* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
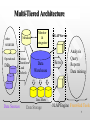
Ayyat IT Group Murad Faridi Muhammad Waqas Salman Raza Junaid Pervaiz Roll NO#2492 Roll NO#2803 Roll NO#2473 Roll NO#2468 Instructor :- “Madam Sana Saeed” 1 OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) Architecture Characteristics Relational OLAP Multidimensional OLAP ROLAP VS. MOLAP HOLAP 2 What Is Data Warehouse? consolidates the information from different data sources, enabling OLAP (online analytical processing), to help decision support. is maintained separately from an operational database (which is used for OLTP – online transaction processing). 3 OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) 4 Multi-Tiered Architecture Metadata other sources Operational DBs Extract Transform Load Refresh Monitor & Integrator Data Warehouse OLAP Server Serve Analysis Query Reports Data mining Data Marts Data Sources Data Storage OLAP Engine Front-End Tools 5 What is OLAP? On-Line Analytical Processing Information technology to help the knowledge worker (executive, manager, analyst) make faster and better decisions. OLAP is an element of decision support systems 6 OLAP • • • • Create an advanced data analysis environment that supports decision making, business modeling and operation research activities. Characteristics of OLAP Use multidimensional data analysis technique Provide advance database support Provide easy-to-use end user interfaces. Support client/server architecture. 7 Two types of database activity OLTP and OLAP OLTP: On-Line Transaction Processing Short transactions, both queries and updates (e.g., update account balance, enroll in course) Queries are simple (e.g., find account balance, find grade in course) Updates are frequent (e.g., concert tickets, seat reservations, shopping carts) 8 OLAP: On-Line Analytical Processing Long transactions, usually complex queries (e.g., all statistics about all sales, grouped by dept and month) “Data mining” operations Infrequent updates 9 OLTP Compared With OLAP On Line Transaction Processing – OLTP – Maintain a database that On Line Analytical Processing - OLAP – Use information in database to guide is an accurate model of strategic decisions some real-world enterprise • Complex aggregation • Short simple transactions queries • Relatively frequent updates • Transactions access only a • Infrequent updates • Transactions access a small fraction of the large fraction of the database database 4/29/2017 10 11 RELATIONAL OLAP Provides functionality by using relational databases and relational query tools to store and analyze multidimensional data. Build on existing relational technologies and represents extension to all those companies that already used RDBMS ROLAP adds the following extensions to traditional RDBMS Multidimensional data schema support within the RDBMS Data access language and query performance are optimized for multidimensional data. Support for very large data bases 12 Multidimensional OLAP MOLAP extends OLAP functionality to MDBMS Best suited to manage, store or analyze multidimensional data. Proprietary techniques used in MDBMS. MDBMS and users visualize the stored data as a 3dimensional cube i.e data cube. MOLAP data bases are known to be much faster than their ROLAP counter parts. Data cubes are held in memory called “cube cache”. 13 What shape am I? I have 6 flat square faces I have 12 straight edges I have 8 corners. I am a …………? Fantastic! I am a cube! ROLAP vs MOLAP Characteristics ROLAP MOLAP SCHEMA Uses star schema Additional dimensions can be added dynamically Uses data cubes Additional dimensions require re-creation of the data cube. Database size Medium to large Small to medium Architecture Client/server Client/server Access Limited to predefined dimensions Support ad-hoc requests Unlimited dimensions 16 ROLAP vs MOLAP Characteristics ROLAP MOLAP Resources High Very high Flexibility High Low Scalability High Low Speed Good Faster with small data sets Average for medium to large data set for small to medium data sets Average for large data sets. 17 Implementation of the OLAP Server ROLAP: Relational OLAP – data is stored in tables in relational database or extended relational databases. They use an RDBMS to manage the warehouse data and aggregations using often a star schema. • They support extensions to SQL. Advantage: Scalable. Disadvantage: No direct access to cells. 18 Implementation of the OLAP Server MOLAP:Multidimensional OLAP - implements the multidimensional view by storing data in special multidimensional data structures. Advantage:Fast indexing to pre-computed aggregations. Only values are stored. Disadvantage: Not very scalable. • 19 Characteristics of OLAP Fast - means that the system targeted to deliver most responses to user within about five second, with the simplest analysis taking no more than one second and very few taking more than 20 sec. Share - means that the system implements all the security requirements for confidentiality and, if multiple write access is needed, concurrent update location at an appropriated level not all applications need users to write data back, but for the growing number that do, the system should be able to handle multiple updates in a timely, secure manner. 20 Analysis - means that the system can cope with any business logic and statistical analysis that it relevant for the application and the user, keep it easy enough for the target user. Although some pre programming may be needed we do not think it acceptable if all application definitions have to be allow the user to define new adhoc calculations as part of the analysis and to report on the data in any desired way, without having to program so we exclude products (like Oracle Discoverer) that do not allow the user to define new adhoc calculation as part of the analysis and to report on the data in any desired product that do not allow adequate end user oriented calculation flexibility. 21 Multidimensional - is the key requirement. OLAP system must provide a multidimensional conceptual view of the data, including full support for hierarchies, as this is certainly the most logical way to analyze business and organizations. Information - are all of the data and derived information needed? Wherever it is and however much is relevant for the application. We are measuring the capacity of various products in terms of how much input data they can handle, not how many gigabytes they take to store it. 22 HOLAP HOLAP is the product of the attempt to incorporate the best features of MOLAP and ROLAP into a single architecture. HOLAP This tool tried to bridge the technology gap of both products by enabling access or use to both multidimensional database (MDDB) and Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) data stores. HOLAP HOLAP systems stores larger quantities of detailed data in the relational tables while the aggregations are stored in the precalculated cubes. HOLAP HOLAP also has the capacity to “drill through” from the cube down to the relational tables for delineated data. Some of the advantages of this system are better scalability, quick data processing and flexibility in accessing of data sources. END What appears to be the end may really be a new beginning. 27