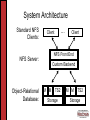
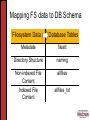
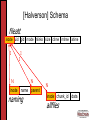
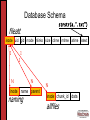
Full-Text Support in a Database Semantic File System Kristen LeFevre & Kevin Roundy Computer Sciences 736 Leveraging DBs in File Systems What do databases have to offer? • Transactions • Concurrency control • Crash recovery • Query power (metadata) • Extensibility – add new objects/modules • Efficient Search! Re-thinking Directories • Current state of directories: LAME! • User remembers what, not where Our System: • Search tools for grouping related files • Semantically meaningful directories [Semantic FS] • Files are stored in tables • Directories are just for looks Related Work • Semantic Filesystems • Use a DB [Inversion Filesystem] • NFS Meets Databases [Halverson] • NFS for portability, transparency, existing code support, familiar semantics • Server-side caching for performance Bringing ideas together: • Use [Halverson]’s infrastructure to implement semantic filesystem ideas Roadmap • Overview of System Design and Implementation • Virtual Directories and Full-Text Queries • Live Demonstration • Conclusions & Future Work System Architecture Standard NFS Clients: Client NFS Front End NFS Server: Object-Relational Database: ... Client Custom Backend M M TS2 Storage M M TS2 Storage Postgres Capabilities An object-relational DB such as Postgres lets you define and add modules. Case in point: Tsearch2 New type: tsvector Related function: to_tsvector to_tsvector(‘a b a c'); Related index: Set triggers to do updates ‘a':1,3 ‘b':2 ‘c':4 idxFTI Mapping FS data to DB Schema Filesystem Data Database Tables Metadata fileatt Directory Structure naming Non-indexed File Content Indexed File Content allfiles allfiles_txt [Halverson] Schema fileatt inode uid gid mode nlinks size ctime mtime atime 1 1 1 N inode N N name parent naming inode chunk_id allfiles data Database Schema strstr(a,”.txt”) fileatt inode uid gid mode nlinks size ctime mtime atime istext 1 1 1 N inode N N name parent naming inode chunk_id allfiles data Database Schema strstr(a,”.txt”) fileatt inode uid gid mode nlinks size ctime mtime atime istext 1 1 1 1 tsearch2 index 1 inode fulltext tsvector N inode N N allfiles_txt name parent naming inode chunk_id allfiles data Roadmap • Overview of System Design and Implementation • Virtual Directories and Full-Text Queries • Live Demonstration • Conclusions & Future Work Virtual Directories and Text Search • Want to handle 2 types of text queries • Boolean keyword queries • e.g. (‘Kristen’ | ‘Kevin’ | ‘Remzi’) & ‘file’ & ‘system’ • IR rank queries • e.g. Rank files with respect to (‘computer’ & ‘architecture’) • More powerful than grep! • Virtual directories proposed for Semantic File systems • Incorporate full-text queries without “breaking” NFS interface for existing applications DBMS Full-Text Support • Keyword Search • Text indices support search over keywords • Words extracted from document, stemmed, “stopwords” removed • Rank • Used existing rank() function as a black-box • rank() counts number of times each word appears in document, and whether search terms are near one another • Optionally, normalize by document length • Other notions of IR rank could easily be substituted Semantics of Virtual Directories • Encountered some tradeoffs • What we did: • Static virtual directories (search once on mkdir) • Directory contents as a snapshot at one point in time • Hard links /CS736 project writeu p papers talk outline NFS reading questions Thread ideas %nfs% NFS vs AFS Semantics of Virtual Directories • Encountered some tradeoffs • Alternatives (all also valid): • Static virtual directory creation with symbolic links • leads to dangling (broken) links • Process query lazily on readdir command • Semantics used in Semantic File System paper • Dynamically update contents of virtual directories on file creation, deletion, or write • Can be implemented using database triggers • More expensive, heavier back-end load Roadmap • Overview of System Design and Implementation • Virtual Directories and Full-Text Queries • Live Demonstration • Conclusions & Future Work Roadmap • Overview of System Design and Implementation • Virtual Directories and Full-Text Queries • Live Demonstration • Conclusions & Future Work Conclusions • Benefits of our proxy architecture: • • • • Standard NFS clients Postgres as black box Simple to expose functionality of DB Use & add DB objects at will Future Work • Performance evaluation to understand the overhead of new functionality • Dynamic index maintenance (file creation & modification) • Virtual directory creation and text querying • Block-level text writes and caching • Query support for other file types • Mechanisms for extracting and indexing meta-data from additional file types (e.g., image files) • Performance Monitoring, Adaptive Indexing and storage format within the NFS Proxy Thanks! Questions? Special Thanks: Remzi Arpaci-Dusseau Alan Halverson David DeWitt