* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AGV03/BIOLV23 Algiers, K Fall 2010 Chapter 5: Cells and Tissues
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
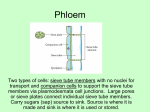
Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 Chapter 5: Cells and Tissues of the Plant Body Plant Structure & Life Span • • ____________________ of a Plant Body – ______________ System – generally ____________________ – ______________ System – generally ____________________ Herbaceous plants – No woody part ____________________ – In temperate climates, aerial parts ____________________ to ground at the end of ____________________ season • Woody plants – • Annuals – • Herbaceous plants that grow, reproduce, & die ____________________ Biennials – • Produce ____________________; persist aboveground ____________________ Herbaceous plants that take ____________________ to complete reproduction Perennials – Woody or herbaceous plants that live ____________________ – In temperate climates, shoots may be ____________________ for part of the year 1 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 Cells & Tissues • Plant cells are organized into ______________ – Tissue – a group _________________________ that form a structural and functional ______________ • ______________Tissue – composed of one cell kind • ______________Tissue – composed of 2 or more cell kinds • ______________Tissue – ______________functions including photosynthesis, storage, & support • ______________Tissue – ______________system of the plant; conducts ______________, dissolved ______________, & ______________ • – ______________& strengthens the plant ______________Tissue – ______________the plant Roots, Stems, Leaves, Flower Parts, and Fruit are referred to as ______________ • Each is composed of all ______________tissue systems • Tissue systems are _________________________ & continuous Ground Tissue Composition • Three simple tissues 1. _________________________ Tissue - Composed of _________________________ cells - Found throughout the plant body (most _________________________) 2 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 - _________________________ plant parts (edible parts) - Photosynthesis, _________________________, secretion - _________________________ & metabolizing - Can _________________________ into other cell types 2. _________________________ Tissue – Composed of _________________________ cells – ______________; supports the non-woody plant organs – Usually ______________; look ______________ – Primary cell walls are _______________________________ (esp. the corners) – ex: near stem surface, leaf vein; ‘strings’ in celery stalk 3. _________________________ Tissue – Composed of _________________________ cells – Also for ______________; ______________ at maturity – Contain ______________& _____________________walls (appear very thick) – _____________________cells - short; shells of nuts, stones of fruit, pear – _____________________– long, tapered, wood, inner bark, leaf veins 3 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 Complex Tissue Composition Vascular System • _____________________ – Conducts ______________ & dissolved ______________ from the root to the stems & leaves; ___________________support – Contains: Tracheids, vessel elements, parenchyma cells, fibers – Tracheids & Vessel elements • ______________ at maturity; ______________ • ___________________ – main water conducting cell; long, tapered contains ______________that water moves through (more common in ______________& ______________relatives) • ________________________ – open at the end; can conduct sideways (can be stacked) no secondary wall; common in ______________plants 4 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 • _____________________ – Conducts ______________ (carbs) throughout the plant; support – Contains: Sieve tube elements, companion cells, fibers, parenchyma cells – _________________________________ are long, thin, and stacked end to end – Contain ______________ for flow ______________ at maturity __________________________ assist in the functioning of sieve-tube elements ______________ cells, with nucleus ______________ but does not ______________ Complex Tissue Composition Dermal Tissue • ___________________ & ___________________ – ___________________ is a single layer of cells; covers the plant – In woody plants, epidermis splits apart to form a ___________________ (many cells thick) as a ___________________ layer – ___________________ – may contain ___________________ (hairs), ___________________ cells & stomata (gas exchange), ___________________ cuticle (wax), contain ____________________________ – ___________________ composed of: – ___________________ cells (______________ at maturity; reduce water loss) – ___________________ ___________________ cells (storage) 5 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 Plant Meristem • • • Plants grow by ______________________________ , elongation, & differentiation – Plant cells divide at the ___________________ – ___________________ Growth – increase in ___________________ – ___________________ Growth – increase in ___________________ (wood) ___________________ Meristem & ___________________ Growth – ___________________ Meristem - Areas at the __________ of roots & shoots – Meristematic cells are __________ , __________ , & __________ – ___________________ epidermis – ___________________ xylem & phloem – ___________________ meristem cortex, pit, ground tissue ___________________ Meristem & ___________________ Growth – ___________________ Meristem - Areas that ___________________ along the entire ___________________ of stem/roots – ______________________ Cambium – cylinder which makes _____________ (2° xylem) & _____________ (2° phloem) – ______________________ Cambium – cylinder in ______________________ ; forms ______________________ & __________________________ Cork cells, Cork parynchyma, & Cork cambium make up the _______________________ (outer bark) 6 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 Review Questions 1. What is the difference between a shoot and root system? 2. What is the difference between a herbaceous and woody plant? 3. What is the difference between an annual, biennial, and perennial plant? 4. What is the difference between simple and complex tissue? 5. Describe the function of ground, vascular, and dermal tissue. 7 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 6. Fill out the chart below Ground Tissue Function Cell types What does it look like Examples Parenchyma Tissue Collenchyma Tissue Sclerenchyma Tissue 7. Describe the function of a xylem, cell types, and describe (& draw) each of the cell types 8 Algiers, K Fall 2010 AGV03/BIOLV23 8. Describe the function of a phloem, cell types, and describe each of the cell types 9. What are the type types of dermal tissue? How are they different? What outgrowths or cell types do they have? 10. Describe the difference between primary and secondary growth 11. What is an apical meristem? Lateral meristem? Describe each. 9