* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
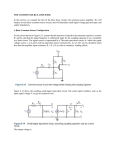
UNIT-5 UNIT V WAVEFORM GENERATORS AND SPECIAL FUNCTION ICs Sine-wave generators, Multivibrators and Triangular wave generator, Saw-tooth wave generator, ICL8038 function generator, Timer IC 555, IC Voltage regulators – Three terminal fixed and adjustable voltage regulators - IC 723 general purpose regulator - Monolithic switching regulator, Switched capacitor filter IC MF10, Frequency to Voltage and Voltage to Frequency converters, Audio Power amplifier, Video Amplifier, Isolation Amplifier, Opto-couplers and fibre optic IC. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 1 UNIT-5 UNIT- V WAVEFORM GENARATORS AND SPECIAL FUNCTION ICS 1. What is a switched capacitor filter? [APRIL/MAY 2008], [MAY/JUNE 2012] A switched capacitor filter is a three terminal element, which consists of capacitors, periodic switches and operational amplifiers and whose open circuit voltage transfer function represents filtering characteristics. The operation of the filter is based on the ability of on-chip capacitors and MOS switches to stimulate resistors. 2. What is a switching regulator? [April/may 2008] Switching regulators are those which operate the power transistor as a high Frequency on/off switch, so that the power transistor does not conduct current Continously.This gives improved efficiency over series regulators. 3. List the characteristics of optocoupler? [April/may 2008] Current intensity ratio Isolation impedance. Response time CMRR. 4. Mention some applications of 555 timers (DEC 2009) Oscillator pulse generator ramp and square wave generator mono-shot multivibrator burglar alarm Traffic light control. 5. What are the three different wave forms generated by ICL8038? [April/may 2010] Square Wave Triangular wave Sine wave 6. How will you increase the output of a general purpose op-amp? [Nov/Dec 2010] Large output voltage swing capability Large output current swing capability Low output impedance Low quiescent power dissipation SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 2 UNIT-5 7. List the applications of 555 timers in monostable mode of operation? (NOV/DEC 2010) *missing pulse detector *Linear ramp generator *Frequency divider *Pulse width modulation. 8. List the applications of 555 timer in Astable mode of operation: (MAY/JUNE 2010) *FSK generator *Pulse-position modulator 9. What is a voltage regulator? A voltage regulator is an electronic circuit that provides a stable dc voltage Independent of the load current, temperature, and ac line voltage variations. 10. Give the classification of voltage regulators? (MAY/JUNE 2011) *Series / Linear regulators *Switching regulators. 11. What is a linear voltage regulator? Series or linear regulator uses a power transistor connected in series between the unregulated dc input and the load and it conducts in the linear region .The output voltage is controlled by the continous voltage drop taking place across the series pass transistor. 12. What are the advantages of IC voltage regulators? (MAY/JUNE 2012), (NOV/DEC 2010) low cost high reliability reduction in size excellent performance 13. Give some examples of monolithic IC voltage regulators: 78XX series fixed output, positive voltage regulators 79XX series fixed output, negative voltage regulators 723 general purpose regulators. 14. What is the purpose of having input and output capacitors in three terminal IC regulators? A capacitor connected between the input terminal and ground cancels the inductive effects due to long distribution leads. The output capacitor improves the transient response. 15. Define line regulation. (MAY/JUNE 2011) Line regulation is defined as the percentage change in the output voltage for a change in the input voltage.It is expressed in millivolts or as a percentage of the output voltage. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 3 UNIT-5 16. Define load regulation. (MAY/JUNE 2011) Load regulation is defined as the change in output voltage for a change in load current. It is expressed in millivolts or as a percentage of the output voltage. 17. What is meant by current limiting? Current limiting refers to the ability of a regulator to prevent the load current from increasing above a preset value. 18. Give the drawbacks of linear regulators? [MAY/JUNE 2012] *The input step down transformer is bulky and expensive because of low line frequency. *Because of low line frequency,large values of filter capacitors are required to decrease the ripple. *Efficiency is reduced due to the continous power dissipation by the transistor as it operates in the linear region 19. What is the advantage of monolithic switching regulators?(MAY 2010) *Greater efficiency is achieved as the power transistor is made to operate as low impedance switch.Power transmitted across the transistor is in discrete pulses rather than as a steady current flow. *By using suitable switching loss reduction technique, the switching frequency can be increased so as to reduce the size and weight of the inductors and capacitors 20. What is an opto-coupler IC? Give examples? [APRIL/MAY 2011] Opto-coupler IC is a combined package of a photo-emitting device and a photosensing device.Examples for opto-coupler circuit : LED and a photo diode, LED and photo transistor, LED and Darlington. Examples for opto-coupler IC : MCT 2F , MCT 2E . 