* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Insecta
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
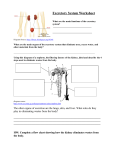
Insects Class Insecta Most numerous and diverse of all the groups of arthropods. • (There are more species of insects than species in all the other classes of animals combined!!) » Have three pairs of legs » Usually have two pairs of wings on the thoracic region of the body, (although some have one pair of wings, or none) » Body organization: head, thorax, and abdomen. • The head usually bears a pair of large compound eyes, a pair of antennae, and usually three ocelli (simple eyes). • General Characteristics – Segmented bodies – Jointed appendages • Specialized for eating, sensing, reproduction, defense and movement – Exoskeleton • Hard covering on the outside of the animal • Limits the growth of the organism (must shed) • Muscles are attached to this layer • Contains protein, lipid, chitin, and often calcium carbonate • secreted by underlying epidermis and shed (molted) at intervals – Bilateral symmetry – Muscular system complex (contains both striated and smooth muscles) – Body cavity • Coelom is reduced; • Most of body cavity consisting of hemocoel (sinuses, or spaces, in the tissues) filled with blood; – Digestion • Complete digestive system – Esophagus, crop, gizzard, midgut, hindgut and anus • mouthparts modified from appendages and adapted for different methods of feeding; – Circulatory System • Open system • dorsal contractile heart, arteries – Respiration • Obtain oxygen through body surface (diffusion), gills, tracheal (air tubes), or book lungs; – Tracheal tubes—carry oxygen to the muscles • Spiracles—small openings in the exoskeleton through which air opens – Water retention—3 structures that aid • Malpighian tubules—excretory structures that remove metabolic wastes from blood and return water to the cells • Exoskeleton—prevents water evaporation • Book Lungs—gas exchange without water loss (also used in respiration) – Excretory system • Paired excretory glands in some • homologous to nephridial system of annelids; • some with other excretory organs, called Malpighian tubules; – Nervous system • Contains same system of annelid (with dorsal brain connected by a double nerve chain of ventral ganglia); • fusion of ganglia in some species; • well-developed sensory organs; – Compounds eyes with many lenses (can see motion and color) – Reproduction • Sexes usually separate, • paired reproductive organs and ducts; • usually internal fertilization; often with metamorphosis;