21. Mention the advantages of opto-couplers? [April/May 2011] Better isolation between the two stages. Impedance problem between the stages is eliminated. *Wide frequency response. Easily interfaced with digital circuit. Compact and light weight. Problems such as noise, transients, contact bounce,.. are eliminated. 22. What is an isolation amplifier? (MAY/JUNE 2010) An isolation amplifier is an amplifier that offers electrical isolation between its input and output terminals. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 4 UNIT-5 23. What is the need for a tuned amplifier? (April/MAY 2009) In radio or TV receivers, it is necessary to select a particular channel among all other available channels.Hence some sort of frequency selective circuit is needed that will allow us to amplify the frequency band required and reject all the other unwanted signals and this function is provided by a tuned amplifier. 24. Give the classification of tuned amplifier? (i) Small signal tuned amplifier *Single tuned *Double tuned *Stagger tuned (ii) Large signal tuned amplifier. 25. Write the frequency of oscillation (f0) equation for triangular wave generator? (NOV/DEC 2010) f0=R3/4R1C1R2 26. How frequency to voltage converted on OP-AMPS. (NOV/DEC 2010) A Frequency to voltage converter produces an output voltage, whose amplitude is a function of frequency of the input signal. The input signal may be a sinewave, a square wave or a pulse train. The F/V converter is essentially an FM detector or discriminator. 27. What is video amplifier? (MAY/JUNE 2010), (NOV/DEC 2006), (MAY/JUNE 2012) The video or wideband amplifiers are designed to provide a relatively flat gain versus frequency response characteristics for the range of frequencies required to transmit video information. 28. Define Multivibrators. Mention its types. (MAY/JUNE 2010) Multivibrators are regenerative circuits, which are mainly used in timing applications. Based on their operational characteristics they can be classified into • Astable Multivibrators • Monostable Multivibrators • Bistable Multivibrators 29. Define Astable Multivibrators. (NOV/DEC 2010) The astable Multivibrators toggles between one state and the other without the Influence of any other external control signal. It is also called as free running multivibrator. 30. Define Monostable Multivibrators The monostable multivibrator or one –shot requires an external signal called a trigger to force the circuitinto a quasi stable state for a particular time or delay. 31. What is audio amplifier? The amplifier receives an input from signal source or from a transducer and gives out an amplified signal to the output device is called an audio amplifier. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 5 UNIT-5 32. Draw the internal diagram of audio amplifier? (MAY/JUNE 2010) 33. What are the main advantages of switched capacitor filter? (NOV/DEC 2011) The main advantages of switched capacitor filter are, a) Low system cost. b) Low external component count. c) High accuracy. d) Excellent temperature stability. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 6 UNIT-5 PART B 1. Explain the internal details of 555Timer circuit. [NOV/DEC-2006] (MAY/JUNE 2012). Timer is a highly stable device for generating accurate time delay or oscillation. Signetics corporation introduced this device as the NE555/SE555 and it is available in two package styles,8pin circular style,TO-99 can or 8-pin mini DIP or as 14-pin DIP. PIN DIAGRAM: A single timer can produce time delay ranging from microseconds to few hours. It can be used with supply voltage in the range of +5V to +18V and can drive load up to 200mA. FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 7 UNIT-5 Referring to the above figure, three 5k internal resistors acts as voltage divider, providing bias voltage of 2 VCC to the upper comparator (UC) and 1 V 3 3 CC to the lower comparator (LC), where VCC is the supply voltage. Since these two voltages fix the necessary comparator threshold voltage, they also aid in determining the timing interval. It is possible to vary it electronically too, by applying the modulating voltage to the control voltage input terminal (pin 5) In applications where no such modulation is needed, it is recommended by manufacturers that a capacitor (0.01F) be connected between control voltage terminal (Pin 5) and ground to by-pass noise or ripple from the power supply. In the standby state (stable) state, the output Q of the control flip-flop (FF) is HIGH. This makes the output LOW because of power amplifier which is basically an inverter. A negative going trigger pulse is applied to pin 2 and should have its dc level greater than the threshold level of the lower comparator i.e., 1 VCC 3 At the negative going edge of the trigger pulse, as the trigger passes through 1 VCC , the output of the 3 lower comparator goes HIGH and gets the flip-flop Q 1, Q 0 . During the positive excursion, when the threshold voltage at pin 6 passes through 2 VCC , the output of 3 the upper comparator goes HIGH and thus resets the flip-flop Q 0, Q 1 SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 8 UNIT-5 The reset input (pin 4) provides a mechanism to reset he F/F in a manner which overrides the effect of any instruction coming to F/F from lower comparator.This overriding reset is effective when the reset input is less than about 0.4V. When this reset is not used, it is returned to VCC. The transistor Q2 serves as buffer to isolate the reset input from F/F and transistor Q1. The transistor Q2 is driven by Vref obtained from supply voltage VCC. APLLICATIONS: Pulse generator, Ramp generator. Mono-shot multivibrator Burglar alarm, Traffic light control, Voltage monitor. 2. Explain its (555 timer) usage as Astable multivibrator? [NOV/DEC-2006] (8m) The device is connected for Astable mode of operation is shown below. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 9 UNIT-5 SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 10 UNIT-5 SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 11 UNIT-5 3. Write short notes on frequency to voltage converters? [APR/MAY-2008] (9m) Or Explain F/V converter with a neat block diagram? [NOV/DEC-2008] (10m) The Frequency to Voltage converter performs the inverse operation of Voltage to frequency converter i.e. it accepts a periodic waveform of frequency f I as input and yields an analog output voltage VO. VO k. f I Where k is the FVC sensitivity, in volts per hertz. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 12 UNIT-5 A charge-balancing VFC can be easily configured as an FVC by applying the input to the comparator and deriving the output from the Op-Amp, which has a resistance R in its feedback path. The input signal usually requires proper conditioning to produce a voltage with reliable zerocrossings for comparator (CMP) On each negative spike of V1, CMP triggers the one-shot (monostable multivibrator) and hence closes the switch (SW) and pulls 1mA out of C1 for duration of TH, given by the equation, TH 7.5V .C 1mA ------------------ (1) In response to this train of current pulses, VO builds up. V f I 10 3 TH O R ------------------ (2) Substituting equation (1) in (2) we get, V 7.5V f I 10 3 .C O 1mA R VO 7.5RCf I SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR ----------------- (A) LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 13 UNIT-5 The value of c is determined on the basis of a maximum duty cycle of 25%. The input offset voltage of Op-Amp (OA) should be nulled to avoid degrading the conversion accuracy. Between consecutive closures of SW, R will cause C1 to discharge, resulting in output ripple. The maximum ripple is , Vr (max) 1mA.TH C1 ------------------ (3) Substituting the equation (1) in (3) we get, 1mA. 7.5V .C Vr (max) Vr (max) 1mA C1 7.5C V C1 ------------------ (B) The above figure shows a VFC-FVC arrangement for transmitting analog information in isolated form. VI is usually a transducer signal that is amplified by Instrumentation amplifier. VFC converts VI to train of current pulses for LED, the phototransistor reconstructs the pulse train at the receiving end, and FVC converts the frequency back to an analog output signal VO. APPLICATIONS: FVCs find application as tachometers in motor speed control and rotational measurements. They are used in conjunction with VFCs to transmit analog information. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 14 UNIT-5 4. Write notes on a Switched mode regulator. [NOV/DEC-2006] (8m) Draw the functional block block diagram of Switching regulator and explain?[apr/may2008](8m) Or Write briefly about switching mode voltage regulator? [NOV/DEC-2007] (8m) In series regulator, the pass transistor is operated in its linear region to provide a controlled voltage drop across it with a steady d.c current flow. Whereas, in the case of switched-mode regulator, the pass transistor is used as a “controlled switch” and is operated at either cutoff or saturated state. Hence the power transmitted across the pass device is in discrete pulse rather than as a steady current flow. When the pass device is at cutoff, there is no current and dissipates no power. When the pass device is in saturation, a negligible voltage drop appears across it and thus dissipates only a small amount of average power, providing maximum current to the load. In either case, the power wasted in the pass device is very little and almost all the power is transmitted to the load. Thus efficiency in switched mode power supply is remarkably high- in the range of 70-90%. Switched mode regulators rely on Pulse Width Modulation to control the average value of the output voltage. The average value of a repetitive pulse waveform depends on the area under the waveform. If the duty cycle is varied as show in Fig(i). The average value of the voltage changes proportionally. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 15 UNIT-5 A switching power supply is shown in fig(ii). The bridge rectifier and capacitor filters are connected directly to the a.c line to give unregulated dc input. The thermistor Rt limits the high initial capacitor charge current. The reference regulator is a series pass regulator of the type shown in the Fig. Its output is a regulated reference voltage Vref which serves as a power supply voltage for all other circuits. Transistors Q1and Q2 is alternately switched OFF and ON at 20kHz.These transistors are either fully ON (VCE (sat) ~0.2 V) or cut-off, so they dissipate very little power. These transistors drive the primary of the main transformer. The secondary is center-tapped and full wave rectification is achieved by diodes D1and D2.This unidirectional square wave is next filtered through a two stage LC filter to produce output voltage VO. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 16 UNIT-5 The feedback circuit of a Pulse-Width Modulator and Steering Logic Circuit achieves the regulation of VO. The output voltage VO is sampled by a R1-R2 divider and a fraction R1/(R1+R2) is compared with a fixed reference voltage Vref in comparator1. The output of this voltage comparison amplifier is called Vcontrol and it is applied to the (-) input terminal of comparator 2 and a triangular waveform of frequency 40 kHz is applied at the (+) input terminal. The comparator 2 functions as a pulse width modulator and its output is a square wave V A [Fig:3(b)] of period T(f = 40kHz).The duty cycle of the square wave is T1/(T1+T2)and varies with Vcontrol which in turn varies with the variation of VO. The output VA1 drives a steering logic circuit shown in the dashed block It consist of a 40kHz oscillator cascaded with a flip-flop to produce two complementary outputs VQ and VQ shown in the [Fig:3(d) and (e)]. The output VA1 andVA2 of AND gates A1 and A2 are shown in [Fig:3(f)&(g)] Depending upon whether transistor Q1 or Q2 is ON, the waveform at the input of the transformer will be a square wave as shown in the [Fig:3(h)] The rectified output VB is shown in the [Fig:3(i] If there is a rise in d.c output voltage Vo, the voltage control, Vcontrol of the comparator 1 also rises. This changes the intersection of the Vcontrol with the triangular waveform and in this case decreases the time period T1 in the waveform of [Fig:3(b)] This in turn decreases the pulse width of the waveform driving the main power transformer. Reduction in the pulse width lowers the average value of the d.c output VO, Thus the initial rise in the d.c output voltage VO has been nullified. ADVANTAGES: The high operation frequency used for the switching transistor allows the use of smaller transformers, capacitors and inductors. Due to these the size and the cost has decrease DISADVANTAGES: Since the rectifier is tied directly to the ac line voltage, the rectifiers, capacitors and switching transistors must be able to withstand the peak line voltage. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 17 UNIT-5 5. With circuit diagram explain the working principle of IC 723 voltage regulator? [NOV/DEC-2006], [MAY/JUNE-2007] Or Draw the internal block diagram of IC LM 723 voltage regulator and explain? [MAY/JUNE-2007] The IC 723 general purpose regulator can be adjusted over a wide range of both positive and negative regulated voltage. This IC is a low current device, but can be boosted to provide 5 amps or more current by connecting external components. The functional block diagram consists of two separate sections. The first section contains a zener diode, a constant current source and reference amplifier to produce a fixed voltage of 7 volts at the terminal Vref. The constant current source forces the zener to operate at a fixed point so that the zener outputs a fixed voltage. The other section of the IC consists of an error amplifier, a series pass transistor Q1 and a current limit transistor Q2. The error amplifier compares a sample of the output voltage applied at the INV input terminal to the reference voltage Vref applied at the NI input terminal. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 18 UNIT-5 The error signal controls the conduction of Q1.These two sections is not internally connected but the various points are brought out on the IC package. IC 723 is available in 14-pin Dualin line package or 10-pin metal can package. The voltage at the NI terminal of the error amplifier due to R1-R2 divider is, V NI Vref R2 R1 R2 --------------------- (1) The difference between VNI and the output voltage VO which is directly fed back to the INV terminal is amplified by the error amplifier. The output of the error amplifier drives the pass transistor Q1 so as to minimize the difference between the NI and INV inputs of error amplifier. Since Q1 is operating as an emitter follower, V O Vref R2 R1 R2 --------------------- (2) If the output voltage becomes low, the voltage at the INV terminal of error amplifier also goes down. This makes the output of the error amplifier to become more positive, thereby driving the transistor Q1 more into conduction. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 19 UNIT-5 This reduces the voltage across Q1 and drives more current into the load causing voltage across load to increase. So the initial drop in the load voltage has been compensated. Similarly any increase in load voltage, or changes in the input voltage get regulated. The reference voltage is typically 7.15V. So the output voltage VO is, V O 7.15 R2 R1 R2 -------------------- (3) Thus the above circuit is used as a Low Voltage regulator (< 7V). 6. Explain the working principle of isolation amplifier? [NOV/DEC-2006], [MAY/JUNE-2012] An isolation amplifier is the amplifier that provides ohmic or electrical isolation between the input and output terminals. .Isolation amplifier is mostly used in application where very large common mode difference between input and output sides of the device. They can provide voltage difference of several thousands of volts between input and output. The isolation in isolation amplifier is achieved by use of transformer or by use of Optocoupler. An important characteristic of this circuit is linearity of the input to output transfer characteristics. But non linear input current to the light output characteristics is the problem with variety of signal coupling. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 20 UNIT-5 By using the above circuit we can obtain high degree of linearity.This circuit consists of isolation amplifier in which LED- Photo transistor pairs are used as Opto isolator. The first LED photo transistor pair in the feedback path of the amplifier A1 and second LED photo transistor pair is used at the input of amplifier A2. Both LED – photo transistor couplers are used with the matched characteristics, are driven by the same amplifier A1. Due to the matched characteristics of the two LED photo transistor pairs, the non linear characteristics and temperature dependence get compensated. In many process control application, where the measurand is converted to a current, the linearized current amplifier are suitable for providing isolation. With equal resistor connected to the positive input of the amplifier, the amplifier gain forces the current through the load ZL and LED1, so that the current in transistor Q1, Q2 are equal. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 21 UNIT-5 With matched characteristics of LED-Photo transistor pairs, the load current is equal to the current Iin through the LED2.The error produced by the bias current of the amplifier is reduced by the use of low input bias current amplifier. A typical high quality low profile Isolation amplifier is ISO 212P manufactured by BurrBrown. The device features single supply operation and employs magnetic coupling to provide isolation on the supply side. APPLICATIONS: It is specifically suited for transducer channel isolation for thermocouples, RTDs, pressure sensors and flow meters. 7. Draw the circuit of an IC tuned amplifier and explain how you will realize RF amplifier with AGC and a video amplifier using this building block?[may/june-2007](16m) Tuned amplifiers circuits are designed to amplify a signal over particular narrow band of frequencies centered at fr. To achieve this tuned amplifiers use a tuned or resonant circuit as load. They employ LC tank circuit whose resonant frequency is given as fr 1 2 LC The maximum response of tuned amplifier is at resonant frequency and it falls sharply below and above the resonant frequency. MC 1550: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 22 UNIT-5 The MC 1550 is the differential amplifier stage in monolithic integrated form. It is very versatile and flexible device. It forms an excellent basic building clock for the design of various communication applications like Tuned amplifier with automatic gain control Video amplifiers Amplitude modulator. This circuit with some external components can be used to design a tuned amplifier which amplifies a signal over a narrow band of frequencies centered at fr. Here the input signal is applied to the base of Q1 through the tuned transformer T1.The load RL is connected across the tuned transformer T2 in the collector circuit of Q3. The transistors Q1 and Q3 provide amplification, whereas Q2 provides the control of magnitude of the gain. The combination of Q1 and Q3 acts as a common-emitter and common-base cascode (CE-CB) pair. The input resistance and current gain of the cascode pair is same as those of CE stage, the output resistance is as same as that of a CB stage and the reverse open circuit voltage amplification is given as hr hre .hrb 10 7 . This extremely small value of hr provided by cascade pair results in simplified tuning, reduced possibility of oscillation and hence the improved stability of the tuned amplifier. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 23 UNIT-5 The voltage VAGC applied to the base of the transistor Q2 is used to provide automatic gain control. The variation in the VAGC cause changes in the division of the current between the transistors Q2 and Q3. When VAGC is greater than VR, Q2 conducts more than Q3, reducing voltage gain. When VR is greater than VAGC, Q3 conducts more than Q2, which increases the voltage gain. At VR greater than VAGC by 120mV, Q2 is cut-off and collector current of Q1 flows through Q3 providing maximum voltage gain. The change in VAGC causes the change in the division of current and not the collector current of Q1. Thus the input impedance of Q1 remains constant and the input circuit is not tuned. The voltage V and resistance R establish the d.c current ID1 through the diode D1. The voltage VBE1 is nearly equal to VD1 and the collector current IC1 is within 5% of ID1. 8. Explain About Video Amplifier? [Nov/Dec-2007], [Nov/Dec-2012]( 8m) INTRODUCTION: A video amplifier has to amplify signal over a wide band of frequency, say D.C to up to few MHz. The shape and form of the video waveform must be persevered during amplification. The shape of the complex waveform depends not only on the frequency contained in the signal but also upon the relative phases. Therefore it is necessary that All the frequencies must be amplified equally to maintain the same relative amplitudes. The relative phases of all the frequency components in the output must be same as that of that input. Hence video amplifier is essentially a wide band amplifier with band width from D.C to high frequency up to few MHz .Many IC video amplifiers, like A733, CA3040, LM733 etc use differential amplifier as inputs and outputs. So that they can accept both singled ended and balanced input signal and produces both single ended and balanced output signal. A733: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 24 UNIT-5 PIN DIAGRAM: SYMBOL: FEATURES: 200 MHz Bandwidth 250 K input resistance. Selectable nominal amplification of 10,100 or 400. No frequency compensation required. DESCRIPTION: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 25 UNIT-5 The A733 is a monolithic two stage video amplifier with differential inputs and differential Outputs. Internal series-shunt feedback provides wide bandwidth, low phase distortion and excellent gain stability. Differential amplifier with transistor Q1and Q2 forms the Input stage and it is biased by transistor Q7 and R1,R2 are load resistors. Second stage is also a differential amplifier with Q3and Q4 here biasing is provided by transistor Q9, and transistors Q5, Q6 are emitter follower stages with current sink transistors Q10 and Q11. This provides the necessary impedance matching between the second differential amplifier stage and load. All the stages are current source biased to obtain high CMRR and SVRR. Fixed differential amplification of 10V/V, 100V/V, and 400V/V may be selected without any external components. The amplification may be adjusted from 10V/V, to 400V/V by the use of single external resistor connected between 1A and 1B or 2A and 2B. No external frequency compensating components are required for any gain option. FREQUENCY RESPONSE: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 26 UNIT-5 As about 100MHz, the gain 3 curve peaks a little. This is because, at this frequency, there is 180 phase shift in the feedback which makes the negative feedback become positive feedback. APPLICATIONS: Application includes general purpose video and pulse amplifier, where wide bandwidth, low phase shift excellent gain is required. Broadband communication, Telephony, Thin and thick film memories and video recorder systems. 9. What are the various blocks that form a basic voltage regulator? Explain the series and shunt voltage regulator. List advantages of IC voltage regulator. [apr/may-2008](16m) A Voltage regulator is an electronic circuit that provides a stable d.c voltage independent of the load current, temperature and a.c line voltage variations. The series regulator circuit consists of following four parts: Reference voltage circuit Error amplifier Series Pass transistor Feedback network SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 27 UNIT-5 SHUNT VOLTAGE REGULATOR: The power transistor Q1 is in series with the unregulated d.c voltage Vin and the regulated output voltage VO. So it must absorb the difference between these two voltages whenever there is any fluctuation in output voltage VO occurs. The transistor Q1 is also connected as an emitter follower and therefore provides sufficient current gain to drive the load. The output voltage is sampled by the R 1-R2 divider and feedback to (-) input terminal of the op-amp error amplifier. This sampled voltage is compared with the reference voltage Vref. The output VO of the error amplifier drives the series transistor Q1. If the output voltage increases ,say, due to variation in load current, the sampled voltage VO also increases, where, R2 R1 R2 SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 28 UNIT-5 This, in turn, reduces the output voltage VO of the diff- amplifier due to 180º phase difference provided by Op-Amp. VO is applied to the base of Q1, which is used as an emitter follower. So VO follows VO , that is VO also reduces. Hence the increase in VO is nullified. Similarly, reduction in output voltage also gets regulated. 10. Discuss the operation of IC 555 as a monostable multivibrator? Draw the waveform and explain? [Apr/may-2008](8m) Or Explain the operation of a monostable multivibrator using 555 timer? [Nov/dec-2008](10m) SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 29 UNIT-5 The above figure shows 555 timer connected for monostable operation and its functional diagram is shown below. In the stable state, FF hold transistor Q1 ON, thus clamping the external timing capacitor C to ground. The output remains LOW. As the trigger passes through 1 VCC , the FF is set, i.e. Q 0 . This makes transistor Q1 OFF 3 and short circuit across the timing capacitor C is released. As Q 0 , output goes HIGH (=VCC).Now the voltage across C rises exponentially through R towards VCC with time constant RC. After a predefined time period T, the capacitor voltage is just greater than 2 VCC and the 3 upper comparator resets the FF (R=1, S=0). This makes Q 1 , and transistor Q2 goes ON, thereby discharging the capacitor C rapidly to ground potential. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 30 UNIT-5 The output returns to stable state. The voltage across the capacitor is given as, VC VCC 1 e t / RC At t =T, VC 2 VCC 3 ------------------ (1) ------------------ (2) Equating equations (1) and (2) we get, 2 VCC VCC 1 e T / RC 3 2 V V V e T / RC CC CC 3 CC 1 V V e T / RC CC 3 CC 1 e T / RC 3 Taking natural logarithm on both sides, 1 T ln 3 RC T ln 3 RC T RC ln( 3) T = 1.1 R.C (Seconds) SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 31 UNIT-5 The timing interval is independent of the supply voltage. Also once triggered the output remains HIGH state until time T is completed, which depends only on R and C. Any additional trigger pulse coming during this time will not change the output state. However if negative going reset pulse is applied to pin 4 during the timing cycle, the transistor Q2 goes OFF, Q1 becomes ON timing capacitor C is immediately discharged. Even if the reset is released the output remains LOW until a negative going trigger pulse is applied at input terminal pin 2. The below figure shows the various combinations of R and C necessary to produce the given time delay. 11. Write short notes on opto couplers? [Apr/May-2008] & [Nov/Dec-2008] ,[may/June 2012] The Optocoupler circuit is a combined package of photo emitting device [LED] and photo sensing device [Photo diode, Photo transistor]. In the above circuit the source V1 and resistance R1 decide the forward current I through LED. Thus LED emits the light. This light is incident on the photo diode. Due to this, the reverse current is set up in the output circuit. This current produces the drop across output resistance R2. The output voltage is given by, Vout V2 I 2 R2 Now if the input voltage is changed, the amount of light emitted by the LED changes. This varies the reverse current in output circuit and hence the output voltage. The output voltage in thus varying in step with the input voltage. This coupling between the LED and photo diode is hence called as “OPTO COUPLER" SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 32 UNIT-5 The above circuit consists of both LED and photo transistor. When the input voltage forward biases the LED, light transmitted to the photo transistor turns it on, resulting current through the external load. LED – DARLINGTON PAIR: In all the above circuits the forward current of LED results in emission of light by LED. The light is detected by the photo sensitive device to produce the output current. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 33 UNIT-5 The ratio of the output current IO to the input LED current (ILED) is called “ Current Transfer ratio” CTR DEVICE LED- Photo Diode LED- Photo Transistor LED- Darlington IO I LED 100% CTR 0.01 to 0.03 0.1 to 1 1 to 5 Thus the circuit connected to its input can be electrically fully isolated from the output circuit and the potential difference of hundreds or thousands of volt can be safely exists between the two circuit without adversely affecting the Opto Coupler action. IC OPTOCOUPLER: MCT2E is optically coupled isolated consists of a Gallium arsenide, Infrared emitting diode, and NPN silicon photo transistor mounted in a standard 6 pin dual in line package. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 34 UNIT-5 FEATURES: The isolated voltage of +2500V The power dissipation is 250 mV High dc current transfer ratio. Input and output isolation resistance us 10 ohm. Low cost. ADVANTAGES: Response time is so small that they can be used to transmit data in MHz range. Unidirectional signal transfer. Easy interfacing with logic device. Much faster than transform Compact and light weight. 12. Explain the power amplifiers and the essential characteristics. [Apr/may-2008] (7m) Industrially standard Op-Amps such 741 can deliver abut 100mW of power with no additional external components. National Semiconductor produces two popular IC audio power amplifiers LM380 and LM384. The LM380 is designed to deliver 2.5W (r.m.s) to a capacitively coupled 8 load whereas LM384 can deliver 5W power and both are available in DIP packages. A copper lead frame is used with the central three pins (3, 4, 5, 10, 11, and 12) on either side of the DIP package forms the heat sink. Thus there is no need to separate heat sink. The use of LM 380 as an audio power amplifier is shown below SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 35 UNIT-5 The IC can be used in inverting and non-inverting configurations. The inverting terminal can be either shorted to ground, left open or returned to ground through a capacitor or a resistor. The capacitor C2 is used to cancel the effects of the inductance in the power supply leads. A lag compensating RC network must be connected from output to ground to avoid oscillations. The gain of the LM380 is internally fixed at 50 but it is possible to get he gain increased up to 300, using positive feedback as shown in the above figure. LM384 has the same connection diagram as that of LM380 except that it is designed to deliver 5W of power. There are also available hybrid power amplifiers which supply more output power than is possible using monolithic power ICs. Some examples are Intersil’s ICH8510/8520/8530 and Burr Brown’s 3573. The 3573 is designed to deliver 100W peak or 40W continuous output power and can be used to drive d.c and a.c motors, electronic valves and push-pull solenoids. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 36 UNIT-5 13. Draw the circuit using op-amp to generate triangular wave? Explain its operation. [NOV/DEC 2012] Comparator compares the voltage at a point ‘P’ continuously with respect to the voltage at the inverting input, which is at ground potential. When the voltage at P goes slightly below zero, the output of comparator will switches to negative saturation. Consider the output of comparator is +Vsat, since this voltage is the input of integrator, then its output will be negative going ramp. Thus one end of the potential divider R1 R2 is at +Vsat and other end is at negative going ramp. When the negative going ramp attains a value say –Vramp the effective voltage at P becomes slightly less than 0V. This switches output of comparator to –Vsat. During this time integrator output will be positive going ramp. When the value of positive going ramp attains +Vramp, voltage at 'P' becomes slightly greater than 0V, there by switching comparator output to +Vsat. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 37 UNIT-5 This cycle repeats and generates a triangular waveform Triangular waveform can also be generated by integrating square wave from an astable multivibrator. Output Waveform Design of Triangular wave generator The frequency of triangular waveform is given by either the following expressions Peak to peak amplitude of ramp voltage is given by SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 38 UNIT-5 Switched capacitor filterThe essence of the switched-capacitor is the use of capacitors and analog switches to perform the same function as a resistor. This replacement resistor, along with op-amp based integrators, then forms an active filter. Before delving too far into actual filter designs, however, it makes sense to ask why one would want to replace the resistor with such an apparently complex assembly of parts as switches and capacitors. It would seem from the multiplication of parts that the switchedcapacitor would be area intensive. As a matter of fact, for the resistor values that one seeks in certain filter designs, this is not the case. Furthermore, the use of the switched-capacitor will be seen to give frequency tunability to active filters. Figure 1[2, 3] shows the basic setup for a switched-capacitor, including two N-channel Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (NMOS) and a capacitor. There are two clock phases, , which are non-overlapping. The MOSFET's, either M1 or M2, will be turned ON when the gate voltage is high, and the equivalent resistance of the channel in that case will be low, . Conversely, when the gate voltage goes LOW, the channel resistance will look like . With such a high ratio of OFF to ON resistances, each MOSFET can be taken for a switch. Furthermore, when the two MOSFET's are driven by non-overlapping clock signals, then M1 and M2 will conduct during alternate half-cycles. Figure 1. Two NMOSFET's, driven by alternating, non-overlapping clock signals, comprise the basic switched capacitor network. SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 39 UNIT-5 This makes the two-MOSFET arrangement equivalent to a single-pole, double-throw switch (SPDT). One can now use a symbolic switch picture, as in Figure 2a below, to represent the circuit. The operation of this circuit is as follows. When the switch is thrown to the left, the capacitor will charge up to . When the switch is thrown to the right, the capacitor will discharge down to/charge up to . As a result of these consecutive switching events, there will be a net charge transfer of . Now, if one flips the switch back and forth at a rate of cycles/sec, then the charge transferred in one second is , which of course has the units of current. One can claim that an average current, . If is much higher than the frequency of the voltage waveforms, then the switching process can be taken to be essentially continuous, and the switched-capacitor can then be modeled as an equivalent resistance, as shown below in Figure 2b. The value of the equivalent resistance is given by: (Eq. 1) Therefore, this equivalent resistance, in conjunction with other capacitors, and Op-amp integrators, can be used to synthesize active filters. It is now clear from Equation (1) how the use of the switched-capacitor leads to tunability in the active filters, by varying the clock frequency. (a) (b) Figure 2. Equivalent resistor model for switched capacitor circuit in Fig. 1. This equivalent resistance has features which make it advantageous when realized in integratedcircuit form: SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 40 UNIT-5 (a) High-value resistors can be implemented in very little silicon area. For example, a 1-M resistor can be realized with a 10-pF capacitor switched at a clock rate of 100 kHz. (b) Very accurate time constants can be realized, because the time constant is proportional to the ratio of capacitances, and inversely proportional to the clock frequency: . Capacitor ratios, especially in monolithic form, are very robust against changes in temperature, and clock frequencies can also be strictly controlled, so that accurate time constants are now available in the switched-capacitor technology. The principal constraint in using the switched-capacitor is that inherent in all sampled-data systems: the clock frequency must be much higher than the critical frequency set by the RC products in the circuit. Furthermore, on either side of the analog switches, i.e., the MOSFET's, there must be essentially zero-impedance nodes (voltage sources). There are a number of other constraints which the unsuspecting designer/user might overlook [3, p. 725]: (a) The equivalent resistance formed by the action of the switched-capacitor cannot be used to close the negative-feedback path in an op-amp all by itself. One must recall that to ensure stability, the op-amp's feedback path must be closed continuously, while the switched-capacitor is a sampled-data construction of a resistor, and thus not continuous. (b) Circuit nodes cannot be left floating. That is, there must always be a resistive path to ground so that charge does not build up on the capacitor plates. (c) The bottom plates of the MOS capacitors must be connected to ground or to a voltage source. There is an intrinsic, parasitic capacitance associated with the MOS capacitor's bottom plate [4]. This parasitic capacitance can be between 5% and 20% of the desired value; furthermore, it behaves nonlinearly with voltage. (d) The noninverting pin of the op-amp should be kept at a constant voltage. If this pin is connected to the signal in some way, then the virtual short circuit between op-amp inputs means that the inverting input is no longer a virtual ground, and so an undesirable alteration of filter response due to the MOS capacitor's parasitic capacitance will occur (see item (c) above). SCE/DEPT.OF ECE/II YEAR LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Page 41